Koen A. J. Eppenhof
Inferring a Third Spatial Dimension from 2D Histological Images
Jan 10, 2018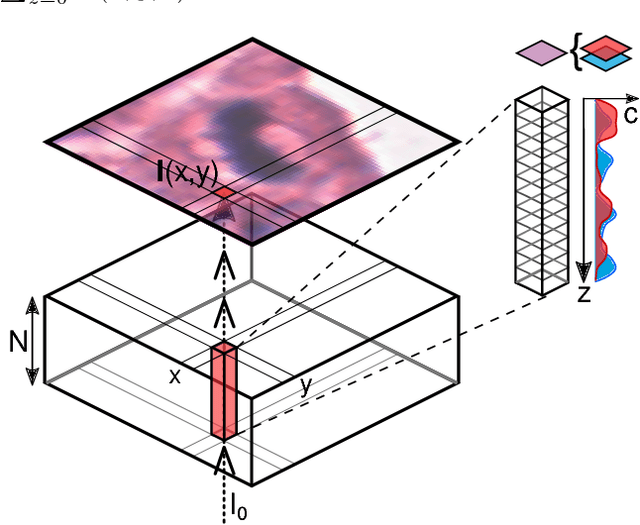
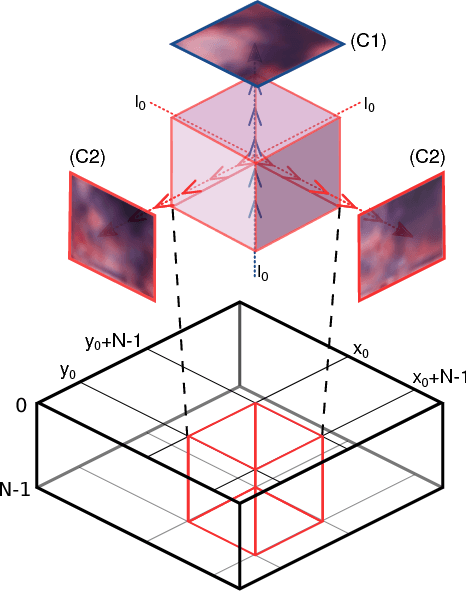
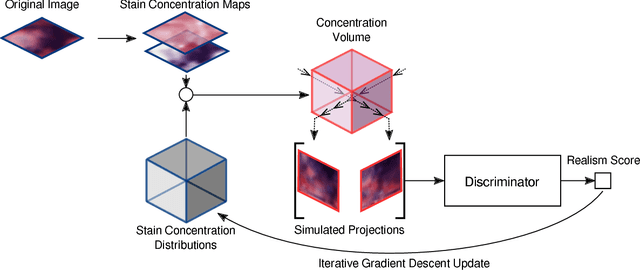
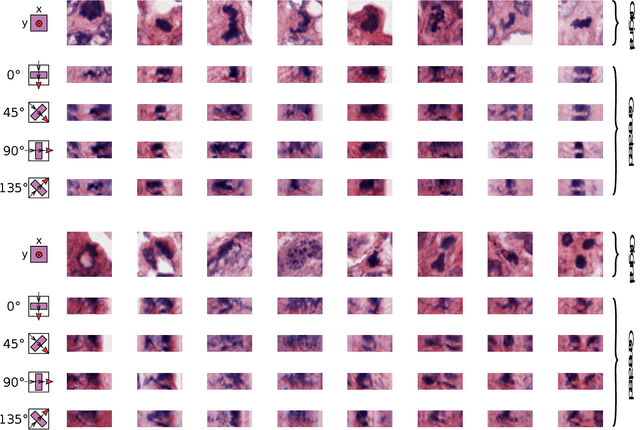
Abstract:Histological images are obtained by transmitting light through a tissue specimen that has been stained in order to produce contrast. This process results in 2D images of the specimen that has a three-dimensional structure. In this paper, we propose a method to infer how the stains are distributed in the direction perpendicular to the surface of the slide for a given 2D image in order to obtain a 3D representation of the tissue. This inference is achieved by decomposition of the staining concentration maps under constraints that ensure realistic decomposition and reconstruction of the original 2D images. Our study shows that it is possible to generate realistic 3D images making this method a potential tool for data augmentation when training deep learning models.
Domain-adversarial neural networks to address the appearance variability of histopathology images
Jul 19, 2017



Abstract:Preparing and scanning histopathology slides consists of several steps, each with a multitude of parameters. The parameters can vary between pathology labs and within the same lab over time, resulting in significant variability of the tissue appearance that hampers the generalization of automatic image analysis methods. Typically, this is addressed with ad-hoc approaches such as staining normalization that aim to reduce the appearance variability. In this paper, we propose a systematic solution based on domain-adversarial neural networks. We hypothesize that removing the domain information from the model representation leads to better generalization. We tested our hypothesis for the problem of mitosis detection in breast cancer histopathology images and made a comparative analysis with two other approaches. We show that combining color augmentation with domain-adversarial training is a better alternative than standard approaches to improve the generalization of deep learning methods.
Adversarial training and dilated convolutions for brain MRI segmentation
Jul 11, 2017


Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been applied to various automatic image segmentation tasks in medical image analysis, including brain MRI segmentation. Generative adversarial networks have recently gained popularity because of their power in generating images that are difficult to distinguish from real images. In this study we use an adversarial training approach to improve CNN-based brain MRI segmentation. To this end, we include an additional loss function that motivates the network to generate segmentations that are difficult to distinguish from manual segmentations. During training, this loss function is optimised together with the conventional average per-voxel cross entropy loss. The results show improved segmentation performance using this adversarial training procedure for segmentation of two different sets of images and using two different network architectures, both visually and in terms of Dice coefficients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge