Klavdiya Bochenina
Synthetic Data-Based Simulators for Recommender Systems: A Survey
Jun 22, 2022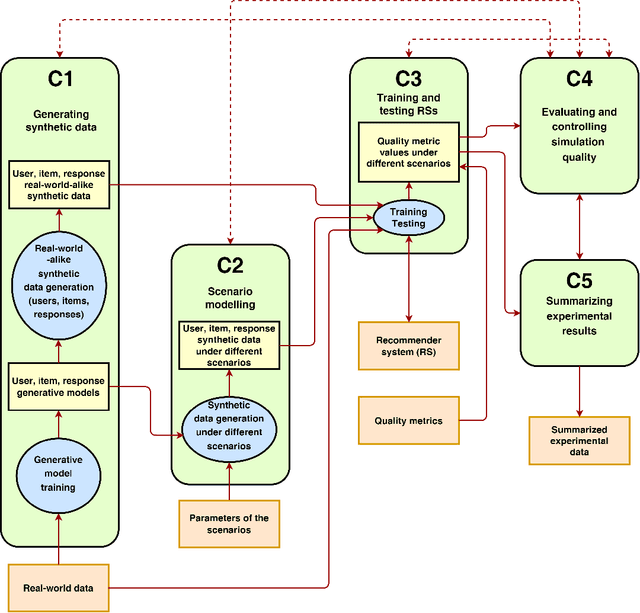
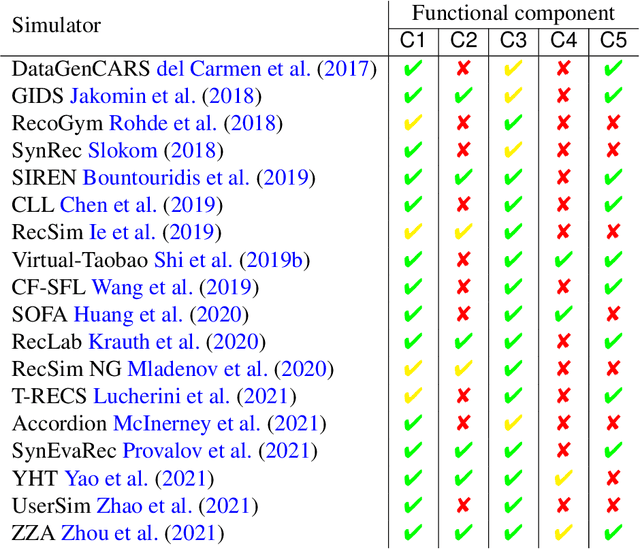

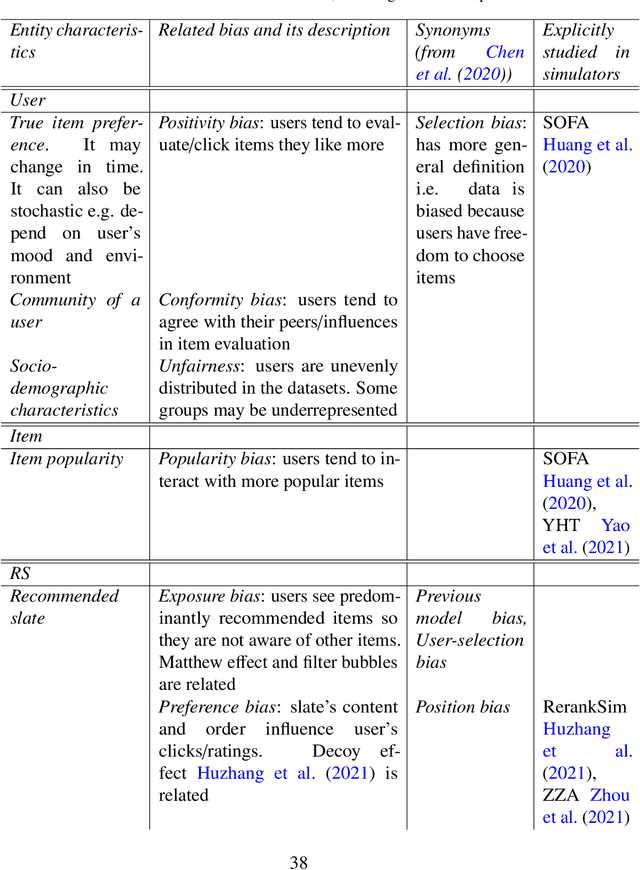
Abstract:This survey aims at providing a comprehensive overview of the recent trends in the field of modeling and simulation (M&S) of interactions between users and recommender systems and applications of the M&S to the performance improvement of industrial recommender engines. We start with the motivation behind the development of frameworks implementing the simulations -- simulators -- and the usage of them for training and testing recommender systems of different types (including Reinforcement Learning ones). Furthermore, we provide a new consistent classification of existing simulators based on their functionality, approbation, and industrial effectiveness and moreover make a summary of the simulators found in the research literature. Besides other things, we discuss the building blocks of simulators: methods for synthetic data (user, item, user-item responses) generation, methods for what-if experimental analysis, methods and datasets used for simulation quality evaluation (including the methods that monitor and/or close possible simulation-to-reality gaps), and methods for summarization of experimental simulation results. Finally, this survey considers emerging topics and open problems in the field.
Argumentative Text Generation in Economic Domain
Jun 18, 2022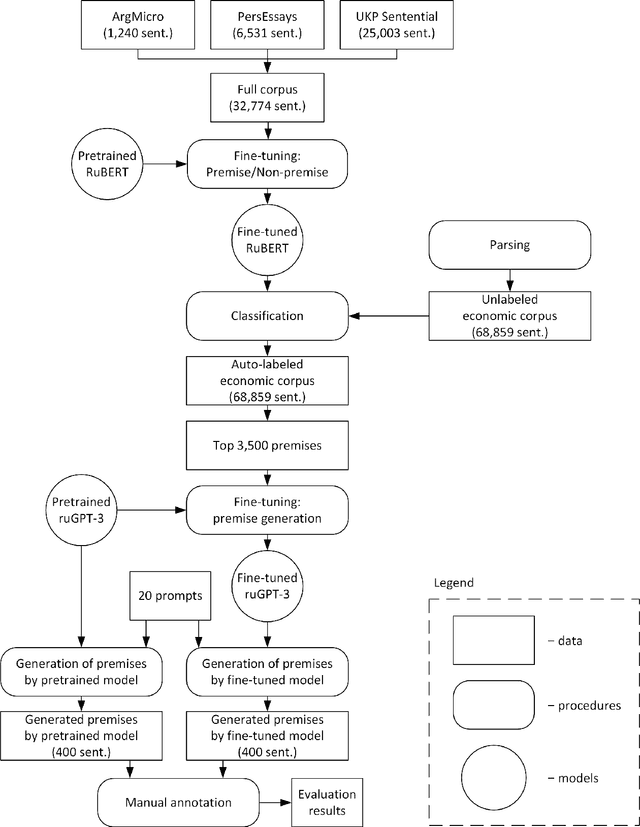



Abstract:The development of large and super-large language models, such as GPT-3, T5, Switch Transformer, ERNIE, etc., has significantly improved the performance of text generation. One of the important research directions in this area is the generation of texts with arguments. The solution of this problem can be used in business meetings, political debates, dialogue systems, for preparation of student essays. One of the main domains for these applications is the economic sphere. The key problem of the argument text generation for the Russian language is the lack of annotated argumentation corpora. In this paper, we use translated versions of the Argumentative Microtext, Persuasive Essays and UKP Sentential corpora to fine-tune RuBERT model. Further, this model is used to annotate the corpus of economic news by argumentation. Then the annotated corpus is employed to fine-tune the ruGPT-3 model, which generates argument texts. The results show that this approach improves the accuracy of the argument generation by more than 20 percentage points (63.2\% vs. 42.5\%) compared to the original ruGPT-3 model.
Lexicon-based Methods vs. BERT for Text Sentiment Analysis
Nov 19, 2021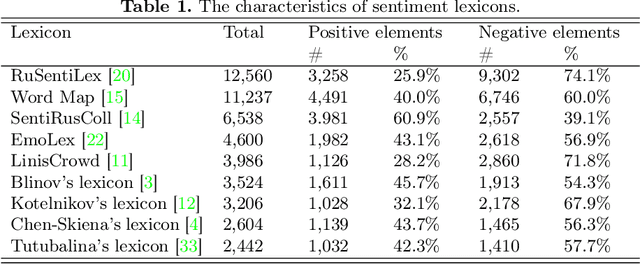

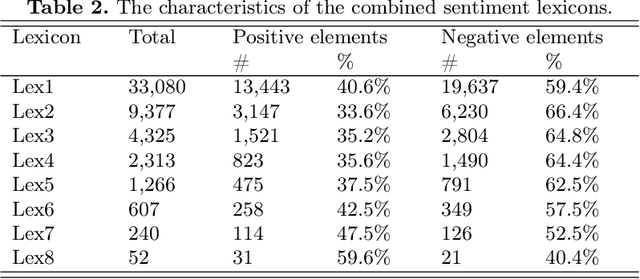
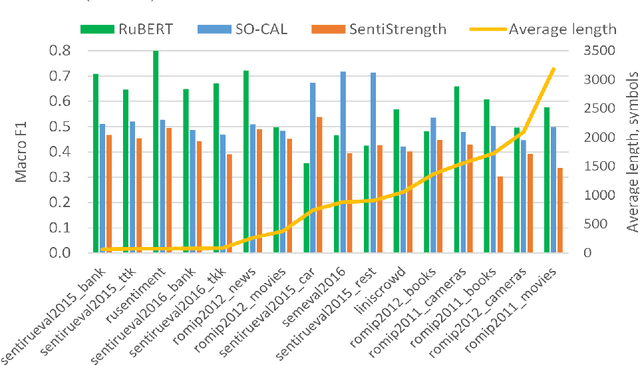
Abstract:The performance of sentiment analysis methods has greatly increased in recent years. This is due to the use of various models based on the Transformer architecture, in particular BERT. However, deep neural network models are difficult to train and poorly interpretable. An alternative approach is rule-based methods using sentiment lexicons. They are fast, require no training, and are well interpreted. But recently, due to the widespread use of deep learning, lexicon-based methods have receded into the background. The purpose of the article is to study the performance of the SO-CAL and SentiStrength lexicon-based methods, adapted for the Russian language. We have tested these methods, as well as the RuBERT neural network model, on 16 text corpora and have analyzed their results. RuBERT outperforms both lexicon-based methods on average, but SO-CAL surpasses RuBERT for four corpora out of 16.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge