Petr Chunaev
Synthetic Data-Based Simulators for Recommender Systems: A Survey
Jun 22, 2022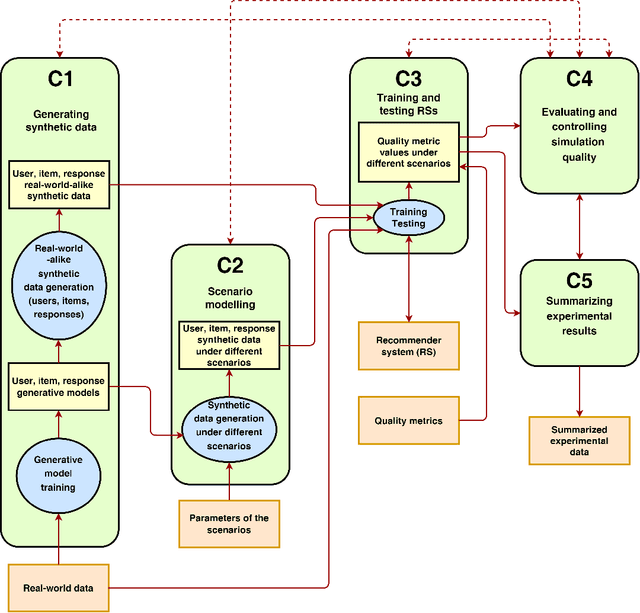
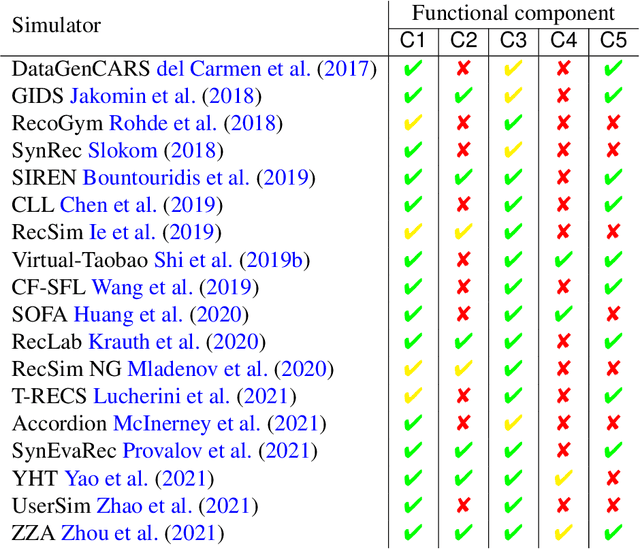

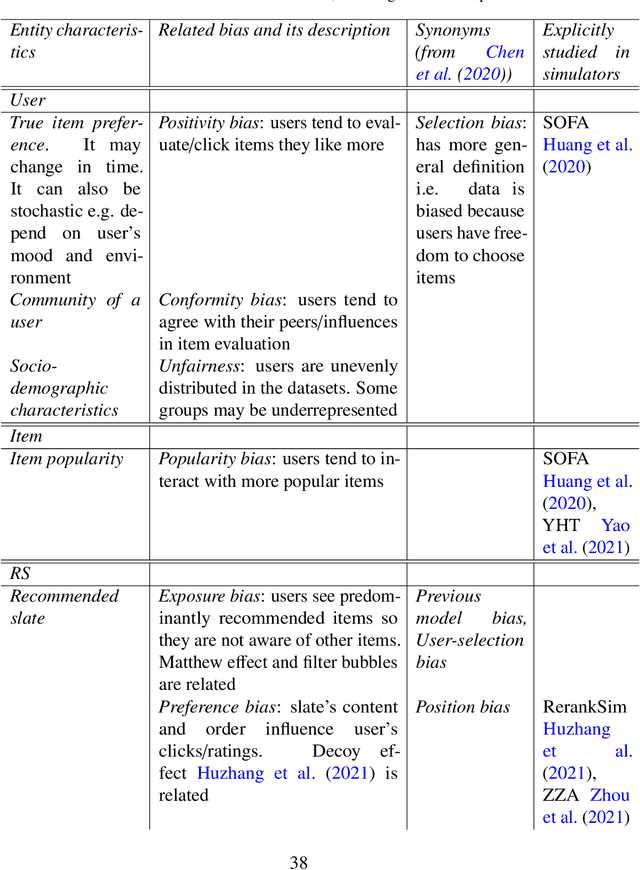
Abstract:This survey aims at providing a comprehensive overview of the recent trends in the field of modeling and simulation (M&S) of interactions between users and recommender systems and applications of the M&S to the performance improvement of industrial recommender engines. We start with the motivation behind the development of frameworks implementing the simulations -- simulators -- and the usage of them for training and testing recommender systems of different types (including Reinforcement Learning ones). Furthermore, we provide a new consistent classification of existing simulators based on their functionality, approbation, and industrial effectiveness and moreover make a summary of the simulators found in the research literature. Besides other things, we discuss the building blocks of simulators: methods for synthetic data (user, item, user-item responses) generation, methods for what-if experimental analysis, methods and datasets used for simulation quality evaluation (including the methods that monitor and/or close possible simulation-to-reality gaps), and methods for summarization of experimental simulation results. Finally, this survey considers emerging topics and open problems in the field.
Community detection in node-attributed social networks: a survey
Dec 20, 2019



Abstract:Community detection is a fundamental problem in social network analysis consisting, roughly speaking, in dividing social actors (modelled as nodes in a social graph) with certain social connections (modelled as edges in the social graph) into densely knitted and highly related groups with each group well separated from the others. Classical approaches for community detection usually deal only with the structure of the network and ignore features of the nodes, although major real-world networks provide additional actors' information such as age, gender, interests, etc., traditionally called node attributes. It is known that the attributes may clarify and enrich the knowledge about the actors and give sense to the detected communities. This has led to a relatively novel direction in community detection --- constructing algorithms that use both the structure and the attributes of the network (modelled already via a node-attributed graph) to yield more informative and qualitative results. During the last decade many methods based on different ideas and techniques have appeared in this direction. Although there exist some partial overviews of them, a recent survey is a necessity as the growing number of the methods may cause uncertainty in practice. In this paper we aim at clarifying the overall situation by proposing a clear classification of the methods and providing a comprehensive survey of the available results. We not only group and analyse the corresponding methods but also focus on practical aspects, including the information which methods outperform others and which datasets and quality measures are used for evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge