Kira Wursthorn
Uncertainty Quantification with Deep Ensembles for 6D Object Pose Estimation
Mar 12, 2024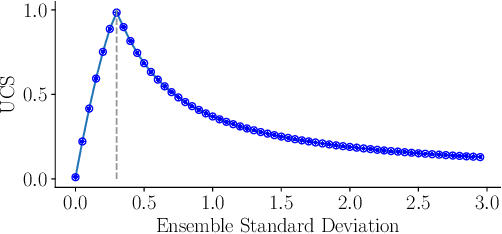
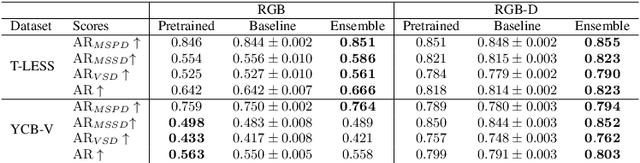
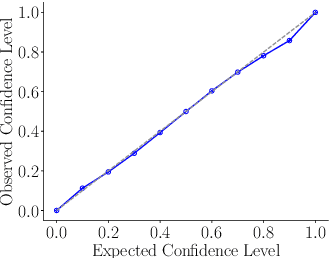
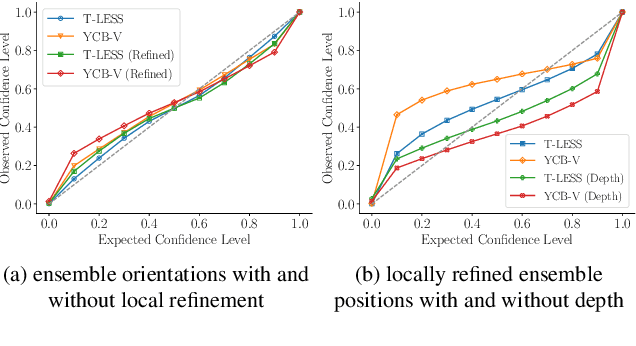
Abstract:The estimation of 6D object poses is a fundamental task in many computer vision applications. Particularly, in high risk scenarios such as human-robot interaction, industrial inspection, and automation, reliable pose estimates are crucial. In the last years, increasingly accurate and robust deep-learning-based approaches for 6D object pose estimation have been proposed. Many top-performing methods are not end-to-end trainable but consist of multiple stages. In the context of deep uncertainty quantification, deep ensembles are considered as state of the art since they have been proven to produce well-calibrated and robust uncertainty estimates. However, deep ensembles can only be applied to methods that can be trained end-to-end. In this work, we propose a method to quantify the uncertainty of multi-stage 6D object pose estimation approaches with deep ensembles. For the implementation, we choose SurfEmb as representative, since it is one of the top-performing 6D object pose estimation approaches in the BOP Challenge 2022. We apply established metrics and concepts for deep uncertainty quantification to evaluate the results. Furthermore, we propose a novel uncertainty calibration score for regression tasks to quantify the quality of the estimated uncertainty.
U-CE: Uncertainty-aware Cross-Entropy for Semantic Segmentation
Jul 19, 2023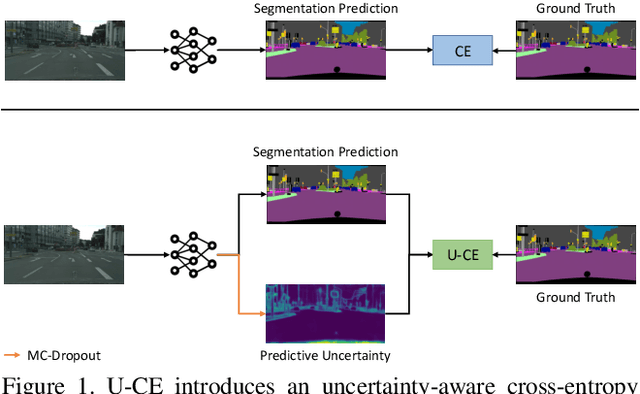
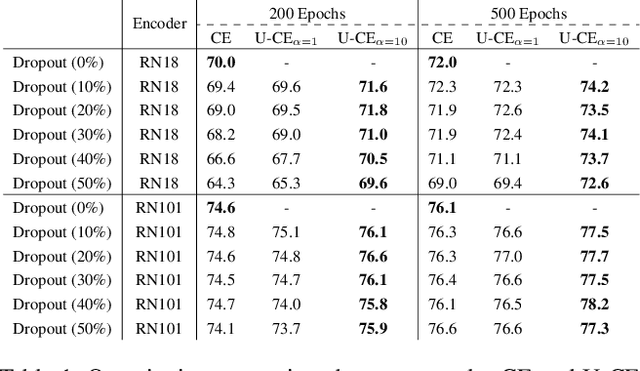
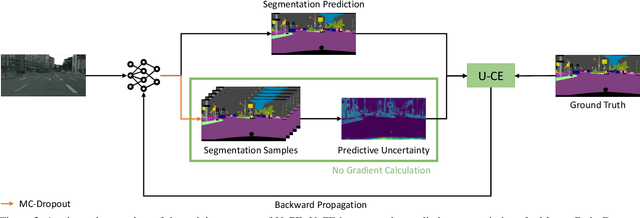
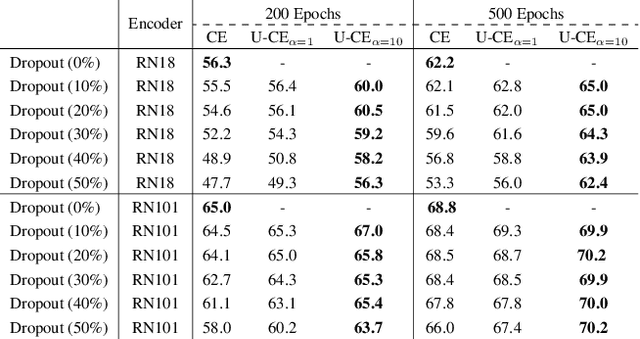
Abstract:Deep neural networks have shown exceptional performance in various tasks, but their lack of robustness, reliability, and tendency to be overconfident pose challenges for their deployment in safety-critical applications like autonomous driving. In this regard, quantifying the uncertainty inherent to a model's prediction is a promising endeavour to address these shortcomings. In this work, we present a novel Uncertainty-aware Cross-Entropy loss (U-CE) that incorporates dynamic predictive uncertainties into the training process by pixel-wise weighting of the well-known cross-entropy loss (CE). Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate the superiority of U-CE over regular CE training on two benchmark datasets, Cityscapes and ACDC, using two common backbone architectures, ResNet-18 and ResNet-101. With U-CE, we manage to train models that not only improve their segmentation performance but also provide meaningful uncertainties after training. Consequently, we contribute to the development of more robust and reliable segmentation models, ultimately advancing the state-of-the-art in safety-critical applications and beyond.
DUDES: Deep Uncertainty Distillation using Ensembles for Semantic Segmentation
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks lack interpretability and tend to be overconfident, which poses a serious problem in safety-critical applications like autonomous driving, medical imaging, or machine vision tasks with high demands on reliability. Quantifying the predictive uncertainty is a promising endeavour to open up the use of deep neural networks for such applications. Unfortunately, current available methods are computationally expensive. In this work, we present a novel approach for efficient and reliable uncertainty estimation which we call Deep Uncertainty Distillation using Ensembles for Segmentation (DUDES). DUDES applies student-teacher distillation with a Deep Ensemble to accurately approximate predictive uncertainties with a single forward pass while maintaining simplicity and adaptability. Experimentally, DUDES accurately captures predictive uncertainties without sacrificing performance on the segmentation task and indicates impressive capabilities of identifying wrongly classified pixels and out-of-domain samples on the Cityscapes dataset. With DUDES, we manage to simultaneously simplify and outperform previous work on Deep Ensemble-based Uncertainty Distillation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge