Kieran Saunders
BaseBoostDepth: Exploiting Larger Baselines For Self-supervised Monocular Depth Estimation
Jul 29, 2024
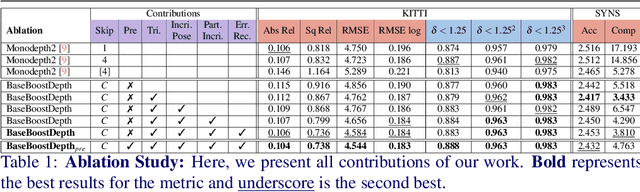
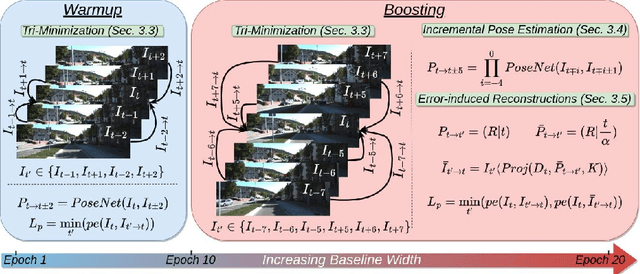
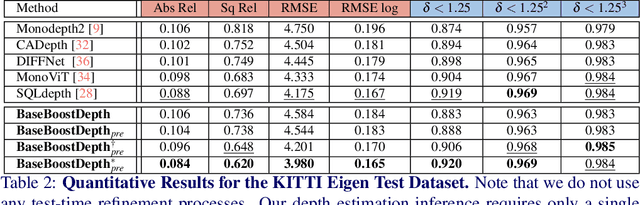
Abstract:In the domain of multi-baseline stereo, the conventional understanding is that, in general, increasing baseline separation substantially enhances the accuracy of depth estimation. However, prevailing self-supervised depth estimation architectures primarily use minimal frame separation and a constrained stereo baseline. Larger frame separations can be employed; however, we show this to result in diminished depth quality due to various factors, including significant changes in brightness, and increased areas of occlusion. In response to these challenges, our proposed method, BaseBoostDepth, incorporates a curriculum learning-inspired optimization strategy to effectively leverage larger frame separations. However, we show that our curriculum learning-inspired strategy alone does not suffice, as larger baselines still cause pose estimation drifts. Therefore, we introduce incremental pose estimation to enhance the accuracy of pose estimations, resulting in significant improvements across all depth metrics. Additionally, to improve the robustness of the model, we introduce error-induced reconstructions, which optimize reconstructions with added error to the pose estimations. Ultimately, our final depth network achieves state-of-the-art performance on KITTI and SYNS-patches datasets across image-based, edge-based, and point cloud-based metrics without increasing computational complexity at test time. The project website can be found at https://kieran514.github.io/BaseBoostDepth-Project.
Self-supervised Monocular Depth Estimation: Let's Talk About The Weather
Jul 17, 2023
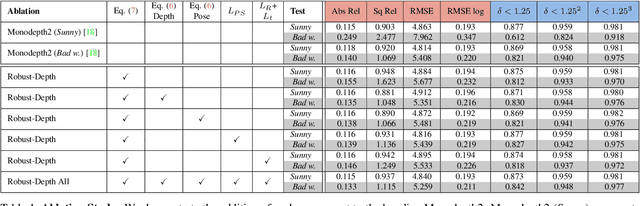

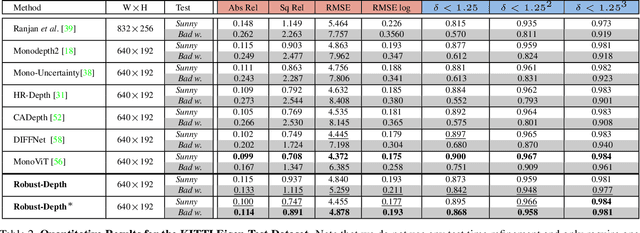
Abstract:Current, self-supervised depth estimation architectures rely on clear and sunny weather scenes to train deep neural networks. However, in many locations, this assumption is too strong. For example in the UK (2021), 149 days consisted of rain. For these architectures to be effective in real-world applications, we must create models that can generalise to all weather conditions, times of the day and image qualities. Using a combination of computer graphics and generative models, one can augment existing sunny-weather data in a variety of ways that simulate adverse weather effects. While it is tempting to use such data augmentations for self-supervised depth, in the past this was shown to degrade performance instead of improving it. In this paper, we put forward a method that uses augmentations to remedy this problem. By exploiting the correspondence between unaugmented and augmented data we introduce a pseudo-supervised loss for both depth and pose estimation. This brings back some of the benefits of supervised learning while still not requiring any labels. We also make a series of practical recommendations which collectively offer a reliable, efficient framework for weather-related augmentation of self-supervised depth from monocular video. We present extensive testing to show that our method, Robust-Depth, achieves SotA performance on the KITTI dataset while significantly surpassing SotA on challenging, adverse condition data such as DrivingStereo, Foggy CityScape and NuScenes-Night. The project website can be found here https://kieran514.github.io/Robust-Depth-Project/.
Dyna-DM: Dynamic Object-aware Self-supervised Monocular Depth Maps
Jun 23, 2022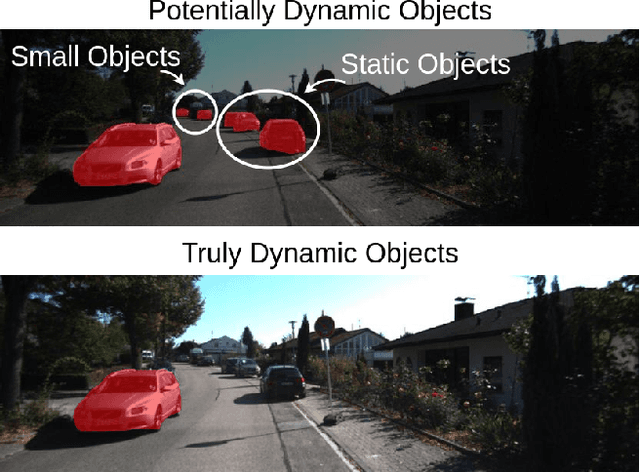
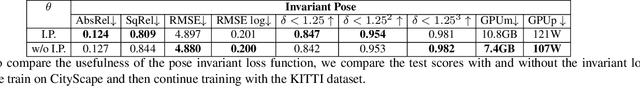
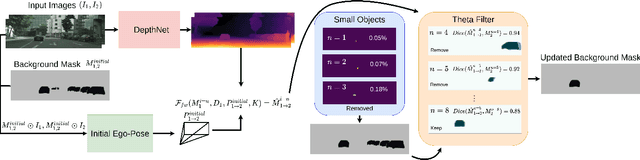
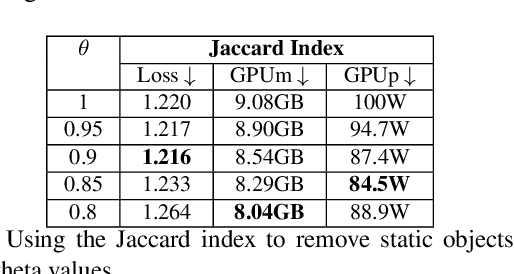
Abstract:Self-supervised monocular depth estimation has been a subject of intense study in recent years, because of its applications in robotics and autonomous driving. Much of the recent work focuses on improving depth estimation by increasing architecture complexity. This paper shows that state-of-the-art performance can also be achieved by improving the learning process rather than increasing model complexity. More specifically, we propose (i) only using invariant pose loss for the first few epochs during training, (ii) disregarding small potentially dynamic objects when training, and (iii) employing an appearance-based approach to separately estimate object pose for truly dynamic objects. We demonstrate that these simplifications reduce GPU memory usage by 29% and result in qualitatively and quantitatively improved depth maps. The code is available at https://github.com/kieran514/Dyna-DM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge