Khaled Benaggoune
A deep learning pipeline for breast cancer ki-67 proliferation index scoring
Mar 14, 2022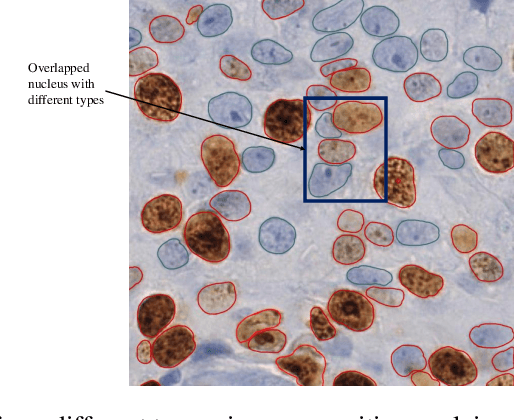
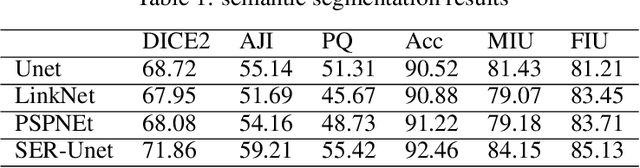
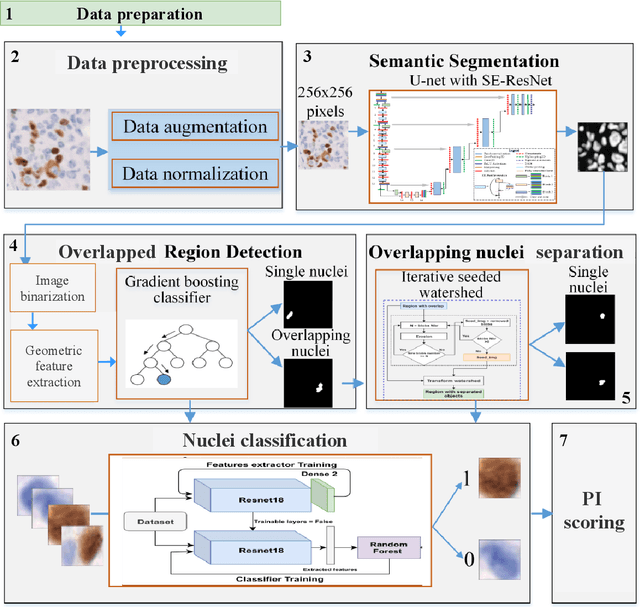
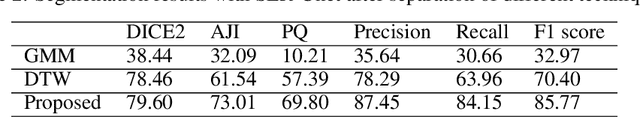
Abstract:The Ki-67 proliferation index is an essential biomarker that helps pathologists to diagnose and select appropriate treatments. However, automatic evaluation of Ki-67 is difficult due to nuclei overlapping and complex variations in their properties. This paper proposes an integrated pipeline for accurate automatic counting of Ki-67, where the impact of nuclei separation techniques is highlighted. First, semantic segmentation is performed by combining the Squeez and Excitation Resnet and Unet algorithms to extract nuclei from the background. The extracted nuclei are then divided into overlapped and non-overlapped regions based on eight geometric and statistical features. A marker-based Watershed algorithm is subsequently proposed and applied only to the overlapped regions to separate nuclei. Finally, deep features are extracted from each nucleus patch using Resnet18 and classified into positive or negative by a random forest classifier. The proposed pipeline's performance is validated on a dataset from the Department of Pathology at H\^opital Nord Franche-Comt\'e hospital.
A CNN-based methodology for breast cancer diagnosis using thermal images
Oct 30, 2019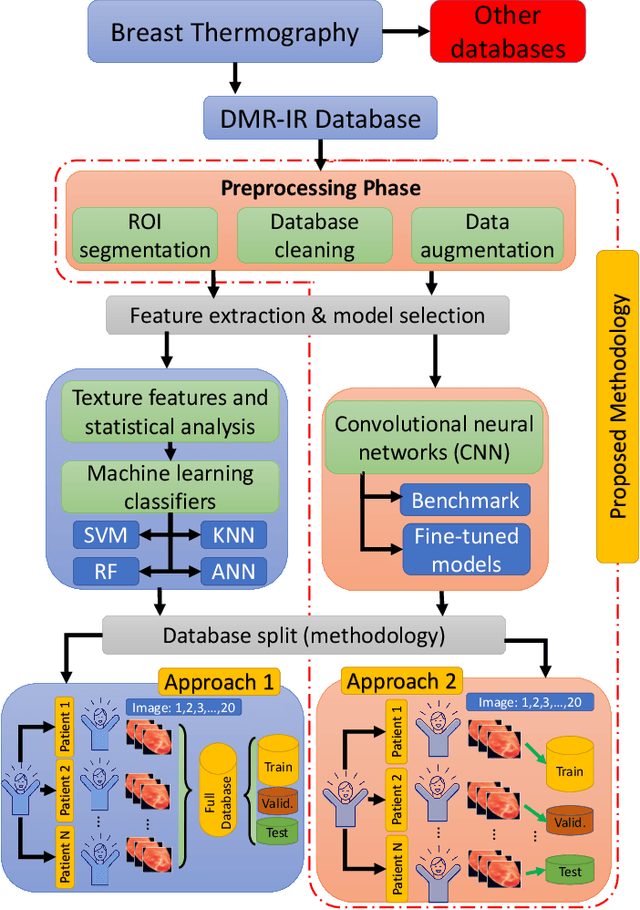
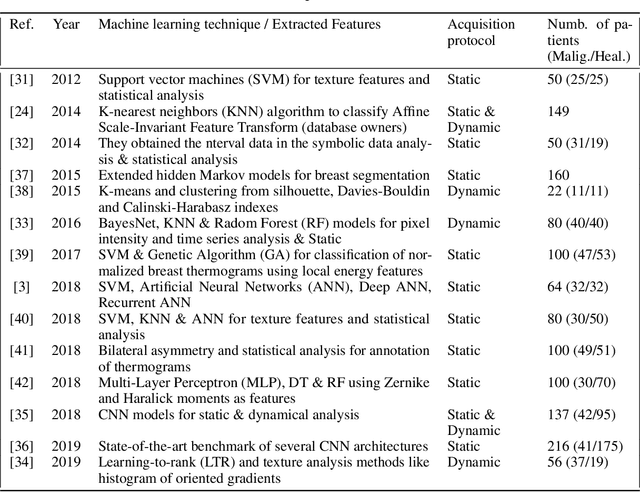
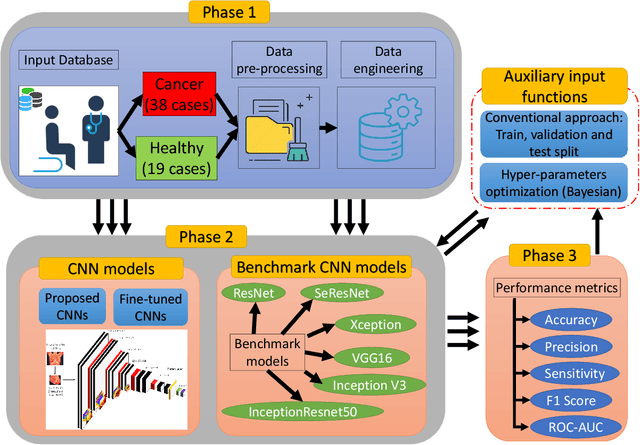
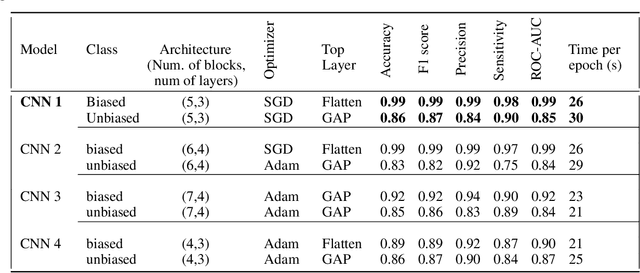
Abstract:Micro Abstract: A recent study from GLOBOCAN disclosed that during 2018 two million women worldwide had been diagnosed from breast cancer. This study presents a computer-aided diagnosis system based on convolutional neural networks as an alternative diagnosis methodology for breast cancer diagnosis with thermal images. Experimental results showed that lower false-positives and false-negatives classification rates are obtained when data pre-processing and data augmentation techniques are implemented in these thermal images. Background: There are many types of breast cancer screening techniques such as, mammography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and blood sample tests, which require either, expensive devices or personal qualified. Currently, some countries still lack access to these main screening techniques due to economic, social or cultural issues. The objective of this study is to demonstrate that computer-aided diagnosis(CAD) systems based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) are faster, reliable and robust than other techniques. Methods: We performed a study of the influence of data pre-processing, data augmentation and database size versus a proposed set of CNN models. Furthermore, we developed a CNN hyper-parameters fine-tuning optimization algorithm using a tree parzen estimator. Results: Among the 57 patients database, our CNN models obtained a higher accuracy (92\%) and F1-score (92\%) that outperforms several state-of-the-art architectures such as ResNet50, SeResNet50 and Inception. Also, we demonstrated that a CNN model that implements data-augmentation techniques reach identical performance metrics in comparison with a CNN that uses a database up to 50\% bigger. Conclusion: This study highlights the benefits of data augmentation and CNNs in thermal breast images. Also, it measures the influence of the database size in the performance of CNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge