Khaled Al Khudir
Kinematic Control of Redundant Robots with Online Handling of Variable Generalized Hard Constraints
Feb 26, 2022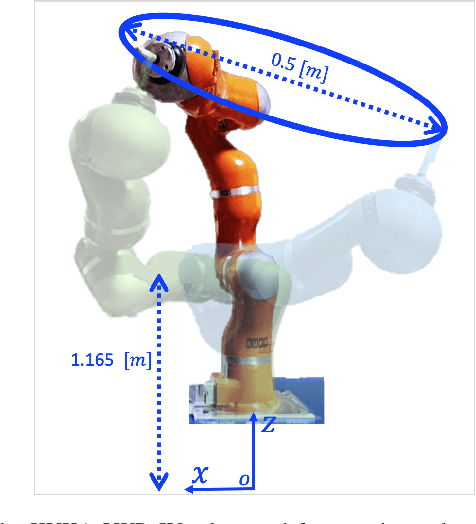
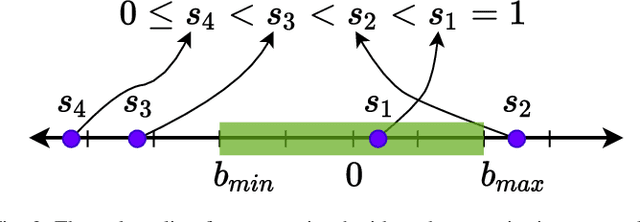
Abstract:We present a generalized version of the Saturation in the Null Space (SNS) algorithm for the task control of redundant robots when hard inequality constraints are simultaneously present both in the joint and in the Cartesian space. These hard bounds should never be violated, are treated equally and in a unified way by the algorithm, and may also be varied, inserted or deleted online. When a joint/Cartesian bound saturates, the robot redundancy is exploited to continue fulfilling the primary task. If no feasible solution exists, an optimal scaling procedure is applied to enforce directional consistency with the original task. Simulation and experimental results on different robotic systems demonstrate the efficiency of the approach. The proposed algorithm can be viewed as a generic platform that is easily applicable to any robotic application in which robots operate in an unstructured environment and online handling of joint and Cartesian constraints is critical.
Motion Control of Redundant Robots with Generalised Inequality Constraints
Oct 04, 2021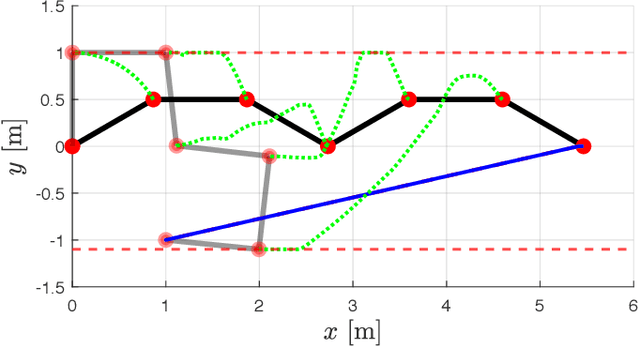
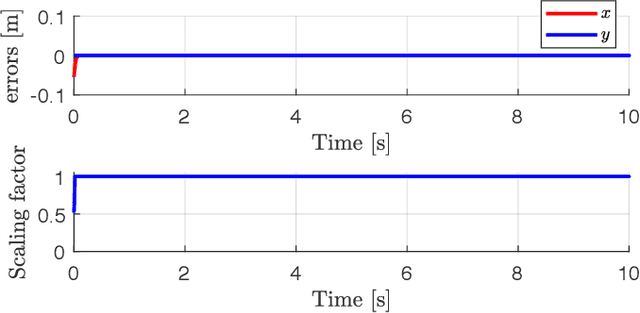
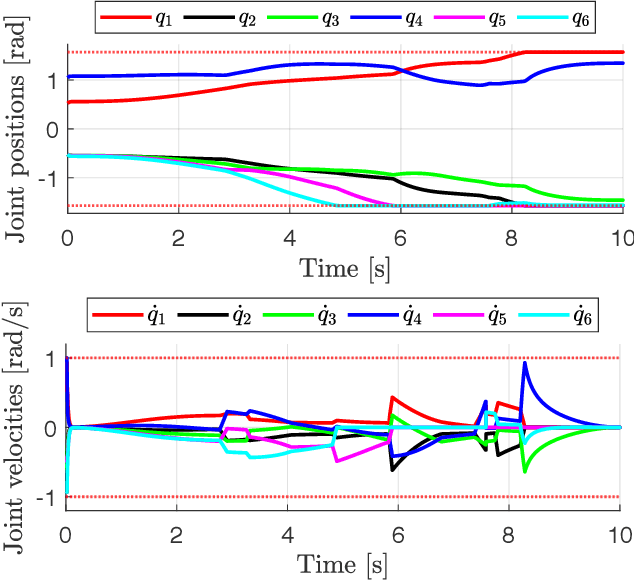
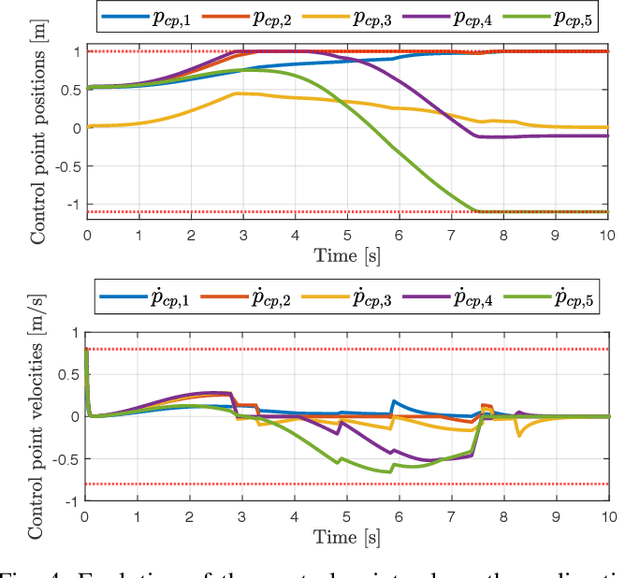
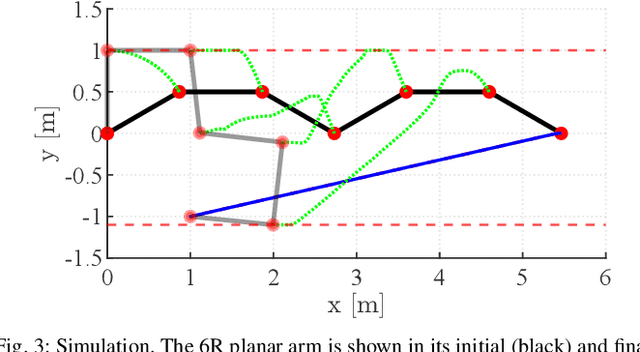
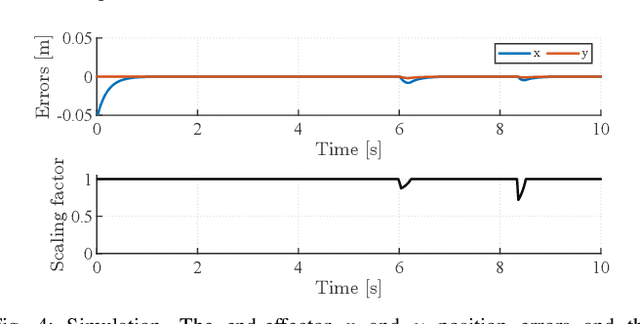
Abstract:We present an improved version of the Saturation in the Null Space (SNS) algorithm for redundancy resolution at the velocity level. In addition to hard bounds on joint space motion, we consider also Cartesian box constraints that cannot be violated at any time. The modified algorithm combines all bounds into a single augmented generalised vector and gives equal, highest priority to all inequality constraints. When needed, feasibility of the original task is enforced by the SNS task scaling procedure. Simulation results are reported for a 6R planar robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge