Kexin Gu Baugh
Neural DNF-MT: A Neuro-symbolic Approach for Learning Interpretable and Editable Policies
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Although deep reinforcement learning has been shown to be effective, the model's black-box nature presents barriers to direct policy interpretation. To address this problem, we propose a neuro-symbolic approach called neural DNF-MT for end-to-end policy learning. The differentiable nature of the neural DNF-MT model enables the use of deep actor-critic algorithms for training. At the same time, its architecture is designed so that trained models can be directly translated into interpretable policies expressed as standard (bivalent or probabilistic) logic programs. Moreover, additional layers can be included to extract abstract features from complex observations, acting as a form of predicate invention. The logic representations are highly interpretable, and we show how the bivalent representations of deterministic policies can be edited and incorporated back into a neural model, facilitating manual intervention and adaptation of learned policies. We evaluate our approach on a range of tasks requiring learning deterministic or stochastic behaviours from various forms of observations. Our empirical results show that our neural DNF-MT model performs at the level of competing black-box methods whilst providing interpretable policies.
Neuro-symbolic Rule Learning in Real-world Classification Tasks
Mar 29, 2023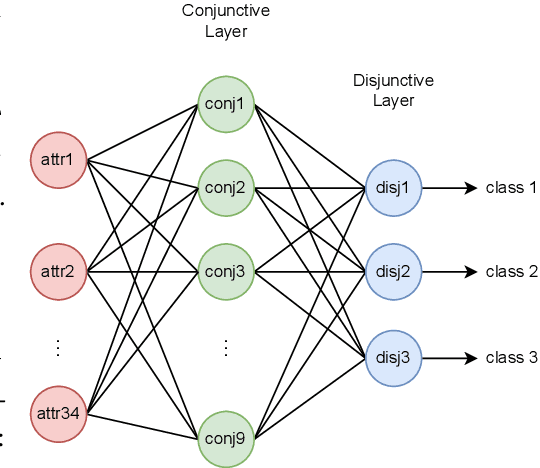
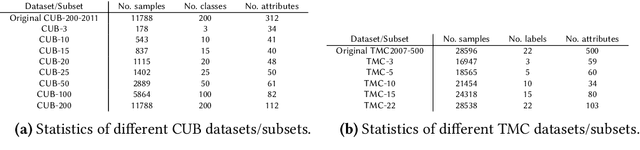
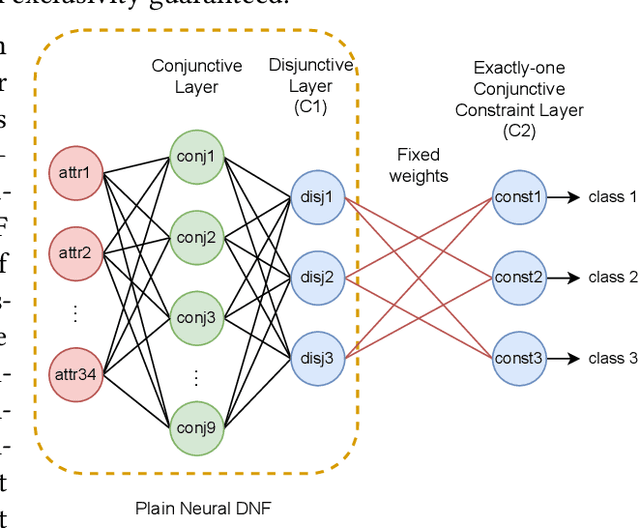
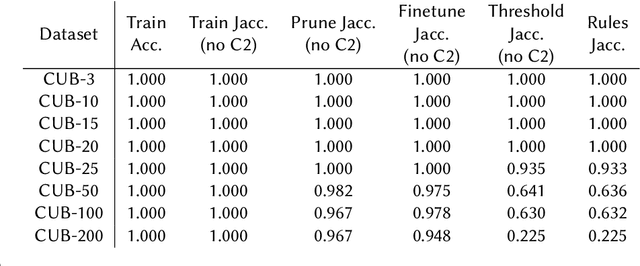
Abstract:Neuro-symbolic rule learning has attracted lots of attention as it offers better interpretability than pure neural models and scales better than symbolic rule learning. A recent approach named pix2rule proposes a neural Disjunctive Normal Form (neural DNF) module to learn symbolic rules with feed-forward layers. Although proved to be effective in synthetic binary classification, pix2rule has not been applied to more challenging tasks such as multi-label and multi-class classifications over real-world data. In this paper, we address this limitation by extending the neural DNF module to (i) support rule learning in real-world multi-class and multi-label classification tasks, (ii) enforce the symbolic property of mutual exclusivity (i.e. predicting exactly one class) in multi-class classification, and (iii) explore its scalability over large inputs and outputs. We train a vanilla neural DNF model similar to pix2rule's neural DNF module for multi-label classification, and we propose a novel extended model called neural DNF-EO (Exactly One) which enforces mutual exclusivity in multi-class classification. We evaluate the classification performance, scalability and interpretability of our neural DNF-based models, and compare them against pure neural models and a state-of-the-art symbolic rule learner named FastLAS. We demonstrate that our neural DNF-based models perform similarly to neural networks, but provide better interpretability by enabling the extraction of logical rules. Our models also scale well when the rule search space grows in size, in contrast to FastLAS, which fails to learn in multi-class classification tasks with 200 classes and in all multi-label settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge