Kevin Riou
Seeing by haptic glance: reinforcement learning-based 3D object Recognition
Feb 15, 2021
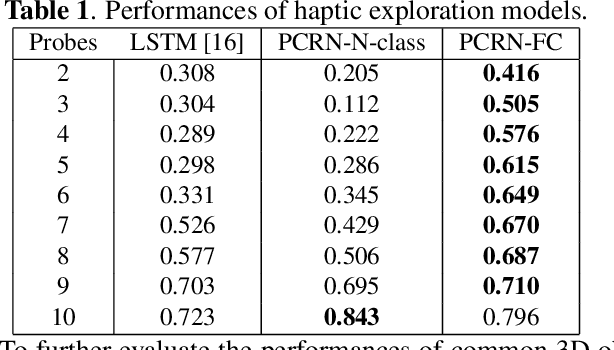
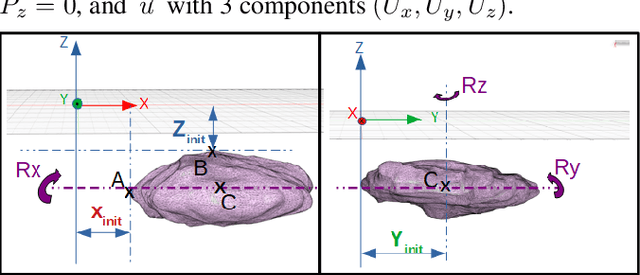

Abstract:Human is able to conduct 3D recognition by a limited number of haptic contacts between the target object and his/her fingers without seeing the object. This capability is defined as `haptic glance' in cognitive neuroscience. Most of the existing 3D recognition models were developed based on dense 3D data. Nonetheless, in many real-life use cases, where robots are used to collect 3D data by haptic exploration, only a limited number of 3D points could be collected. In this study, we thus focus on solving the intractable problem of how to obtain cognitively representative 3D key-points of a target object with limited interactions between the robot and the object. A novel reinforcement learning based framework is proposed, where the haptic exploration procedure (the agent iteratively predicts the next position for the robot to explore) is optimized simultaneously with the objective 3D recognition with actively collected 3D points. As the model is rewarded only when the 3D object is accurately recognized, it is driven to find the sparse yet efficient haptic-perceptual 3D representation of the object. Experimental results show that our proposed model outperforms the state of the art models.
Few-Shot Object Detection in Real Life: Case Study on Auto-Harvest
Nov 05, 2020
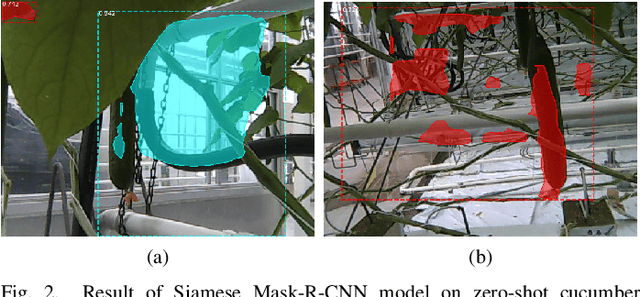


Abstract:Confinement during COVID-19 has caused serious effects on agriculture all over the world. As one of the efficient solutions, mechanical harvest/auto-harvest that is based on object detection and robotic harvester becomes an urgent need. Within the auto-harvest system, robust few-shot object detection model is one of the bottlenecks, since the system is required to deal with new vegetable/fruit categories and the collection of large-scale annotated datasets for all the novel categories is expensive. There are many few-shot object detection models that were developed by the community. Yet whether they could be employed directly for real life agricultural applications is still questionable, as there is a context-gap between the commonly used training datasets and the images collected in real life agricultural scenarios. To this end, in this study, we present a novel cucumber dataset and propose two data augmentation strategies that help to bridge the context-gap. Experimental results show that 1) the state-of-the-art few-shot object detection model performs poorly on the novel `cucumber' category; and 2) the proposed augmentation strategies outperform the commonly used ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge