Kevin Mertes
Ptychography using Blind Multi-Mode PMACE
Jan 11, 2025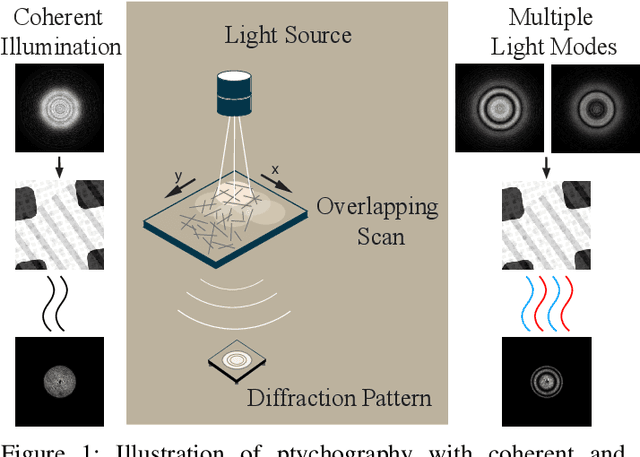
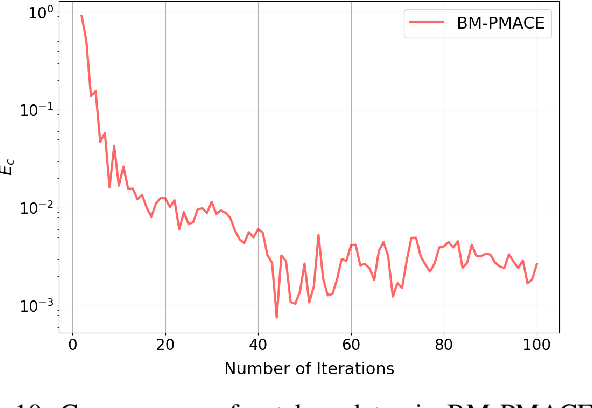
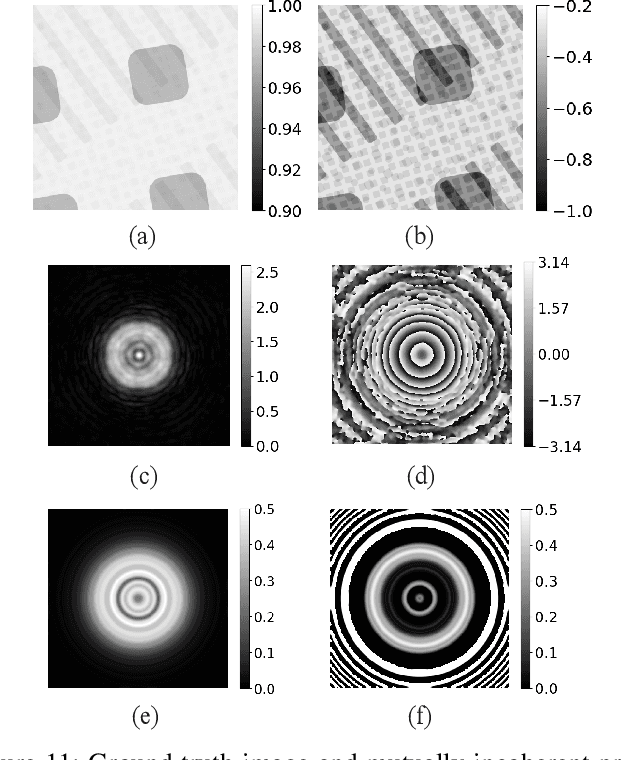
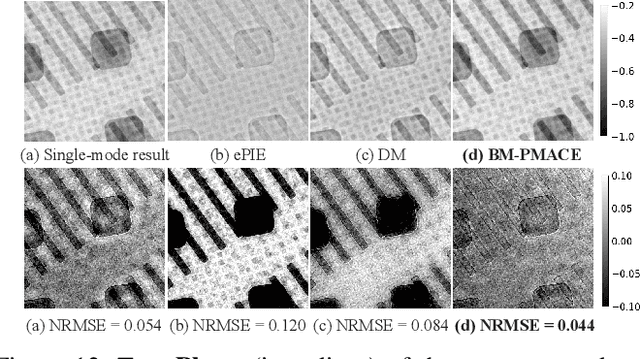
Abstract:Ptychography is an imaging technique that enables nanometer-scale reconstruction of complex transmittance images by scanning objects with overlapping illumination patterns. However, the illumination function is typically unknown, which presents challenges for reconstruction, especially when using partially coherent light sources. In this paper, we introduce Blind Multi-Mode Projected Multi-Agent Consensus Equilibrium (BM-PMACE) for blind ptychographic reconstruction. We extend the PMACE framework for distributed inverse problems to jointly estimate the complex transmittance image and multiple, unknown, partially coherent probe functions. Importantly, our method maintains local probe estimates to exploit complementary information at multiple probe locations. Our method also incorporates a dynamic strategy for integrating additional probe modes. Through experimental simulations and validations using both synthetic and measured data, we demonstrate that BM-PMACE outperforms existing approaches in reconstruction quality and convergence rate.
Projected Multi-Agent Consensus Equilibrium (PMACE) for Distributed Reconstruction with Application to Ptychography
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:Multi-Agent Consensus Equilibrium (MACE) formulates an inverse imaging problem as a balance among multiple update agents such as data-fitting terms and denoisers. However, each such agent operates on a separate copy of the full image, leading to redundant memory use and slow convergence when each agent affects only a small subset of the full image. In this paper, we extend MACE to Projected Multi-Agent Consensus Equilibrium (PMACE), in which each agent updates only a projected component of the full image, thus greatly reducing memory use for some applications.We describe PMACE in terms of an equilibrium problem and an equivalent fixed point problem and show that in most cases the PMACE equilibrium is not the solution of an optimization problem. To demonstrate the value of PMACE, we apply it to the problem of ptychography, in which a sample is reconstructed from the diffraction patterns resulting from coherent X-ray illumination at multiple overlapping spots. In our PMACE formulation, each spot corresponds to a separate data-fitting agent, with the final solution found as an equilibrium among all the agents. Our results demonstrate that the PMACE reconstruction algorithm generates more accurate reconstructions at a lower computational cost than existing ptychography algorithms when the spots are sparsely sampled.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge