Keer Xu
PRiSM: Benchmarking Phone Realization in Speech Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Phone recognition (PR) serves as the atomic interface for language-agnostic modeling for cross-lingual speech processing and phonetic analysis. Despite prolonged efforts in developing PR systems, current evaluations only measure surface-level transcription accuracy. We introduce PRiSM, the first open-source benchmark designed to expose blind spots in phonetic perception through intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation of PR systems. PRiSM standardizes transcription-based evaluation and assesses downstream utility in clinical, educational, and multilingual settings with transcription and representation probes. We find that diverse language exposure during training is key to PR performance, encoder-CTC models are the most stable, and specialized PR models still outperform Large Audio Language Models. PRiSM releases code, recipes, and datasets to move the field toward multilingual speech models with robust phonetic ability: https://github.com/changelinglab/prism.
Linguistically Conditioned Semantic Textual Similarity
Jun 06, 2024
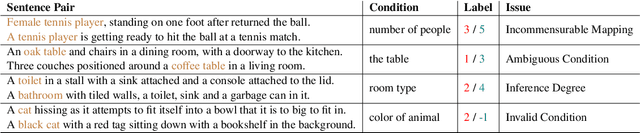
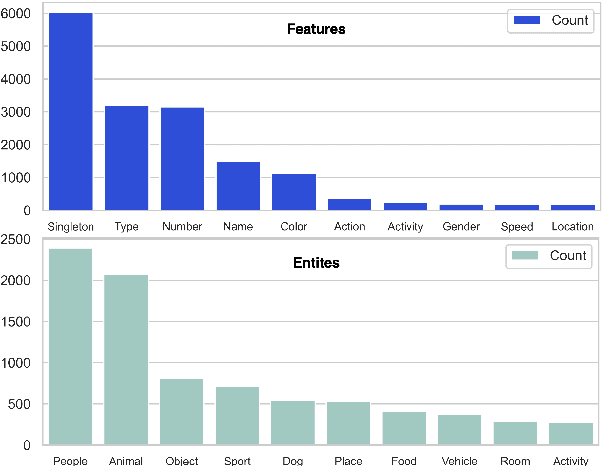

Abstract:Semantic textual similarity (STS) is a fundamental NLP task that measures the semantic similarity between a pair of sentences. In order to reduce the inherent ambiguity posed from the sentences, a recent work called Conditional STS (C-STS) has been proposed to measure the sentences' similarity conditioned on a certain aspect. Despite the popularity of C-STS, we find that the current C-STS dataset suffers from various issues that could impede proper evaluation on this task. In this paper, we reannotate the C-STS validation set and observe an annotator discrepancy on 55% of the instances resulting from the annotation errors in the original label, ill-defined conditions, and the lack of clarity in the task definition. After a thorough dataset analysis, we improve the C-STS task by leveraging the models' capability to understand the conditions under a QA task setting. With the generated answers, we present an automatic error identification pipeline that is able to identify annotation errors from the C-STS data with over 80% F1 score. We also propose a new method that largely improves the performance over baselines on the C-STS data by training the models with the answers. Finally we discuss the conditionality annotation based on the typed-feature structure (TFS) of entity types. We show in examples that the TFS is able to provide a linguistic foundation for constructing C-STS data with new conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge