Kazybek Adam
Wafer Quality Inspection using Memristive LSTM, ANN, DNN and HTM
Sep 27, 2018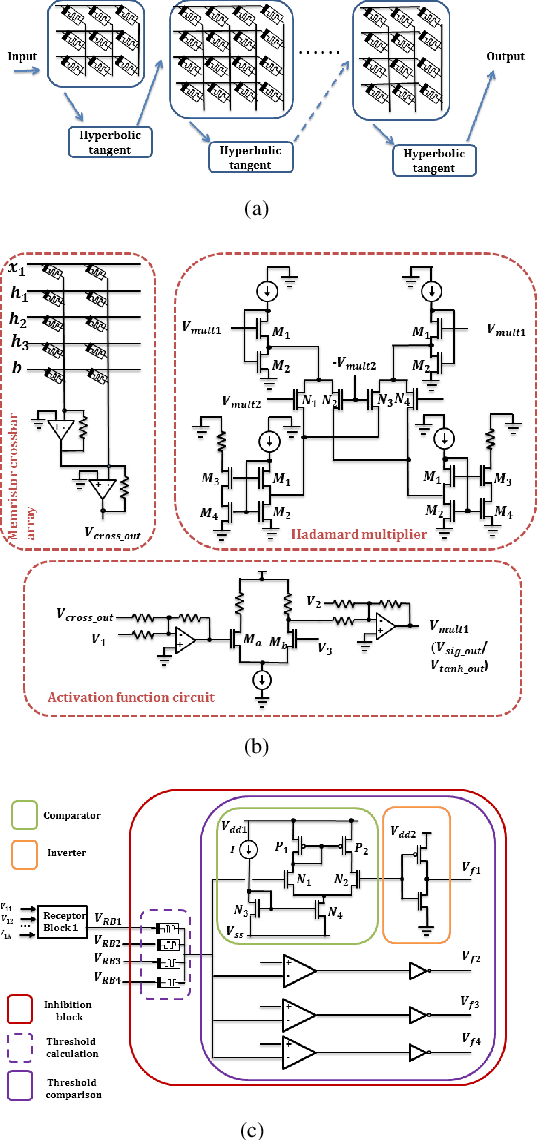
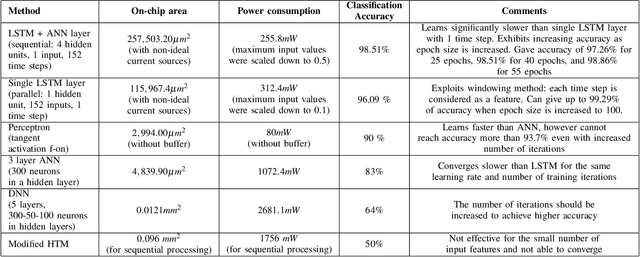
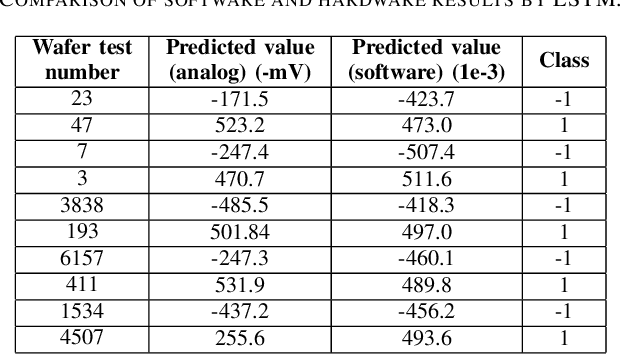
Abstract:The automated wafer inspection and quality control is a complex and time-consuming task, which can speed up using neuromorphic memristive architectures, as a separate inspection device or integrating directly into sensors. This paper presents the performance analysis and comparison of different neuromorphic architectures for patterned wafer quality inspection and classification. The application of non-volatile memristive devices in these architectures ensures low power consumption, small on-chip area scalability. We demonstrate that Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) outperforms other architectures for the same number of training iterations, and has relatively low on-chip area and power consumption.
Memristive LSTM network hardware architecture for time-series predictive modeling problem
Sep 10, 2018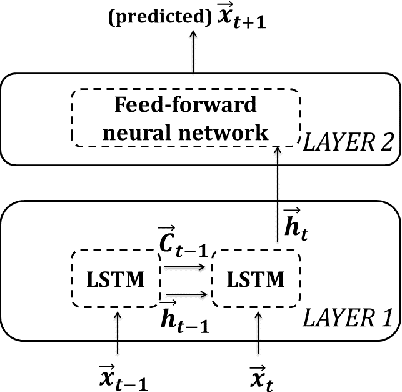
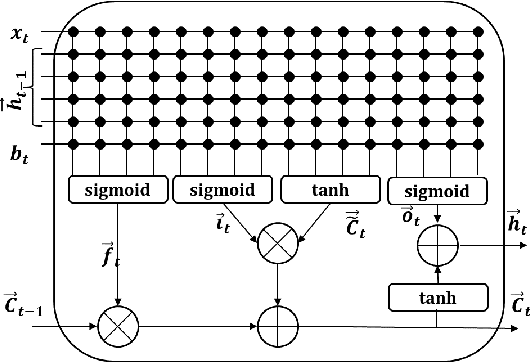
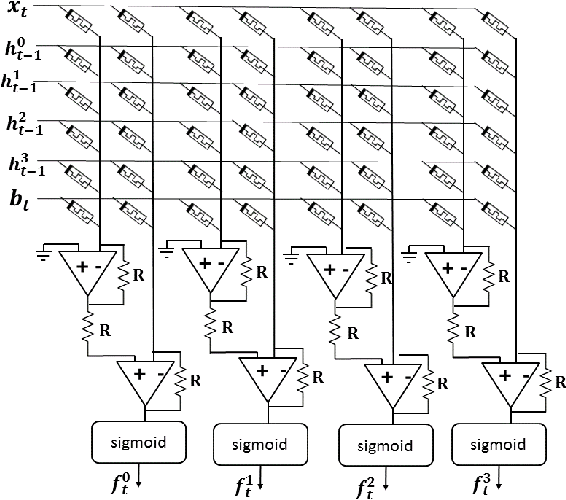
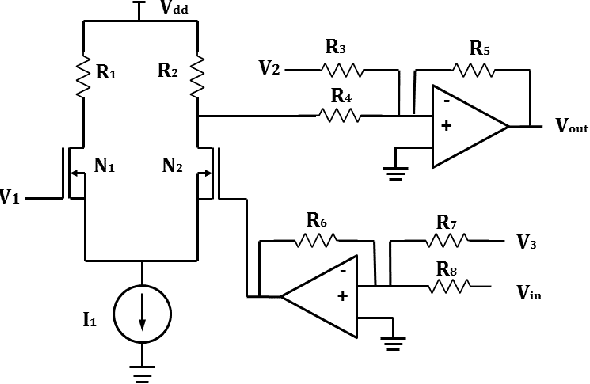
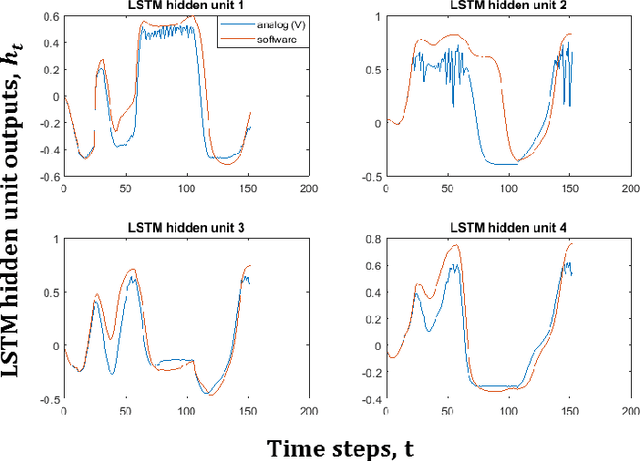
Abstract:Analysis of time-series data allows to identify long-term trends and make predictions that can help to improve our lives. With the rapid development of artificial neural networks, long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network (RNN) configuration is found to be capable in dealing with time-series forecasting problems where data points are time-dependent and possess seasonality trends. Gated structure of LSTM cell and flexibility in network topology (one-to-many, many-to-one, etc.) allows to model systems with multiple input variables and control several parameters such as the size of the look-back window to make a prediction and number of time steps to be predicted. These make LSTM attractive tool over conventional methods such as autoregression models, the simple average, moving average, naive approach, ARIMA, Holt's linear trend method, Holt's Winter seasonal method, and others. In this paper, we propose a hardware implementation of LSTM network architecture for time-series forecasting problem. All simulations were performed using TSMC 0.18um CMOS technology and HP memristor model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge