Kazuyuki Hara
Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis Model from Endomyocardial Biopsy Specimens: Appropriate Feature Space and Class Boundary in Small Sample Size Data
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:As the number of patients with heart failure increases, machine learning (ML) has garnered attention in cardiomyopathy diagnosis, driven by the shortage of pathologists. However, endomyocardial biopsy specimens are often small sample size and require techniques such as feature extraction and dimensionality reduction. This study aims to determine whether texture features are effective for feature extraction in the pathological diagnosis of cardiomyopathy. Furthermore, model designs that contribute toward improving generalization performance are examined by applying feature selection (FS) and dimensional compression (DC) to several ML models. The obtained results were verified by visualizing the inter-class distribution differences and conducting statistical hypothesis testing based on texture features. Additionally, they were evaluated using predictive performance across different model designs with varying combinations of FS and DC (applied or not) and decision boundaries. The obtained results confirmed that texture features may be effective for the pathological diagnosis of cardiomyopathy. Moreover, when the ratio of features to the sample size is high, a multi-step process involving FS and DC improved the generalization performance, with the linear kernel support vector machine achieving the best results. This process was demonstrated to be potentially effective for models with reduced complexity, regardless of whether the decision boundaries were linear, curved, perpendicular, or parallel to the axes. These findings are expected to facilitate the development of an effective cardiomyopathy diagnostic model for its rapid adoption in medical practice.
Analysis of Dropout in Online Learning
Nov 09, 2017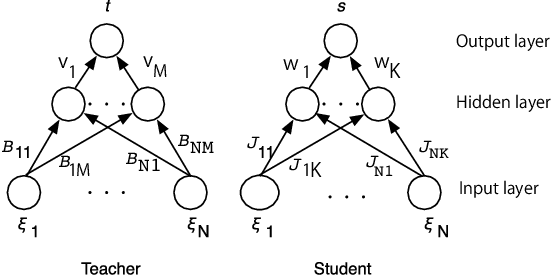
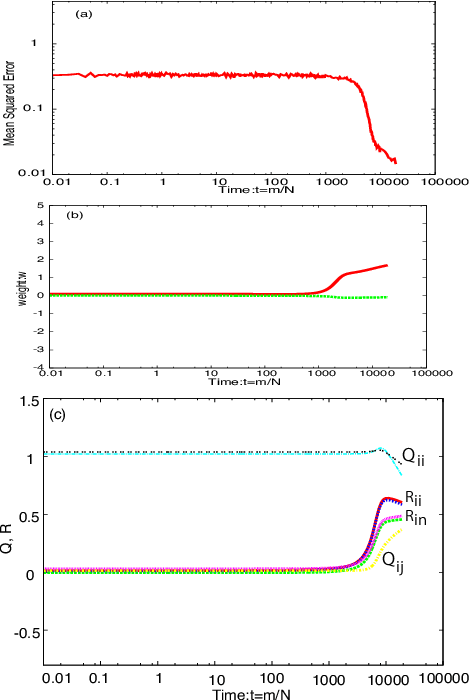
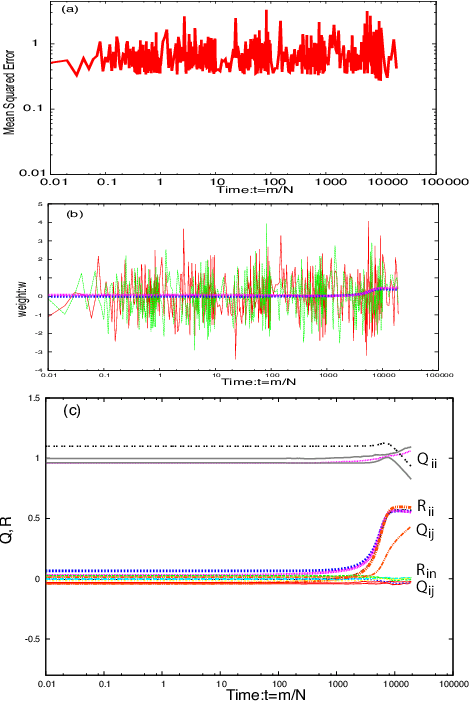
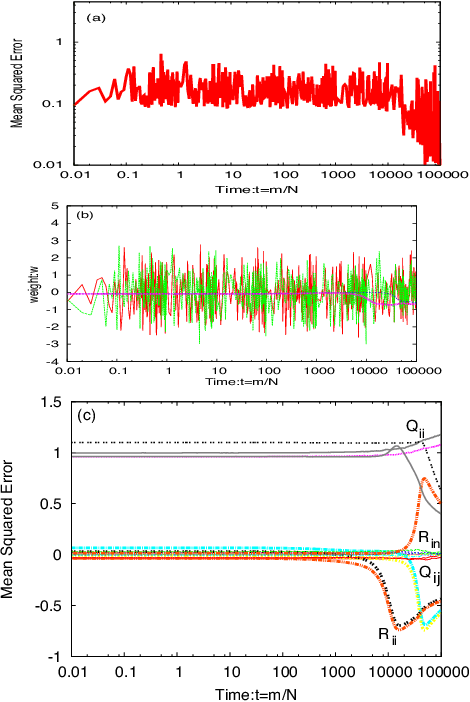
Abstract:Deep learning is the state-of-the-art in fields such as visual object recognition and speech recognition. This learning uses a large number of layers and a huge number of units and connections. Therefore, overfitting is a serious problem with it, and the dropout which is a kind of regularization tool is used. However, in online learning, the effect of dropout is not well known. This paper presents our investigation on the effect of dropout in online learning. We analyzed the effect of dropout on convergence speed near the singular point. Our results indicated that dropout is effective in online learning. Dropout tends to avoid the singular point for convergence speed near that point.
* 8 pages, 6 pages
Statistical Mechanics of Node-perturbation Learning with Noisy Baseline
Jun 20, 2017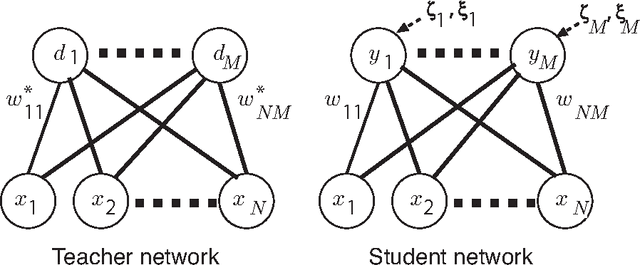
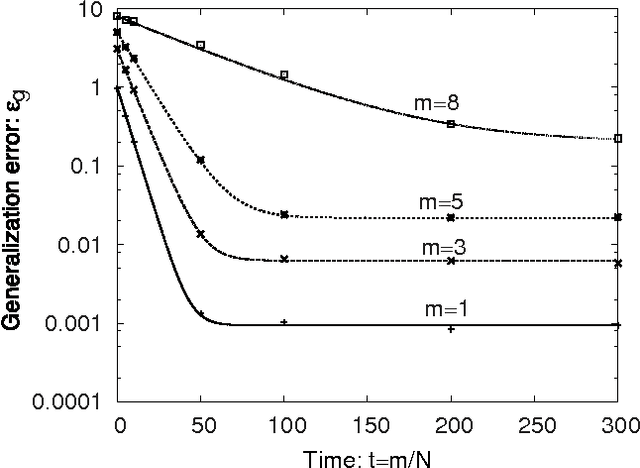
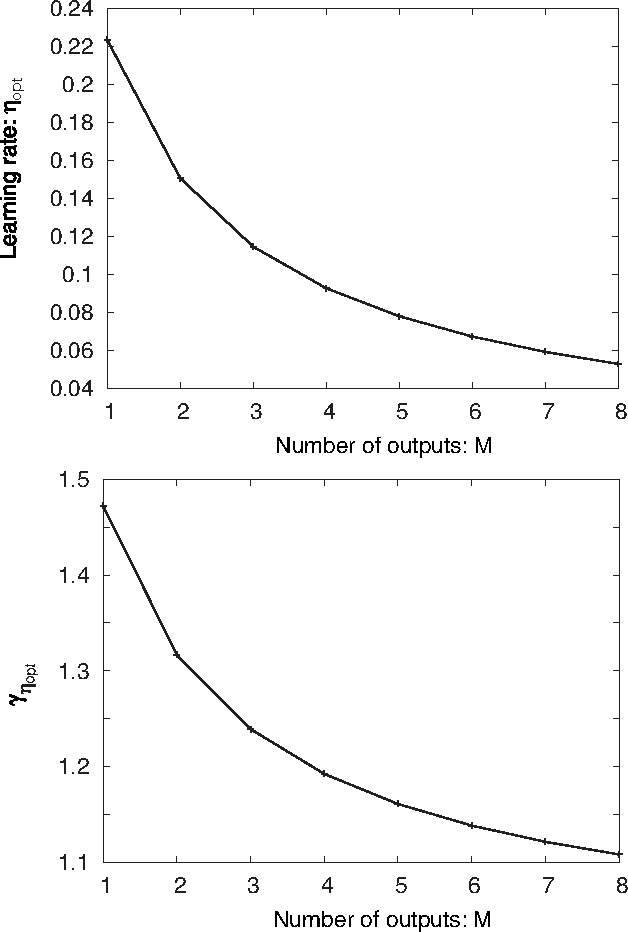
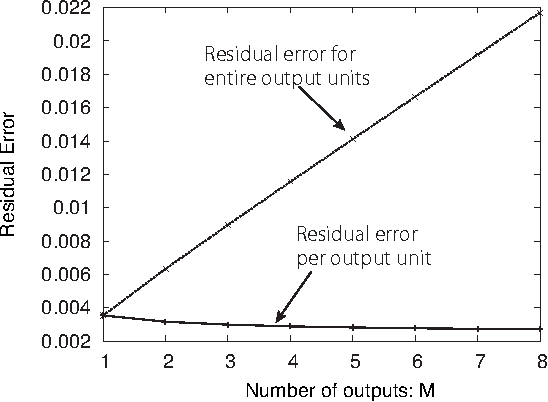
Abstract:Node-perturbation learning is a type of statistical gradient descent algorithm that can be applied to problems where the objective function is not explicitly formulated, including reinforcement learning. It estimates the gradient of an objective function by using the change in the object function in response to the perturbation. The value of the objective function for an unperturbed output is called a baseline. Cho et al. proposed node-perturbation learning with a noisy baseline. In this paper, we report on building the statistical mechanics of Cho's model and on deriving coupled differential equations of order parameters that depict learning dynamics. We also show how to derive the generalization error by solving the differential equations of order parameters. On the basis of the results, we show that Cho's results are also apply in general cases and show some general performances of Cho's model.
* 16 pages, 7 figures, submitted to JPSJ
Analysis of dropout learning regarded as ensemble learning
Jun 20, 2017
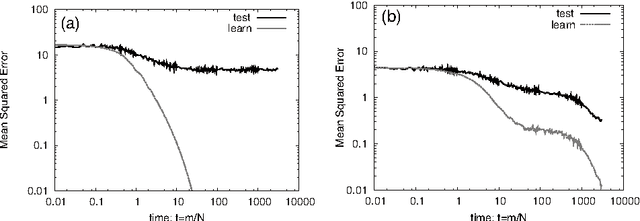
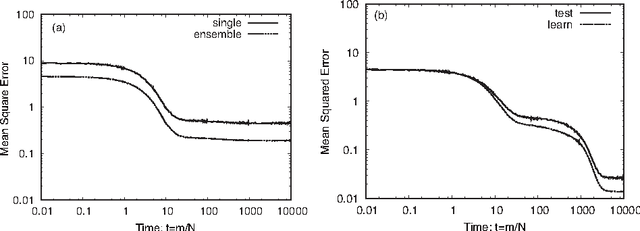
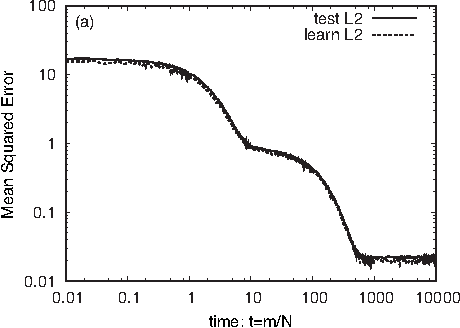
Abstract:Deep learning is the state-of-the-art in fields such as visual object recognition and speech recognition. This learning uses a large number of layers, huge number of units, and connections. Therefore, overfitting is a serious problem. To avoid this problem, dropout learning is proposed. Dropout learning neglects some inputs and hidden units in the learning process with a probability, p, and then, the neglected inputs and hidden units are combined with the learned network to express the final output. We find that the process of combining the neglected hidden units with the learned network can be regarded as ensemble learning, so we analyze dropout learning from this point of view.
* 9 pages, 8 figures, submitted to Conference
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge