Katherine Xu
Vibe Spaces for Creatively Connecting and Expressing Visual Concepts
Dec 16, 2025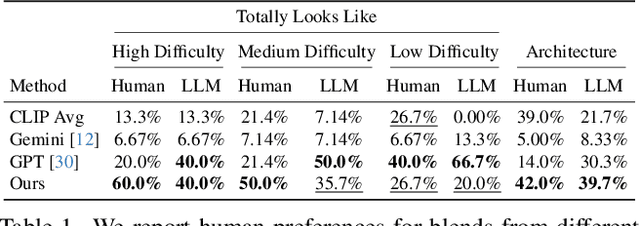

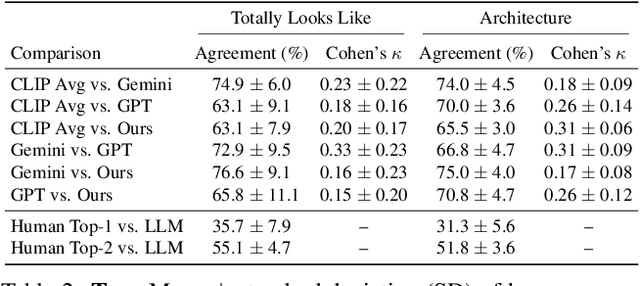
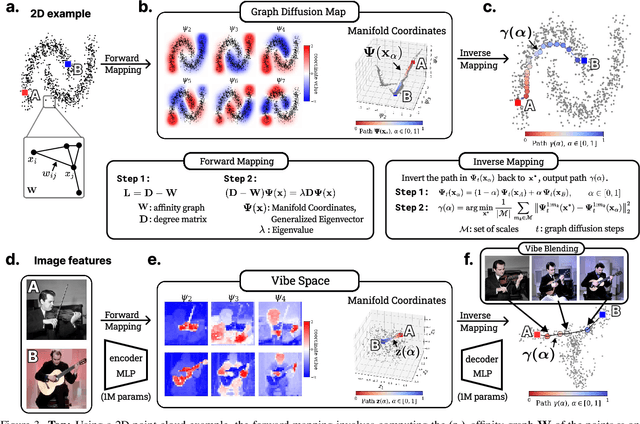
Abstract:Creating new visual concepts often requires connecting distinct ideas through their most relevant shared attributes -- their vibe. We introduce Vibe Blending, a novel task for generating coherent and meaningful hybrids that reveals these shared attributes between images. Achieving such blends is challenging for current methods, which struggle to identify and traverse nonlinear paths linking distant concepts in latent space. We propose Vibe Space, a hierarchical graph manifold that learns low-dimensional geodesics in feature spaces like CLIP, enabling smooth and semantically consistent transitions between concepts. To evaluate creative quality, we design a cognitively inspired framework combining human judgments, LLM reasoning, and a geometric path-based difficulty score. We find that Vibe Space produces blends that humans consistently rate as more creative and coherent than current methods.
"I Know It When I See It": Mood Spaces for Connecting and Expressing Visual Concepts
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Expressing complex concepts is easy when they can be labeled or quantified, but many ideas are hard to define yet instantly recognizable. We propose a Mood Board, where users convey abstract concepts with examples that hint at the intended direction of attribute changes. We compute an underlying Mood Space that 1) factors out irrelevant features and 2) finds the connections between images, thus bringing relevant concepts closer. We invent a fibration computation to compress/decompress pre-trained features into/from a compact space, 50-100x smaller. The main innovation is learning to mimic the pairwise affinity relationship of the image tokens across exemplars. To focus on the coarse-to-fine hierarchical structures in the Mood Space, we compute the top eigenvector structure from the affinity matrix and define a loss in the eigenvector space. The resulting Mood Space is locally linear and compact, allowing image-level operations, such as object averaging, visual analogy, and pose transfer, to be performed as a simple vector operation in Mood Space. Our learning is efficient in computation without any fine-tuning, needs only a few (2-20) exemplars, and takes less than a minute to learn.
Good Seed Makes a Good Crop: Discovering Secret Seeds in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
May 23, 2024
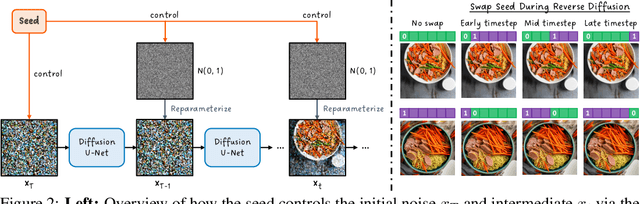


Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have facilitated creative and photorealistic image synthesis. By varying the random seeds, we can generate various images for a fixed text prompt. Technically, the seed controls the initial noise and, in multi-step diffusion inference, the noise used for reparameterization at intermediate timesteps in the reverse diffusion process. However, the specific impact of the random seed on the generated images remains relatively unexplored. In this work, we conduct a large-scale scientific study into the impact of random seeds during diffusion inference. Remarkably, we reveal that the best 'golden' seed achieved an impressive FID of 21.60, compared to the worst 'inferior' seed's FID of 31.97. Additionally, a classifier can predict the seed number used to generate an image with over 99.9% accuracy in just a few epochs, establishing that seeds are highly distinguishable based on generated images. Encouraged by these findings, we examined the influence of seeds on interpretable visual dimensions. We find that certain seeds consistently produce grayscale images, prominent sky regions, or image borders. Seeds also affect image composition, including object location, size, and depth. Moreover, by leveraging these 'golden' seeds, we demonstrate improved image generation such as high-fidelity inference and diversified sampling. Our investigation extends to inpainting tasks, where we uncover some seeds that tend to insert unwanted text artifacts. Overall, our extensive analyses highlight the importance of selecting good seeds and offer practical utility for image generation.
Detecting Image Attribution for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models in RGB and Beyond
Apr 10, 2024
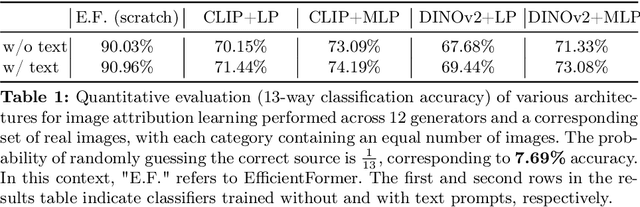

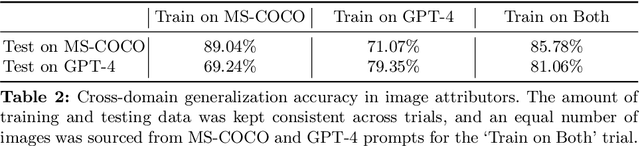
Abstract:Modern text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models can generate images with remarkable realism and creativity. These advancements have sparked research in fake image detection and attribution, yet prior studies have not fully explored the practical and scientific dimensions of this task. In addition to attributing images to 12 state-of-the-art T2I generators, we provide extensive analyses on what inference stage hyperparameters and image modifications are discernible. Our experiments reveal that initialization seeds are highly detectable, along with other subtle variations in the image generation process to some extent. We further investigate what visual traces are leveraged in image attribution by perturbing high-frequency details and employing mid-level representations of image style and structure. Notably, altering high-frequency information causes only slight reductions in accuracy, and training an attributor on style representations outperforms training on RGB images. Our analyses underscore that fake images are detectable and attributable at various levels of visual granularity than previously explored.
Amodal Completion via Progressive Mixed Context Diffusion
Dec 24, 2023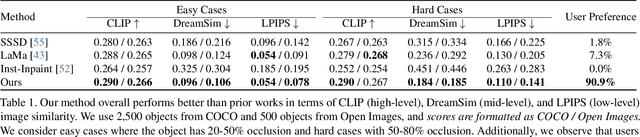
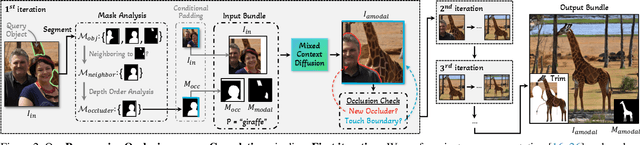
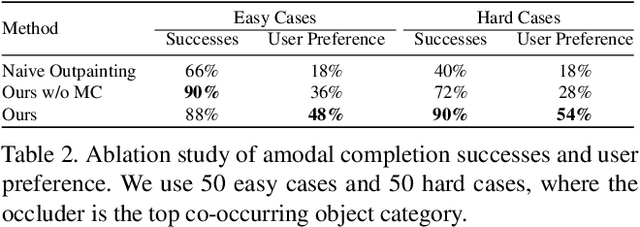
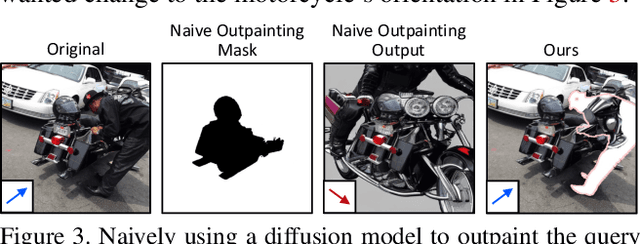
Abstract:Our brain can effortlessly recognize objects even when partially hidden from view. Seeing the visible of the hidden is called amodal completion; however, this task remains a challenge for generative AI despite rapid progress. We propose to sidestep many of the difficulties of existing approaches, which typically involve a two-step process of predicting amodal masks and then generating pixels. Our method involves thinking outside the box, literally! We go outside the object bounding box to use its context to guide a pre-trained diffusion inpainting model, and then progressively grow the occluded object and trim the extra background. We overcome two technical challenges: 1) how to be free of unwanted co-occurrence bias, which tends to regenerate similar occluders, and 2) how to judge if an amodal completion has succeeded. Our amodal completion method exhibits improved photorealistic completion results compared to existing approaches in numerous successful completion cases. And the best part? It doesn't require any special training or fine-tuning of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge