Katharina Kinder-Kurlanda
Are LLMs (Really) Ideological? An IRT-based Analysis and Alignment Tool for Perceived Socio-Economic Bias in LLMs
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce an Item Response Theory (IRT)-based framework to detect and quantify socioeconomic bias in large language models (LLMs) without relying on subjective human judgments. Unlike traditional methods, IRT accounts for item difficulty, improving ideological bias estimation. We fine-tune two LLM families (Meta-LLaMa 3.2-1B-Instruct and Chat- GPT 3.5) to represent distinct ideological positions and introduce a two-stage approach: (1) modeling response avoidance and (2) estimating perceived bias in answered responses. Our results show that off-the-shelf LLMs often avoid ideological engagement rather than exhibit bias, challenging prior claims of partisanship. This empirically validated framework enhances AI alignment research and promotes fairer AI governance.
Articulation Work and Tinkering for Fairness in Machine Learning
Jul 23, 2024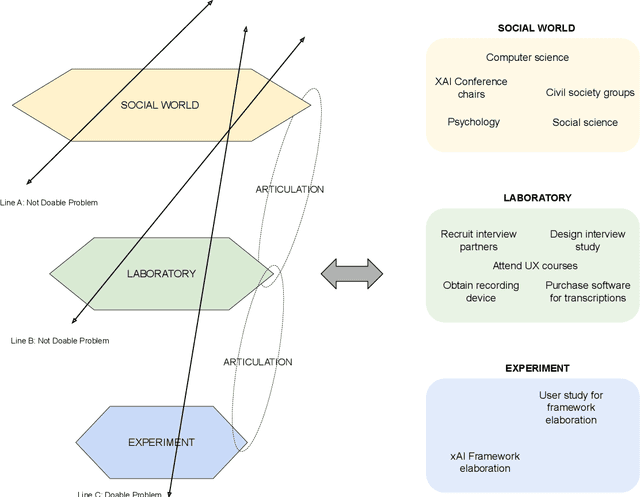
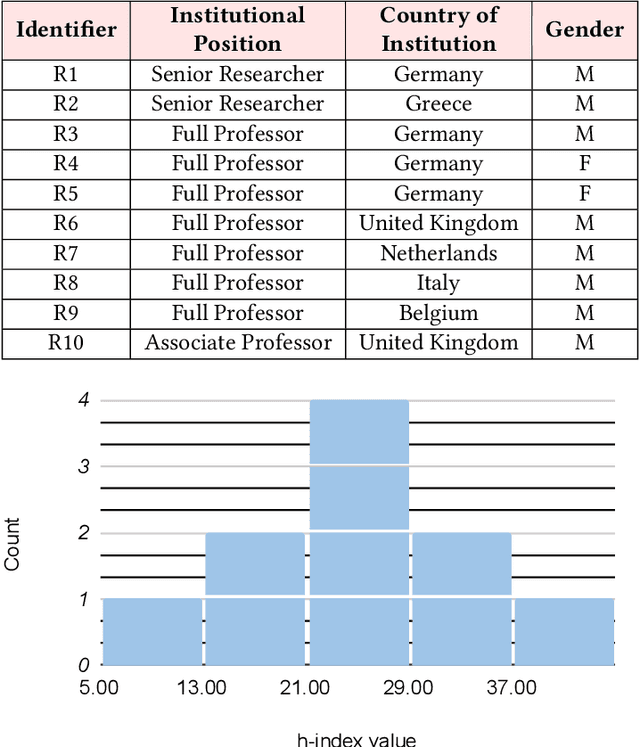
Abstract:The field of fair AI aims to counter biased algorithms through computational modelling. However, it faces increasing criticism for perpetuating the use of overly technical and reductionist methods. As a result, novel approaches appear in the field to address more socially-oriented and interdisciplinary (SOI) perspectives on fair AI. In this paper, we take this dynamic as the starting point to study the tension between computer science (CS) and SOI research. By drawing on STS and CSCW theory, we position fair AI research as a matter of 'organizational alignment': what makes research 'doable' is the successful alignment of three levels of work organization (the social world, the laboratory and the experiment). Based on qualitative interviews with CS researchers, we analyze the tasks, resources, and actors required for doable research in the case of fair AI. We find that CS researchers engage with SOI to some extent, but organizational conditions, articulation work, and ambiguities of the social world constrain the doability of SOI research. Based on our findings, we identify and discuss problems for aligning CS and SOI as fair AI continues to evolve.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge