Kanyao Han
From Symbolic to Natural-Language Relations: Rethinking Knowledge Graph Construction in the Era of Large Language Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have commonly been constructed using predefined symbolic relation schemas, typically implemented as categorical relation labels. This design has notable shortcomings: real-world relations are often contextual, nuanced, and sometimes uncertain, and compressing it into discrete relation labels abstracts away critical semantic detail. Nevertheless, symbolic-relation KGs remain widely used because they have been operationally effective and broadly compatible with pre-LLM downstream models and algorithms, in which KG knowledge could be retrieved or encoded into quantified features and embeddings at scale. The emergence of LLMs has reshaped how knowledge is created and consumed. LLMs support scalable synthesis of domain facts directly in concise natural language, and prompting-based inference favors context-rich free-form text over quantified representations. This position paper argues that these changes call for rethinking the representation of relations themselves rather than merely using LLMs to populate conventional schemas more efficiently. We therefore advocate moving from symbolic to natural-language relation descriptions, and we propose hybrid design principles that preserve a minimal structural backbone while enabling more flexible and context-sensitive relational representations.
SciPrompt: Knowledge-augmented Prompting for Fine-grained Categorization of Scientific Topics
Oct 02, 2024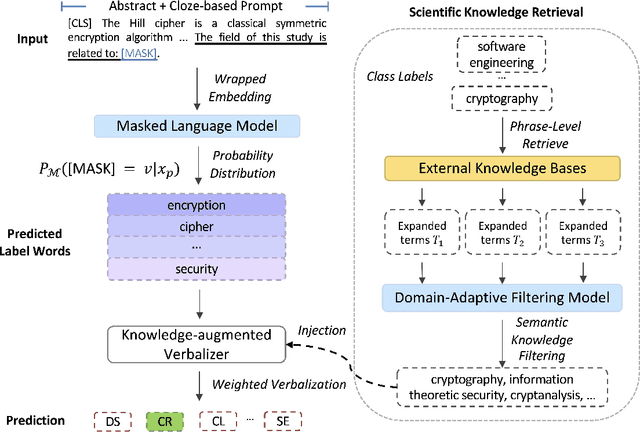
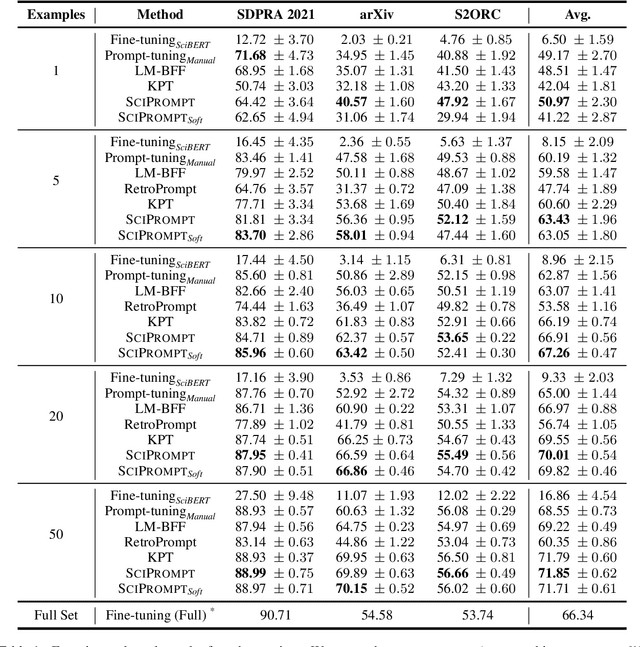
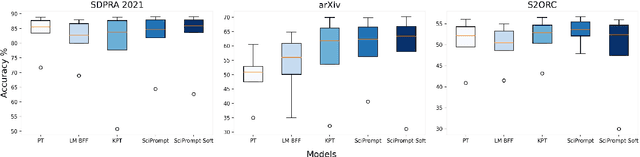
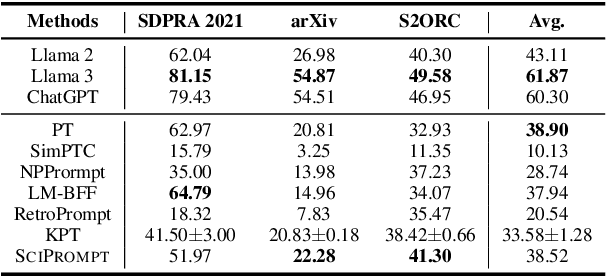
Abstract:Prompt-based fine-tuning has become an essential method for eliciting information encoded in pre-trained language models for a variety of tasks, including text classification. For multi-class classification tasks, prompt-based fine-tuning under low-resource scenarios has resulted in performance levels comparable to those of fully fine-tuning methods. Previous studies have used crafted prompt templates and verbalizers, mapping from the label terms space to the class space, to solve the classification problem as a masked language modeling task. However, cross-domain and fine-grained prompt-based fine-tuning with an automatically enriched verbalizer remains unexplored, mainly due to the difficulty and costs of manually selecting domain label terms for the verbalizer, which requires humans with domain expertise. To address this challenge, we introduce SciPrompt, a framework designed to automatically retrieve scientific topic-related terms for low-resource text classification tasks. To this end, we select semantically correlated and domain-specific label terms within the context of scientific literature for verbalizer augmentation. Furthermore, we propose a new verbalization strategy that uses correlation scores as additional weights to enhance the prediction performance of the language model during model tuning. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art, prompt-based fine-tuning methods on scientific text classification tasks under few and zero-shot settings, especially in classifying fine-grained and emerging scientific topics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge