Kananart Kuwaranancharoen
On the Benefits of Leveraging Structural Information in Planning Over the Learned Model
Mar 15, 2023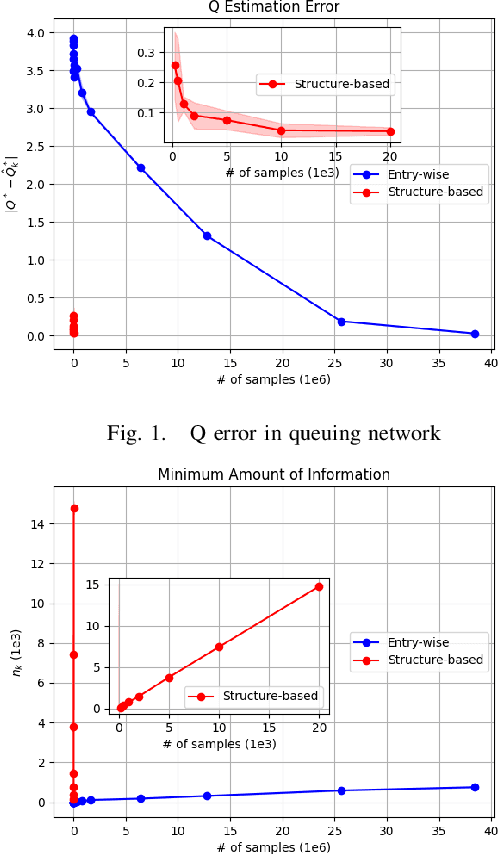
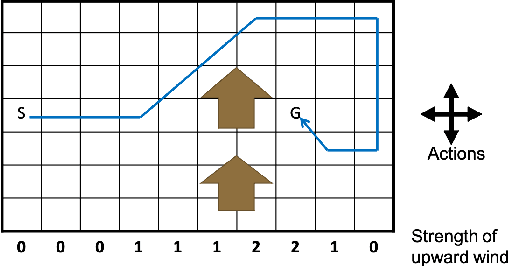
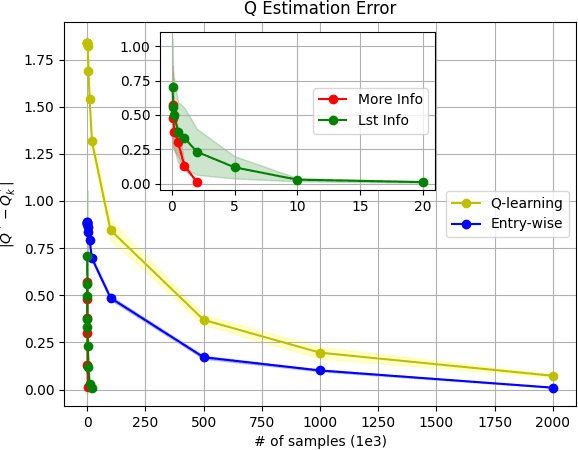
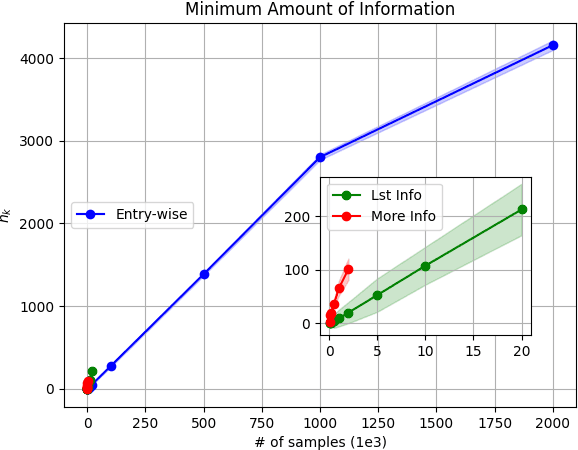
Abstract:Model-based Reinforcement Learning (RL) integrates learning and planning and has received increasing attention in recent years. However, learning the model can incur a significant cost (in terms of sample complexity), due to the need to obtain a sufficient number of samples for each state-action pair. In this paper, we investigate the benefits of leveraging structural information about the system in terms of reducing sample complexity. Specifically, we consider the setting where the transition probability matrix is a known function of a number of structural parameters, whose values are initially unknown. We then consider the problem of estimating those parameters based on the interactions with the environment. We characterize the difference between the Q estimates and the optimal Q value as a function of the number of samples. Our analysis shows that there can be a significant saving in sample complexity by leveraging structural information about the model. We illustrate the findings by considering several problems including controlling a queuing system with heterogeneous servers, and seeking an optimal path in a stochastic windy gridworld.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge