Kamen Brestnichki
Multilingual Factor Analysis
May 14, 2019
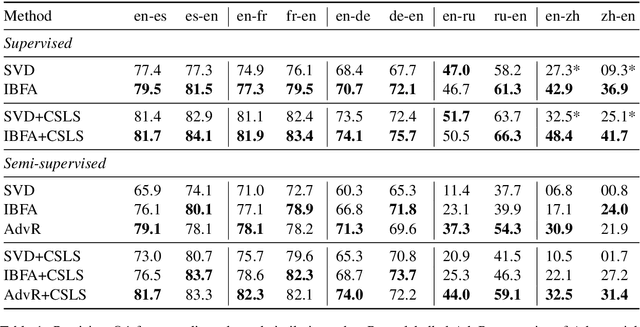

Abstract:In this work we approach the task of learning multilingual word representations in an offline manner by fitting a generative latent variable model to a multilingual dictionary. We model equivalent words in different languages as different views of the same word generated by a common latent variable representing their latent lexical meaning. We explore the task of alignment by querying the fitted model for multilingual embeddings achieving competitive results across a variety of tasks. The proposed model is robust to noise in the embedding space making it a suitable method for distributed representations learned from noisy corpora.
Model Comparison for Semantic Grouping
May 01, 2019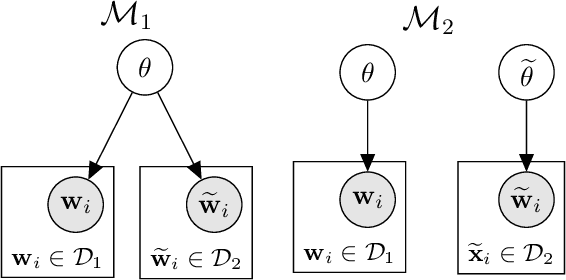
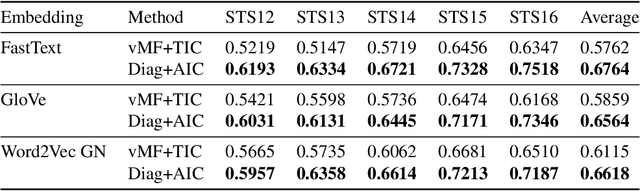
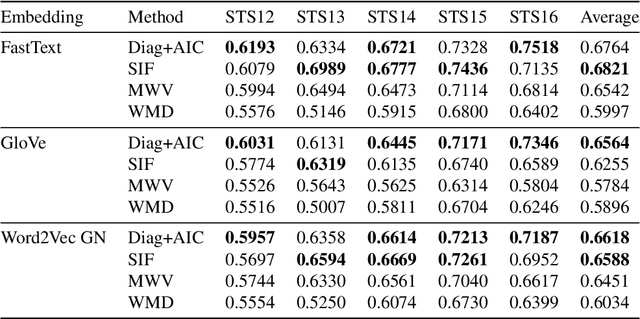
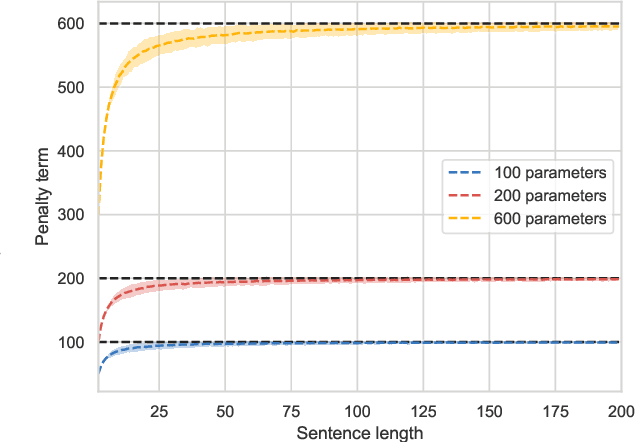
Abstract:We introduce a probabilistic framework for quantifying the semantic similarity between two groups of embeddings. We formulate the task of semantic similarity as a model comparison task in which we contrast a generative model which jointly models two sentences versus one that does not. We illustrate how this framework can be used for the Semantic Textual Similarity tasks using clear assumptions about how the embeddings of words are generated. We apply model comparison that utilises information criteria to address some of the shortcomings of Bayesian model comparison, whilst still penalising model complexity. We achieve competitive results by applying the proposed framework with an appropriate choice of likelihood on the STS datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge