Kaiyu Shi
Memory-Efficient Pipeline-Parallel DNN Training
Jun 16, 2020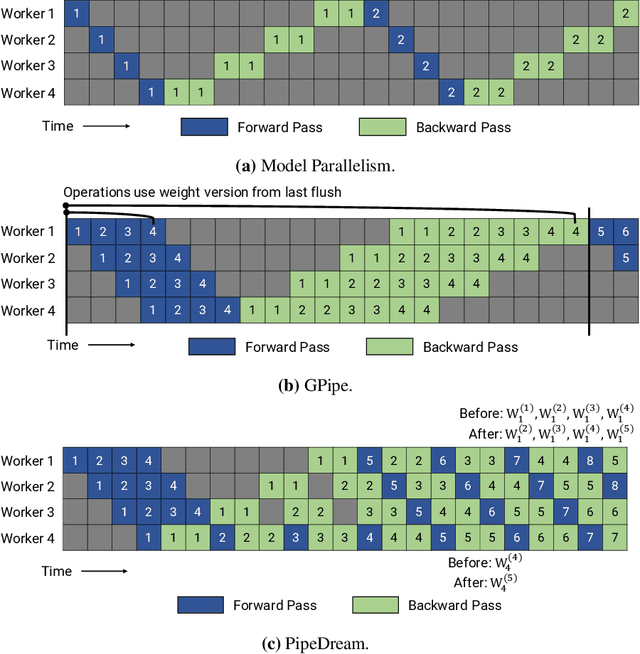
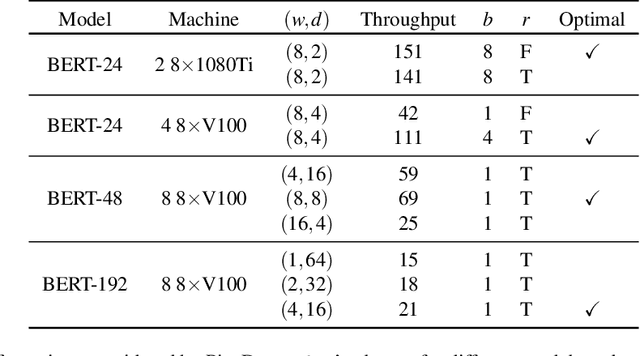
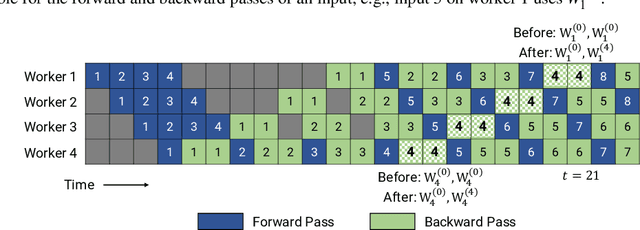
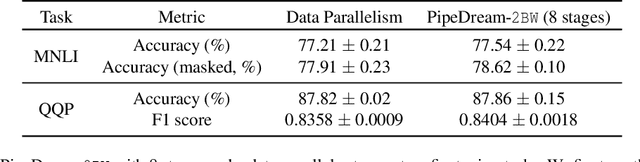
Abstract:Many state-of-the-art results in domains such as NLP and computer vision have been obtained by scaling up the number of parameters in existing models. However, the weight parameters and intermediate outputs of these large models often do not fit in the main memory of a single accelerator device; this means that it is necessary to use multiple accelerators to train large models, which is challenging to do in a time-efficient way. In this work, we propose PipeDream-2BW, a system that performs memory-efficient pipeline parallelism, a hybrid form of parallelism that combines data and model parallelism with input pipelining. Our system uses a novel pipelining and weight gradient coalescing strategy, combined with the double buffering of weights, to ensure high throughput, low memory footprint, and weight update semantics similar to data parallelism. In addition, PipeDream-2BW automatically partitions the model over the available hardware resources, while being cognizant of constraints such as compute capabilities, memory capacities, and interconnect topologies, and determines when to employ existing memory-savings techniques, such as activation recomputation, that trade off extra computation for lower memory footprint. PipeDream-2BW is able to accelerate the training of large language models with up to 2.5 billion parameters by up to 6.9x compared to optimized baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge