Kaito Majima
Generating News-Centric Crossword Puzzles As A Constraint Satisfaction and Optimization Problem
Aug 09, 2023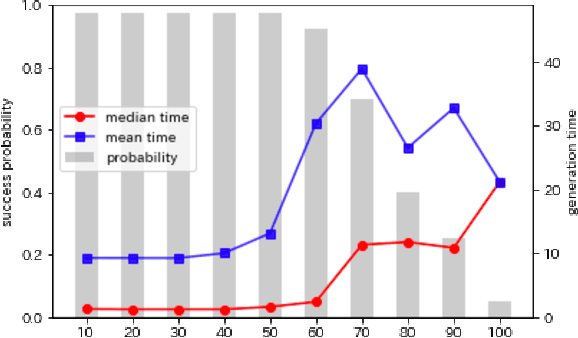
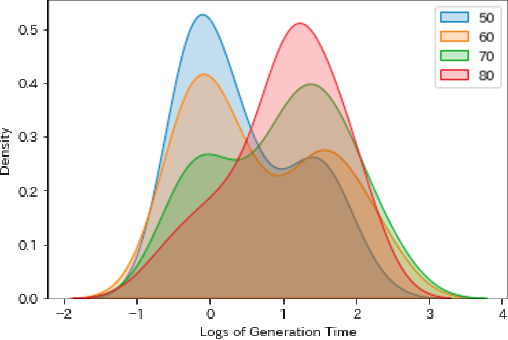
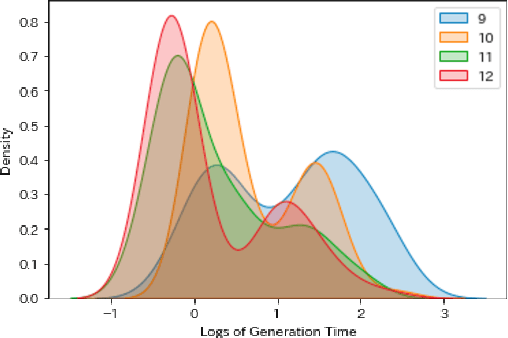
Abstract:Crossword puzzles have traditionally served not only as entertainment but also as an educational tool that can be used to acquire vocabulary and language proficiency. One strategy to enhance the educational purpose is personalization, such as including more words on a particular topic. This paper focuses on the case of encouraging people's interest in news and proposes a framework for automatically generating news-centric crossword puzzles. We designed possible scenarios and built a prototype as a constraint satisfaction and optimization problem, that is, containing as many news-derived words as possible. Our experiments reported the generation probabilities and time required under several conditions. The results showed that news-centric crossword puzzles can be generated even with few news-derived words. We summarize the current issues and future research directions through a qualitative evaluation of the prototype. This is the first proposal that a formulation of a constraint satisfaction and optimization problem can be beneficial as an educational application.
Constrained Generalized Additive 2 Model with Consideration of High-Order Interactions
Jun 05, 2021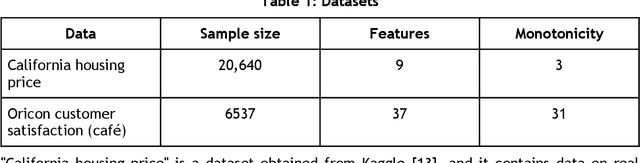
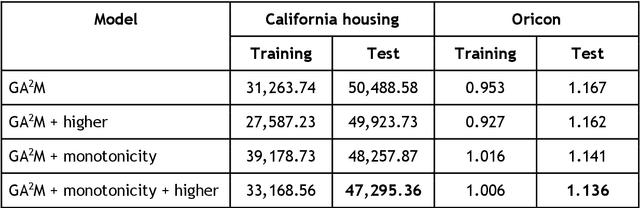
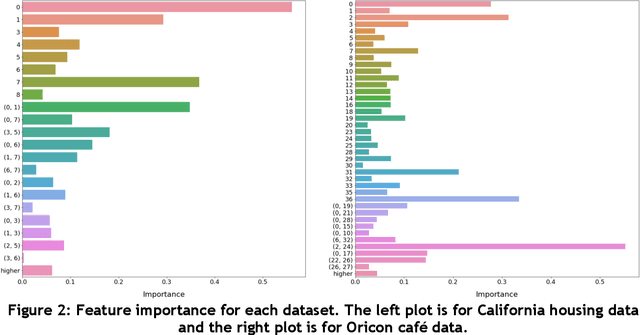
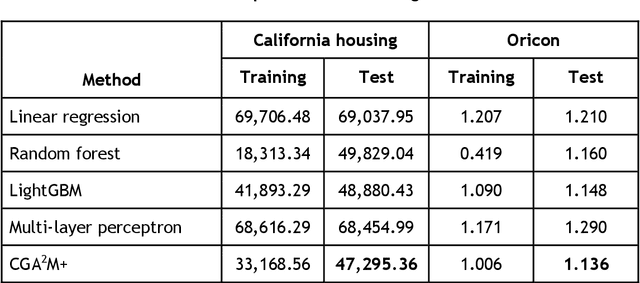
Abstract:In recent years, machine learning and AI have been introduced in many industrial fields. In fields such as finance, medicine, and autonomous driving, where the inference results of a model may have serious consequences, high interpretability as well as prediction accuracy is required. In this study, we propose CGA2M+, which is based on the Generalized Additive 2 Model (GA2M) and differs from it in two major ways. The first is the introduction of monotonicity. Imposing monotonicity on some functions based on an analyst's knowledge is expected to improve not only interpretability but also generalization performance. The second is the introduction of a higher-order term: given that GA2M considers only second-order interactions, we aim to balance interpretability and prediction accuracy by introducing a higher-order term that can capture higher-order interactions. In this way, we can improve prediction performance without compromising interpretability by applying learning innovation. Numerical experiments showed that the proposed model has high predictive performance and interpretability. Furthermore, we confirmed that generalization performance is improved by introducing monotonicity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge