K. P. Naveen
Efficient-UCBV: An Almost Optimal Algorithm using Variance Estimates
Nov 09, 2017


Abstract:We propose a novel variant of the UCB algorithm (referred to as Efficient-UCB-Variance (EUCBV)) for minimizing cumulative regret in the stochastic multi-armed bandit (MAB) setting. EUCBV incorporates the arm elimination strategy proposed in UCB-Improved \citep{auer2010ucb}, while taking into account the variance estimates to compute the arms' confidence bounds, similar to UCBV \citep{audibert2009exploration}. Through a theoretical analysis we establish that EUCBV incurs a \emph{gap-dependent} regret bound of {\scriptsize $O\left( \dfrac{K\sigma^2_{\max} \log (T\Delta^2 /K)}{\Delta}\right)$} after $T$ trials, where $\Delta$ is the minimal gap between optimal and sub-optimal arms; the above bound is an improvement over that of existing state-of-the-art UCB algorithms (such as UCB1, UCB-Improved, UCBV, MOSS). Further, EUCBV incurs a \emph{gap-independent} regret bound of {\scriptsize $O\left(\sqrt{KT}\right)$} which is an improvement over that of UCB1, UCBV and UCB-Improved, while being comparable with that of MOSS and OCUCB. Through an extensive numerical study we show that EUCBV significantly outperforms the popular UCB variants (like MOSS, OCUCB, etc.) as well as Thompson sampling and Bayes-UCB algorithms.
Thresholding Bandits with Augmented UCB
May 09, 2017
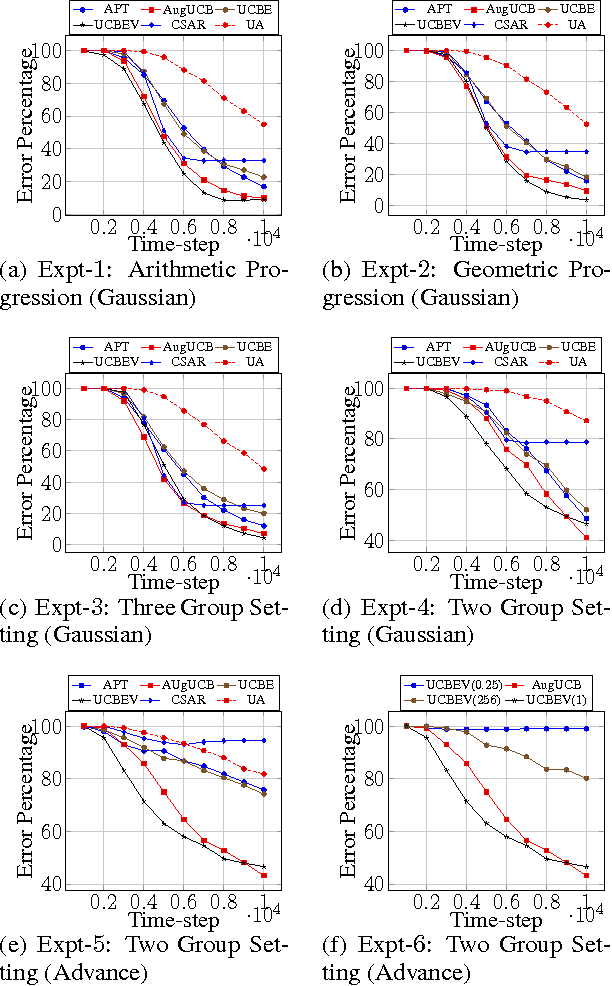
Abstract:In this paper we propose the Augmented-UCB (AugUCB) algorithm for a fixed-budget version of the thresholding bandit problem (TBP), where the objective is to identify a set of arms whose quality is above a threshold. A key feature of AugUCB is that it uses both mean and variance estimates to eliminate arms that have been sufficiently explored; to the best of our knowledge this is the first algorithm to employ such an approach for the considered TBP. Theoretically, we obtain an upper bound on the loss (probability of mis-classification) incurred by AugUCB. Although UCBEV in literature provides a better guarantee, it is important to emphasize that UCBEV has access to problem complexity (whose computation requires arms' mean and variances), and hence is not realistic in practice; this is in contrast to AugUCB whose implementation does not require any such complexity inputs. We conduct extensive simulation experiments to validate the performance of AugUCB. Through our simulation work, we establish that AugUCB, owing to its utilization of variance estimates, performs significantly better than the state-of-the-art APT, CSAR and other non variance-based algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge