Junho Jo
Natural and Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution with Explicit Natural Manifold Discrimination
Nov 09, 2019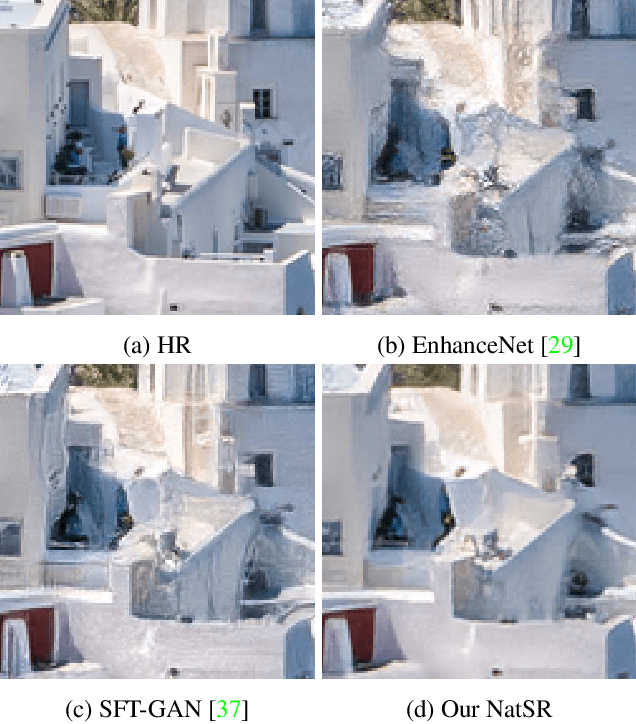
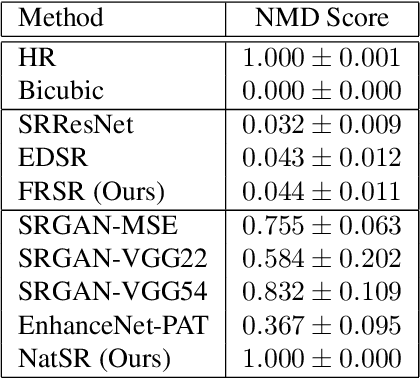
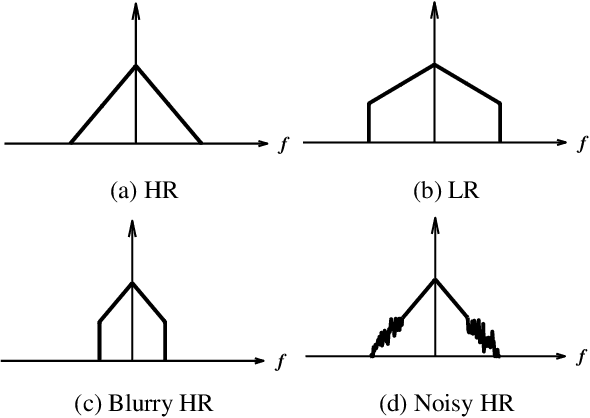
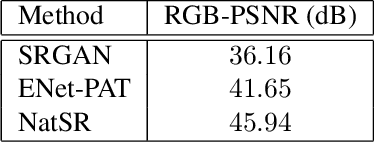
Abstract:Recently, many convolutional neural networks for single image super-resolution (SISR) have been proposed, which focus on reconstructing the high-resolution images in terms of objective distortion measures. However, the networks trained with objective loss functions generally fail to reconstruct the realistic fine textures and details that are essential for better perceptual quality. Recovering the realistic details remains a challenging problem, and only a few works have been proposed which aim at increasing the perceptual quality by generating enhanced textures. However, the generated fake details often make undesirable artifacts and the overall image looks somewhat unnatural. Therefore, in this paper, we present a new approach to reconstructing realistic super-resolved images with high perceptual quality, while maintaining the naturalness of the result. In particular, we focus on the domain prior properties of SISR problem. Specifically, we define the naturalness prior in the low-level domain and constrain the output image in the natural manifold, which eventually generates more natural and realistic images. Our results show better naturalness compared to the recent super-resolution algorithms including perception-oriented ones.
Handwritten Text Segmentation via End-to-End Learning of Convolutional Neural Network
Jun 12, 2019



Abstract:We present a new handwritten text segmentation method by training a convolutional neural network (CNN) in an end-to-end manner. Many conventional methods addressed this problem by extracting connected components and then classifying them. However, this two-step approach has limitations when handwritten components and machine-printed parts are overlapping. Unlike conventional methods, we develop an end-to-end deep CNN for this problem, which does not need any preprocessing steps. Since there is no publicly available dataset for this goal and pixel-wise annotations are time-consuming and costly, we also propose a data synthesis algorithm that generates realistic training samples. For training our network, we develop a cross-entropy based loss function that addresses the imbalance problems. Experimental results on synthetic and real images show the effectiveness of the proposed method. Specifically, the proposed network has been trained solely on synthetic images, nevertheless the removal of handwritten text in real documents improves OCR performance from 71.13% to 92.50%, showing the generalization performance of our network and synthesized images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge