Julian Brand
Comparison of Depth Estimation Setups from Stereo Endoscopy and Optical Tracking for Point Measurements
Jan 26, 2022
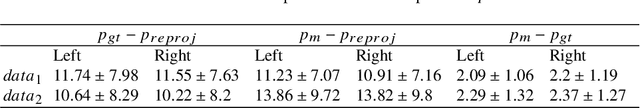
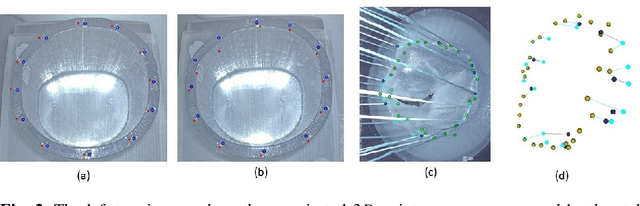
Abstract:To support minimally-invasive intraoperative mitral valve repair, quantitative measurements from the valve can be obtained using an infra-red tracked stylus. It is desirable to view such manually measured points together with the endoscopic image for further assistance. Therefore, hand-eye calibration is required that links both coordinate systems and is a prerequisite to project the points onto the image plane. A complementary approach to this is to use a vision-based endoscopic stereo-setup to detect and triangulate points of interest, to obtain the 3D coordinates. In this paper, we aim to compare both approaches on a rigid phantom and two patient-individual silicone replica which resemble the intraoperative scenario. The preliminary results indicate that 3D landmark estimation, either labeled manually or through partly automated detection with a deep learning approach, provides more accurate triangulated depth measurements when performed with a tailored image-based method than with stylus measurements.
Point detection through multi-instance deep heatmap regression for sutures in endoscopy
Nov 16, 2021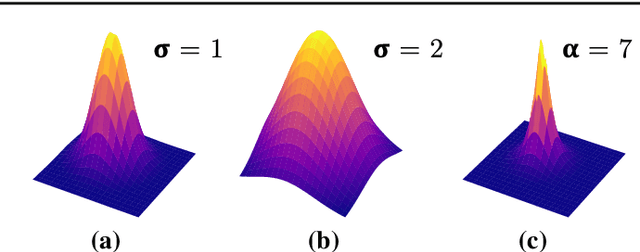
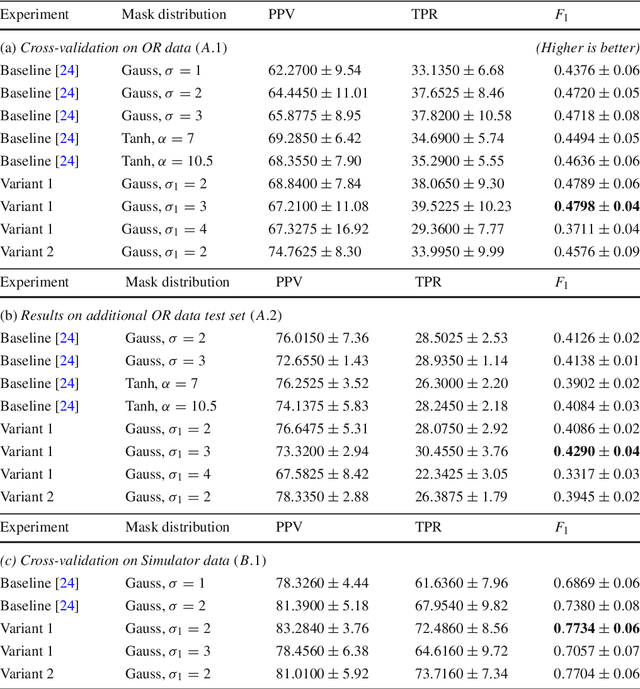
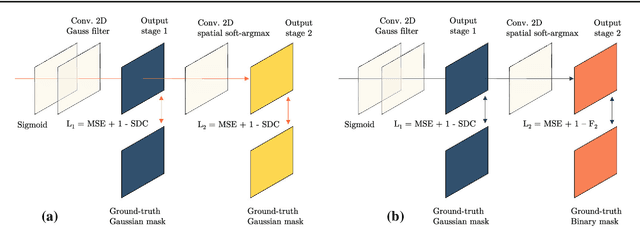
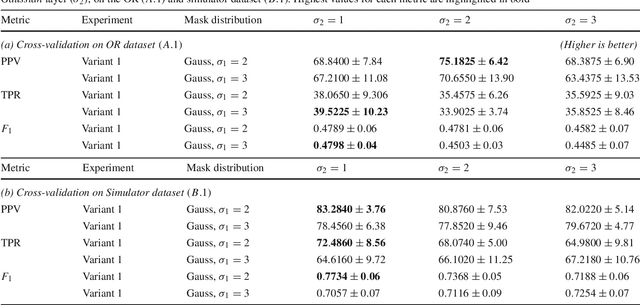
Abstract:Purpose: Mitral valve repair is a complex minimally invasive surgery of the heart valve. In this context, suture detection from endoscopic images is a highly relevant task that provides quantitative information to analyse suturing patterns, assess prosthetic configurations and produce augmented reality visualisations. Facial or anatomical landmark detection tasks typically contain a fixed number of landmarks, and use regression or fixed heatmap-based approaches to localize the landmarks. However in endoscopy, there are a varying number of sutures in every image, and the sutures may occur at any location in the annulus, as they are not semantically unique. Method: In this work, we formulate the suture detection task as a multi-instance deep heatmap regression problem, to identify entry and exit points of sutures. We extend our previous work, and introduce the novel use of a 2D Gaussian layer followed by a differentiable 2D spatial Soft-Argmax layer to function as a local non-maximum suppression. Results: We present extensive experiments with multiple heatmap distribution functions and two variants of the proposed model. In the intra-operative domain, Variant 1 showed a mean F1 of +0.0422 over the baseline. Similarly, in the simulator domain, Variant 1 showed a mean F1 of +0.0865 over the baseline. Conclusion: The proposed model shows an improvement over the baseline in the intra-operative and the simulator domains. The data is made publicly available within the scope of the MICCAI AdaptOR2021 Challenge https://adaptor2021.github.io/, and the code at https://github.com/Cardio-AI/suture-detection-pytorch/. DOI:10.1007/s11548-021-02523-w. The link to the open access article can be found here: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11548-021-02523-w
* Accepted to International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 15 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge