Judith Wewerka
Knowledge Graph Enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a critical tool for mitigating potential failures, particular during ramp-up phases of new products. However, its effectiveness is often limited by the missing reasoning capabilities of the FMEA tools, which are usually tabular structured. Meanwhile, large language models (LLMs) offer novel prospects for fine-tuning on custom datasets for reasoning within FMEA contexts. However, LLMs face challenges in tasks that require factual knowledge, a gap that retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches aim to fill. RAG retrieves information from a non-parametric data store and uses a language model to generate responses. Building on this idea, we propose to advance the non-parametric data store with a knowledge graph (KG). By enhancing the RAG framework with a KG, our objective is to leverage analytical and semantic question-answering capabilities on FMEA data. This paper contributes by presenting a new ontology for FMEA observations, an algorithm for creating vector embeddings from the FMEA KG, and a KG enhanced RAG framework. Our approach is validated through a human study and we measure the performance of the context retrieval recall and precision.
Interactive and Intelligent Root Cause Analysis in Manufacturing with Causal Bayesian Networks and Knowledge Graphs
Jan 20, 2024



Abstract:Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in the manufacturing of electric vehicles is the process of identifying fault causes. Traditionally, the RCA is conducted manually, relying on process expert knowledge. Meanwhile, sensor networks collect significant amounts of data in the manufacturing process. Using this data for RCA makes it more efficient. However, purely data-driven methods like Causal Bayesian Networks have problems scaling to large-scale, real-world manufacturing processes due to the vast amount of potential cause-effect relationships (CERs). Furthermore, purely data-driven methods have the potential to leave out already known CERs or to learn spurious CERs. The paper contributes by proposing an interactive and intelligent RCA tool that combines expert knowledge of an electric vehicle manufacturing process and a data-driven machine learning method. It uses reasoning over a large-scale Knowledge Graph of the manufacturing process while learning a Causal Bayesian Network. In addition, an Interactive User Interface enables a process expert to give feedback to the root cause graph by adding and removing information to the Knowledge Graph. The interactive and intelligent RCA tool reduces the learning time of the Causal Bayesian Network while decreasing the number of spurious CERs. Thus, the interactive and intelligent RCA tool closes the feedback loop between expert and machine learning method.
Robotic Process Automation -- A Systematic Literature Review and Assessment Framework
Dec 22, 2020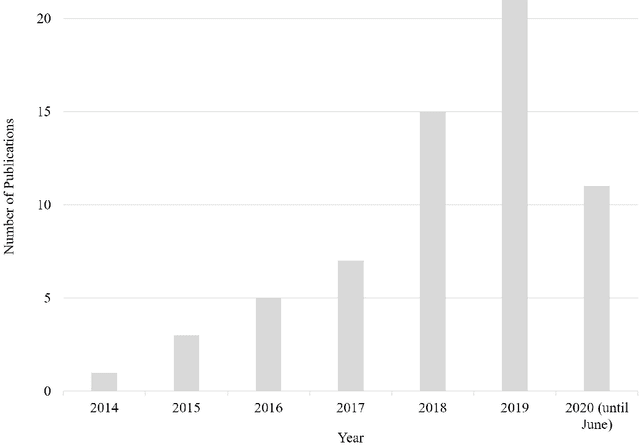



Abstract:Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the automation of rule-based routine processes to increase efficiency and to reduce costs. Due to the utmost importance of process automation in industry, RPA attracts increasing attention in the scientific field as well. This paper presents the state-of-the-art in the RPA field by means of a Systematic Literature Review (SLR). In this SLR, 63 publications are identified, categorised, and analysed along well-defined research questions. From the SLR findings, moreover, a framework for systematically analysing, assessing, and comparing existing as well as upcoming RPA works is derived. The discovered thematic clusters advise further investigations in order to develop an even more detailed structural research approach for RPA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge