Juan Sandoval
Evaluation of Position and Velocity Based Forward Dynamics Compliance Control (FDCC) for Robotic Interactions in Position Controlled Robots
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:In robotic manipulation, end-effector compliance is an essential precondition for performing contact-rich tasks, such as machining, assembly, and human-robot interaction. Most robotic arms are position-controlled stiff systems at a hardware level. Thus, adding compliance becomes essential. Compliance in those systems has been recently achieved using Forward dynamics compliance control (FDCC), which, owing to its virtual forward dynamics model, can be implemented on both position and velocity-controlled robots. This paper evaluates the choice of control interface (and hence the control domain), which, although considered trivial, is essential due to differences in their characteristics. In some cases, the choice is restricted to the available hardware interface. However, given the option to choose, the velocity-based control interface makes a better candidate for compliance control because of smoother compliant behaviour, reduced interaction forces, and work done. To prove these points, in this paper FDCC is evaluated on the UR10e six-DOF manipulator with velocity and position control modes. The evaluation is based on force-control benchmarking metrics using 3D-printed artefacts. Real experiments favour the choice of velocity control over position control.
Emulating On-Orbit Interactions Using Forward Dynamics Based Cartesian Motion
Sep 30, 2022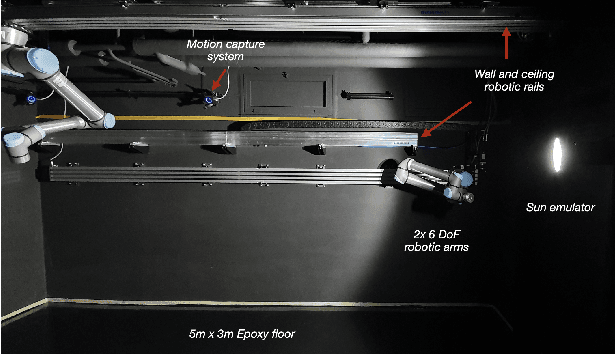



Abstract:The paper presents a novel Hardware-In-the-Loop (HIL) emulation framework of on-orbit interactions using on-ground robotic manipulators. It combines Virtual Forward Dynamic Model (VFDM) for Cartesian motion control of robotic manipulators with an Orbital Dynamics Simulator (ODS) based on the Clohessy Wiltshire (CW) Model. VFDM-based Inverse Kinematics (IK) solver is known to have better motion tracking, path accuracy, and solver convergency than traditional IK solvers. Therefore it provides a stable Cartesian motion for manipulator-based HIL on-orbit emulations. The framework is tested on a ROS-based robotics testbed to emulate two scenarios: free-floating satellite motion and free-floating interaction (collision). Mock-ups of two satellites are mounted at the robots' end-effectors. Forces acting on the mock-ups are measured through an in-built F/T sensor on each robotic arm. During the tests, the relative motion of the mock-ups is expressed with respect to a moving observer rotating at a fixed angular velocity in a circular orbit rather than their motion in the inertial frame. The ODS incorporates the force and torque values on the fly and delivers the corresponding satellite motions to the virtual forward dynamics model as online trajectories. Results are comparable to other free-floating HIL emulators. Fidelity between the simulated motion and robot-mounted mock-up motion is confirmed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge