Juan Guerrero Montero
Reliable identification of selection mechanisms in language change
May 25, 2023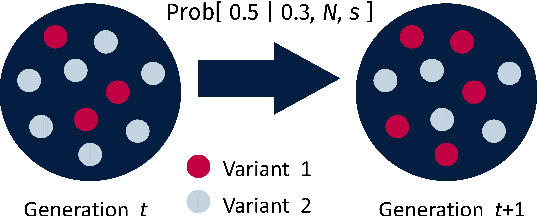

Abstract:Language change is a cultural evolutionary process in which variants of linguistic variables change in frequency through processes analogous to mutation, selection and genetic drift. In this work, we apply a recently-introduced method to corpus data to quantify the strength of selection in specific instances of historical language change. We first demonstrate, in the context of English irregular verbs, that this method is more reliable and interpretable than similar methods that have previously been applied. We further extend this study to demonstrate that a bias towards phonological simplicity overrides that favouring grammatical simplicity when these are in conflict. Finally, with reference to Spanish spelling reforms, we show that the method can also detect points in time at which selection strengths change, a feature that is generically expected for socially-motivated language change. Together, these results indicate how hypotheses for mechanisms of language change can be tested quantitatively using historical corpus data.
Self-contained Beta-with-Spikes Approximation for Inference Under a Wright-Fisher Model
Mar 08, 2023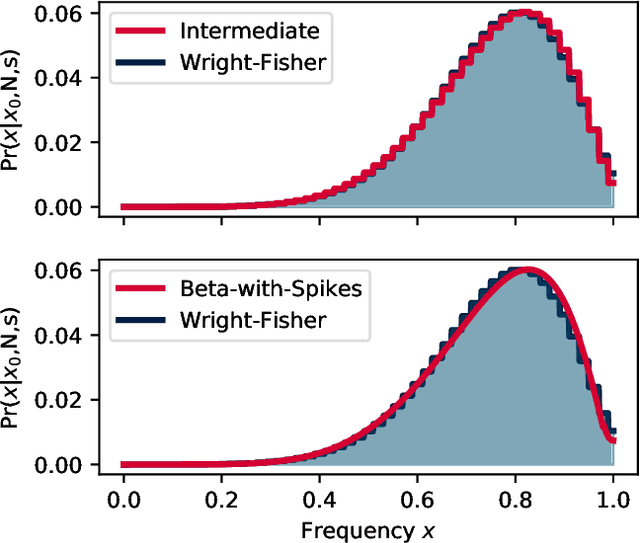
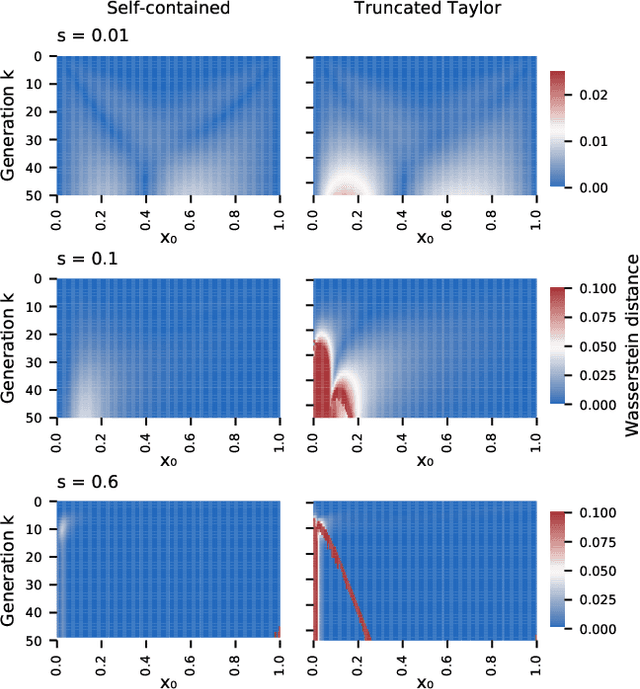
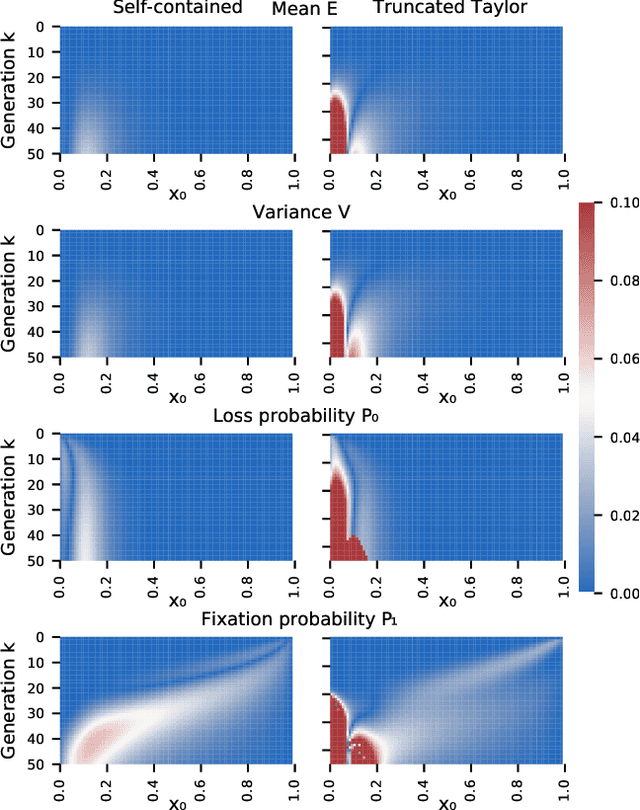
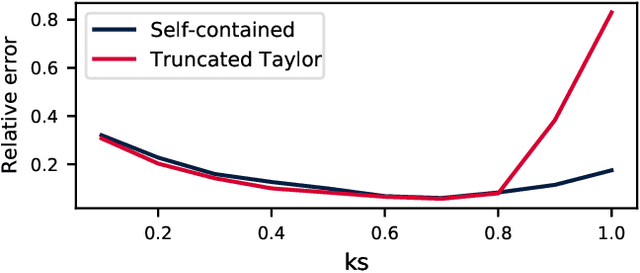
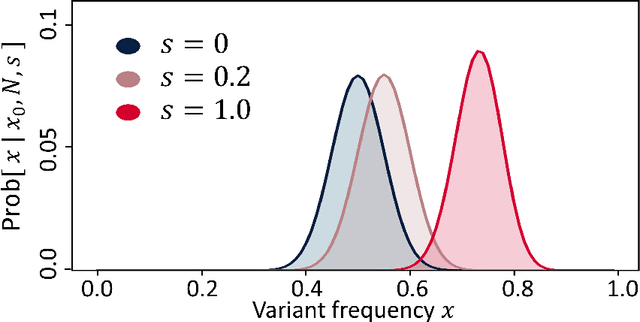
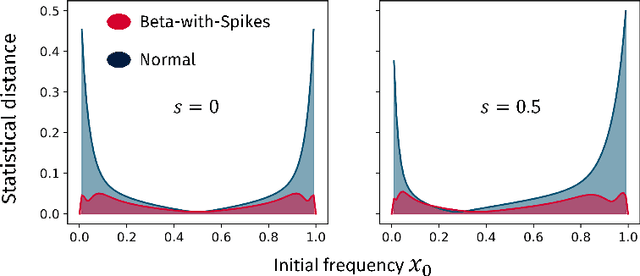
Abstract:We construct a reliable estimation of evolutionary parameters within the Wright-Fisher model, which describes changes in allele frequencies due to selection and genetic drift, from time-series data. Such data exists for biological populations, for example via artificial evolution experiments, and for the cultural evolution of behavior, such as linguistic corpora that document historical usage of different words with similar meanings. Our method of analysis builds on a Beta-with-Spikes approximation to the distribution of allele frequencies predicted by the Wright-Fisher model. We introduce a self-contained scheme for estimating the parameters in the approximation, and demonstrate its robustness with synthetic data, especially in the strong-selection and near-extinction regimes where previous approaches fail. We further apply to allele frequency data for baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), finding a significant signal of selection in cases where independent evidence supports such a conclusion. We further demonstrate the possibility of detecting time-points at which evolutionary parameters change in the context of a historical spelling reform in the Spanish language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge