Juan A. Rodriguez-Aguilar
A model to support collective reasoning: Formalization, analysis and computational assessment
Jul 14, 2020



Abstract:Inspired by e-participation systems, in this paper we propose a new model to represent human debates and methods to obtain collective conclusions from them. This model overcomes drawbacks of existing approaches by allowing users to introduce new pieces of information into the discussion, to relate them to existing pieces, and also to express their opinion on the pieces proposed by other users. In addition, our model does not assume that users' opinions are rational in order to extract information from it, an assumption that significantly limits current approaches. Instead, we define a weaker notion of rationality that characterises coherent opinions, and we consider different scenarios based on the coherence of individual opinions and the level of consensus that users have on the debate structure. Considering these two factors, we analyse the outcomes of different opinion aggregation functions that compute a collective decision based on the individual opinions and the debate structure. In particular, we demonstrate that aggregated opinions can be coherent even if there is a lack of consensus and individual opinions are not coherent. We conclude our analysis with a computational evaluation demonstrating that collective opinions can be computed efficiently for real-sized debates.
Decentralized dynamic task allocation for UAVs with limited communication range
Aug 31, 2018



Abstract:We present the Limited-range Online Routing Problem (LORP), which involves a team of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) with limited communication range that must autonomously coordinate to service task requests. We first show a general approach to cast this dynamic problem as a sequence of decentralized task allocation problems. Then we present two solutions both based on modeling the allocation task as a Markov Random Field to subsequently assess decisions by means of the decentralized Max-Sum algorithm. Our first solution assumes independence between requests, whereas our second solution also considers the UAVs' workloads. A thorough empirical evaluation shows that our workload-based solution consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in a wide range of scenarios, lowering the average service time up to 16%. In the best-case scenario there is no gap between our decentralized solution and centralized techniques. In the worst-case scenario we manage to reduce by 25% the gap between current decentralized and centralized techniques. Thus, our solution becomes the method of choice for our problem.
Synergistic Team Composition
Feb 27, 2017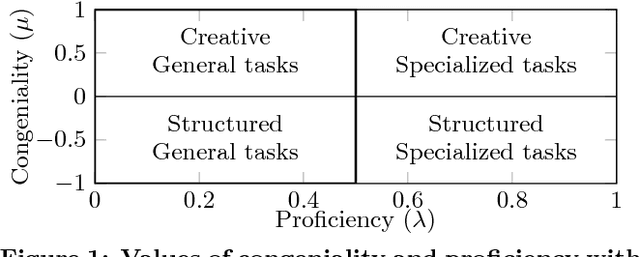
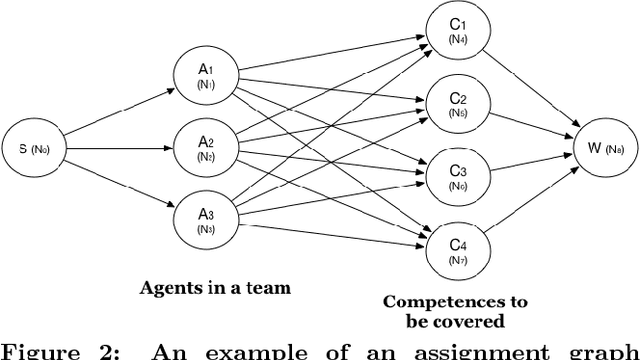

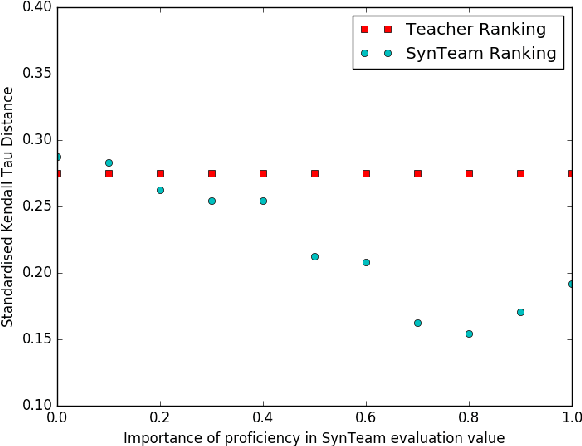
Abstract:Effective teams are crucial for organisations, especially in environments that require teams to be constantly created and dismantled, such as software development, scientific experiments, crowd-sourcing, or the classroom. Key factors influencing team performance are competences and personality of team members. Hence, we present a computational model to compose proficient and congenial teams based on individuals' personalities and their competences to perform tasks of different nature. With this purpose, we extend Wilde's post-Jungian method for team composition, which solely employs individuals' personalities. The aim of this study is to create a model to partition agents into teams that are balanced in competences, personality and gender. Finally, we present some preliminary empirical results that we obtained when analysing student performance. Results show the benefits of a more informed team composition that exploits individuals' competences besides information about their personalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge