Jovan Kalajdjieski
AI-Driven Guided Response for Security Operation Centers with Microsoft Copilot for Security
Jul 12, 2024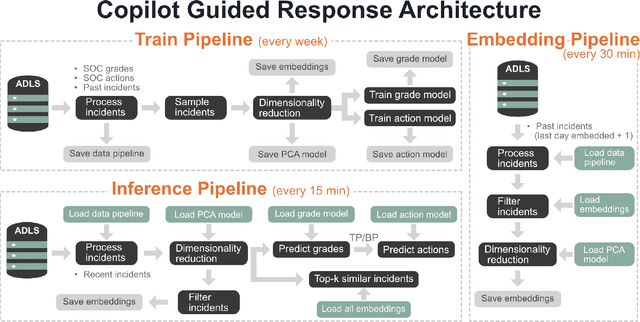
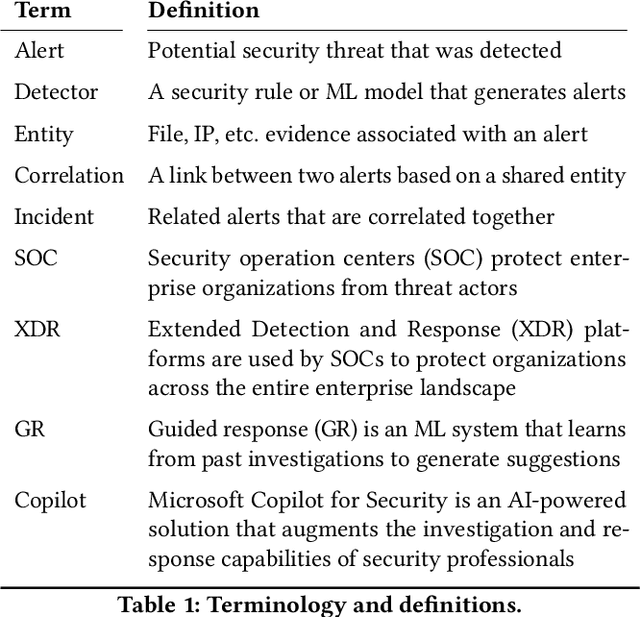
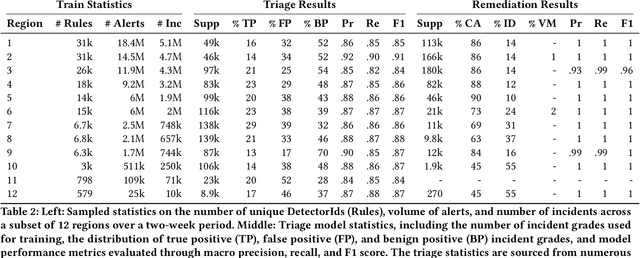
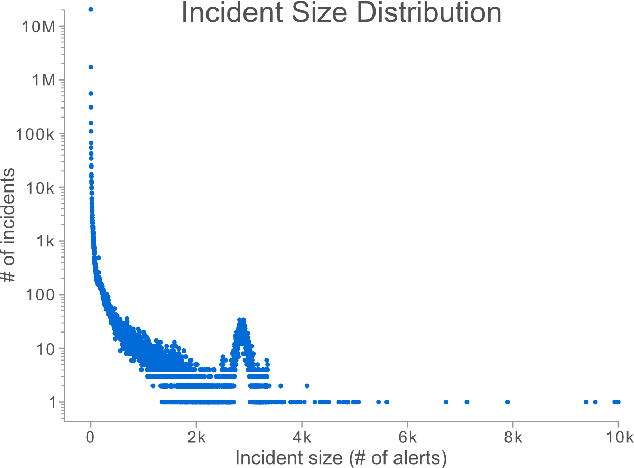
Abstract:Security operation centers contend with a constant stream of security incidents, ranging from straightforward to highly complex. To address this, we developed Copilot Guided Response (CGR), an industry-scale ML architecture that guides security analysts across three key tasks -- (1) investigation, providing essential historical context by identifying similar incidents; (2) triaging to ascertain the nature of the incident -- whether it is a true positive, false positive, or benign positive; and (3) remediation, recommending tailored containment actions. CGR is integrated into the Microsoft Defender XDR product and deployed worldwide, generating millions of recommendations across thousands of customers. Our extensive evaluation, incorporating internal evaluation, collaboration with security experts, and customer feedback, demonstrates that CGR delivers high-quality recommendations across all three tasks. We provide a comprehensive overview of the CGR architecture, setting a precedent as the first cybersecurity company to openly discuss these capabilities in such depth. Additionally, we GUIDE, the largest public collection of real-world security incidents, spanning 13M evidences across 1M annotated incidents. By enabling researchers and practitioners to conduct research on real-world data, GUIDE advances the state of cybersecurity and supports the development of next-generation machine learning systems.
Recent Advances in SQL Query Generation: A Survey
May 15, 2020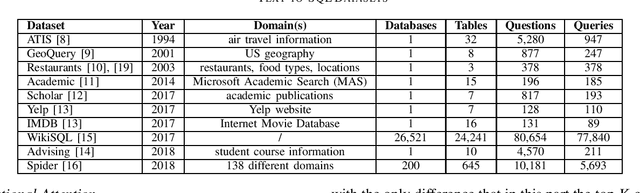
Abstract:Natural language is hypothetically the best user interface for many domains. However, general models that provide an interface between natural language and any other domain still do not exist. Providing natural language interface to relational databases could possibly attract a vast majority of users that are or are not proficient with query languages. With the rise of deep learning techniques, there is extensive ongoing research in designing a suitable natural language interface to relational databases. This survey aims to overview some of the latest methods and models proposed in the area of SQL query generation from natural language. We describe models with various architectures such as convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, pointer networks, reinforcement learning, etc. Several datasets intended to address the problem of SQL query generation are interpreted and briefly overviewed. In the end, evaluation metrics utilized in the field are presented mainly as a combination of execution accuracy and logical form accuracy.
Comparative Analysis of Word Embeddings for Capturing Word Similarities
May 08, 2020



Abstract:Distributed language representation has become the most widely used technique for language representation in various natural language processing tasks. Most of the natural language processing models that are based on deep learning techniques use already pre-trained distributed word representations, commonly called word embeddings. Determining the most qualitative word embeddings is of crucial importance for such models. However, selecting the appropriate word embeddings is a perplexing task since the projected embedding space is not intuitive to humans. In this paper, we explore different approaches for creating distributed word representations. We perform an intrinsic evaluation of several state-of-the-art word embedding methods. Their performance on capturing word similarities is analysed with existing benchmark datasets for word pairs similarities. The research in this paper conducts a correlation analysis between ground truth word similarities and similarities obtained by different word embedding methods.
* Part of the 6th International Conference on Natural Language Processing (NATP 2020)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge