Joshua Atkins
Ambisonics Super-Resolution Using A Waveform-Domain Neural Network
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Ambisonics is a spatial audio format describing a sound field. First-order Ambisonics (FOA) is a popular format comprising only four channels. This limited channel count comes at the expense of spatial accuracy. Ideally one would be able to take the efficiency of a FOA format without its limitations. We have devised a data-driven spatial audio solution that retains the efficiency of the FOA format but achieves quality that surpasses conventional renderers. Utilizing a fully convolutional time-domain audio neural network (Conv-TasNet), we created a solution that takes a FOA input and provides a higher order Ambisonics (HOA) output. This data driven approach is novel when compared to typical physics and psychoacoustic based renderers. Quantitative evaluations showed a 0.6dB average positional mean squared error difference between predicted and actual 3rd order HOA. The median qualitative rating showed an 80% improvement in perceived quality over the traditional rendering approach.
ImmerseDiffusion: A Generative Spatial Audio Latent Diffusion Model
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:We introduce ImmerseDiffusion, an end-to-end generative audio model that produces 3D immersive soundscapes conditioned on the spatial, temporal, and environmental conditions of sound objects. ImmerseDiffusion is trained to generate first-order ambisonics (FOA) audio, which is a conventional spatial audio format comprising four channels that can be rendered to multichannel spatial output. The proposed generative system is composed of a spatial audio codec that maps FOA audio to latent components, a latent diffusion model trained based on various user input types, namely, text prompts, spatial, temporal and environmental acoustic parameters, and optionally a spatial audio and text encoder trained in a Contrastive Language and Audio Pretraining (CLAP) style. We propose metrics to evaluate the quality and spatial adherence of the generated spatial audio. Finally, we assess the model performance in terms of generation quality and spatial conformance, comparing the two proposed modes: ``descriptive", which uses spatial text prompts) and ``parametric", which uses non-spatial text prompts and spatial parameters. Our evaluations demonstrate promising results that are consistent with the user conditions and reflect reliable spatial fidelity.
Design and Optimization of a Speech Recognition Front-End for Distant-Talking Control of a Music Playback Device
May 05, 2014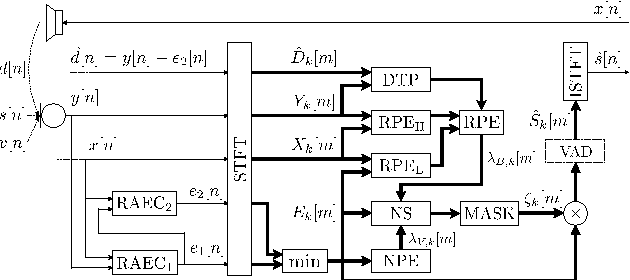

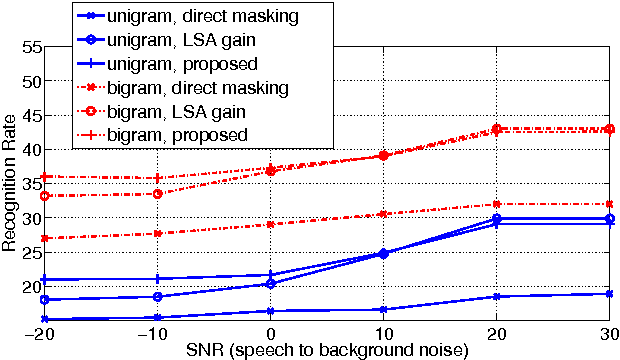
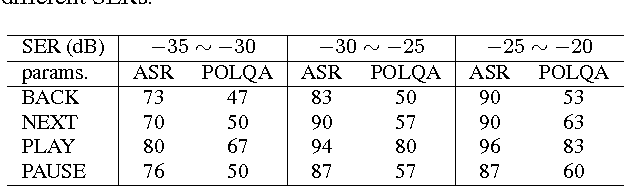
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenging scenario for the distant-talking control of a music playback device, a common portable speaker with four small loudspeakers in close proximity to one microphone. The user controls the device through voice, where the speech-to-music ratio can be as low as -30 dB during music playback. We propose a speech enhancement front-end that relies on known robust methods for echo cancellation, double-talk detection, and noise suppression, as well as a novel adaptive quasi-binary mask that is well suited for speech recognition. The optimization of the system is then formulated as a large scale nonlinear programming problem where the recognition rate is maximized and the optimal values for the system parameters are found through a genetic algorithm. We validate our methodology by testing over the TIMIT database for different music playback levels and noise types. Finally, we show that the proposed front-end allows a natural interaction with the device for limited-vocabulary voice commands.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge