Jorn Veenstra
Representing Text Chunks
Jul 06, 1999



Abstract:Dividing sentences in chunks of words is a useful preprocessing step for parsing, information extraction and information retrieval. (Ramshaw and Marcus, 1995) have introduced a "convenient" data representation for chunking by converting it to a tagging task. In this paper we will examine seven different data representations for the problem of recognizing noun phrase chunks. We will show that the the data representation choice has a minor influence on chunking performance. However, equipped with the most suitable data representation, our memory-based learning chunker was able to improve the best published chunking results for a standard data set.
* 7 pages
Memory-Based Shallow Parsing
Jun 02, 1999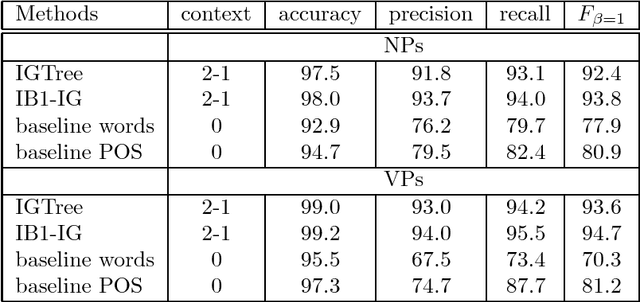

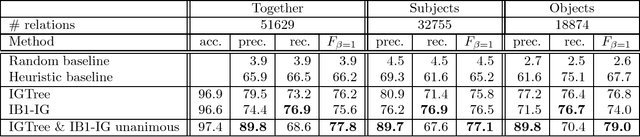
Abstract:We present a memory-based learning (MBL) approach to shallow parsing in which POS tagging, chunking, and identification of syntactic relations are formulated as memory-based modules. The experiments reported in this paper show competitive results, the F-value for the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) treebank is: 93.8% for NP chunking, 94.7% for VP chunking, 77.1% for subject detection and 79.0% for object detection.
Cascaded Grammatical Relation Assignment
Jun 02, 1999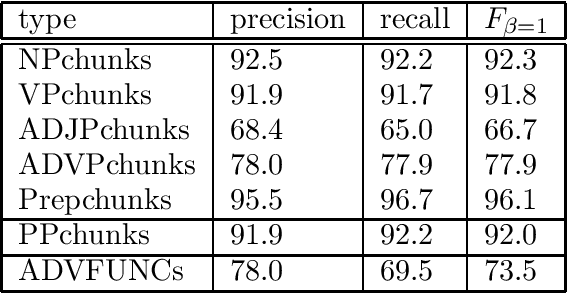
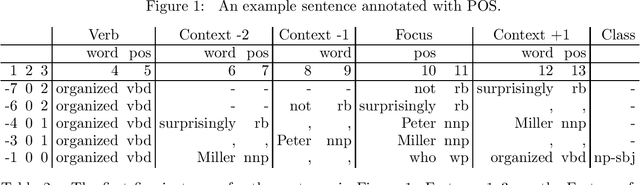

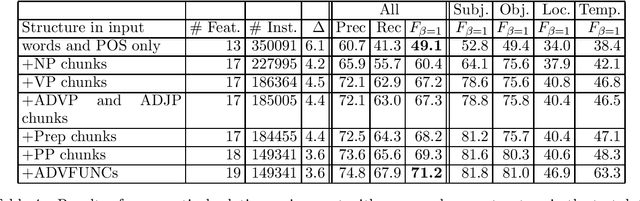
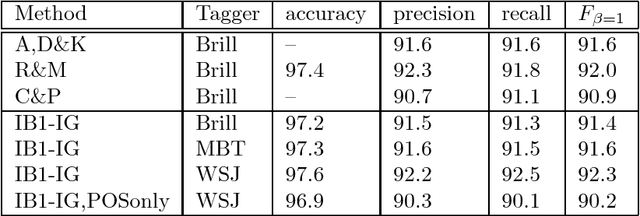
Abstract:In this paper we discuss cascaded Memory-Based grammatical relations assignment. In the first stages of the cascade, we find chunks of several types (NP,VP,ADJP,ADVP,PP) and label them with their adverbial function (e.g. local, temporal). In the last stage, we assign grammatical relations to pairs of chunks. We studied the effect of adding several levels to this cascaded classifier and we found that even the less performing chunkers enhanced the performance of the relation finder.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge