JooYoung Lee
Misinformation is not about Bad Facts: An Analysis of the Production and Consumption of Fringe Content
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:What if misinformation is not an information problem at all? Our findings suggest that online fringe ideologies spread through the use of content that is consensus-based and "factually correct". We found that Australian news publishers with both moderate and far-right political leanings contain comparable levels of information completeness and quality; and furthermore, that far-right Twitter users often share from moderate sources. However, a stark difference emerges when we consider two additional factors: 1) the narrow topic selection of articles by far-right users, suggesting that they cherrypick only news articles that engage with specific topics of their concern, and 2) the difference between moderate and far-right publishers when we examine the writing style of their articles. Furthermore, we can even identify users prone to sharing misinformation based on their communication style. These findings have important implications for countering online misinformation, as they highlight the powerful role that users' personal bias towards specific topics, and publishers' writing styles, have in amplifying fringe ideologies online.
A Conjoint Application of Data Mining Techniques for Analysis of Global Terrorist Attacks -- Prevention and Prediction for Combating Terrorism
Jan 19, 2019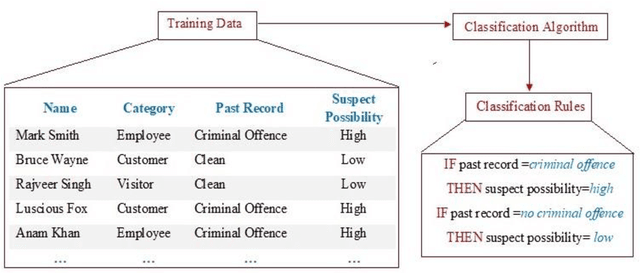
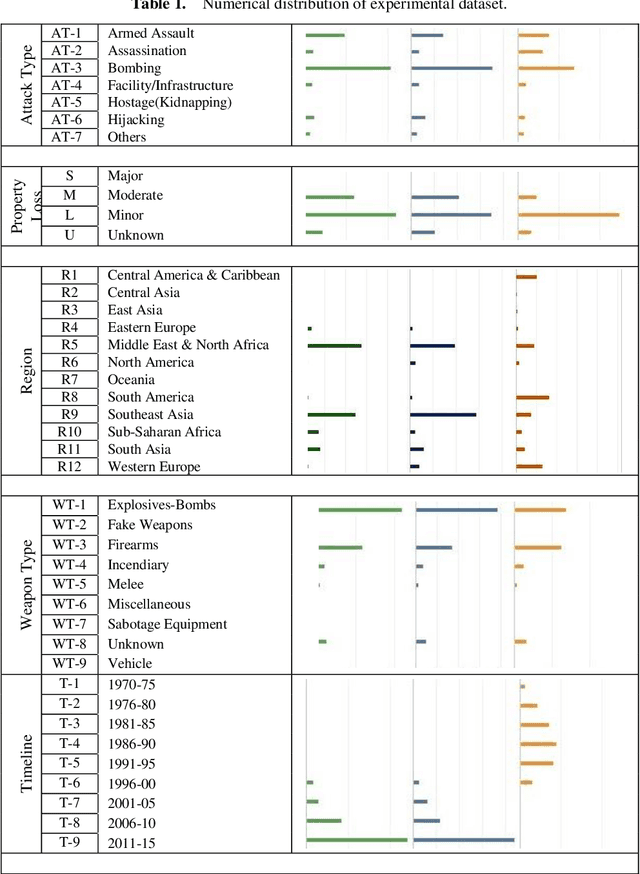
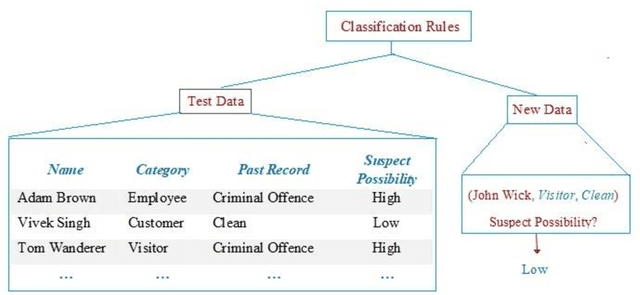

Abstract:Terrorism has become one of the most tedious problems to deal with and a prominent threat to mankind. To enhance counter-terrorism, several research works are developing efficient and precise systems, data mining is not an exception. Immense data is floating in our lives, though the scarce availability of authentic terrorist attack data in the public domain makes it complicated to fight terrorism. This manuscript focuses on data mining classification techniques and discusses the role of United Nations in counter-terrorism. It analyzes the performance of classifiers such as Lazy Tree, Multilayer Perceptron, Multiclass and Na\"ive Bayes classifiers for observing the trends for terrorist attacks around the world. The database for experiment purpose is created from different public and open access sources for years 1970-2015 comprising of 156,772 reported attacks causing massive losses of lives and property. This work enumerates the losses occurred, trends in attack frequency and places more prone to it, by considering the attack responsibilities taken as evaluation class.
Self-adaptive node-based PCA encodings
Jun 16, 2017Abstract:In this paper we propose an algorithm, Simple Hebbian PCA, and prove that it is able to calculate the principal component analysis (PCA) in a distributed fashion across nodes. It simplifies existing network structures by removing intralayer weights, essentially cutting the number of weights that need to be trained in half.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge