Jonne Pohjankukka
Utilizing remote sensing data in forest inventory sampling via Bayesian optimization
Sep 17, 2020

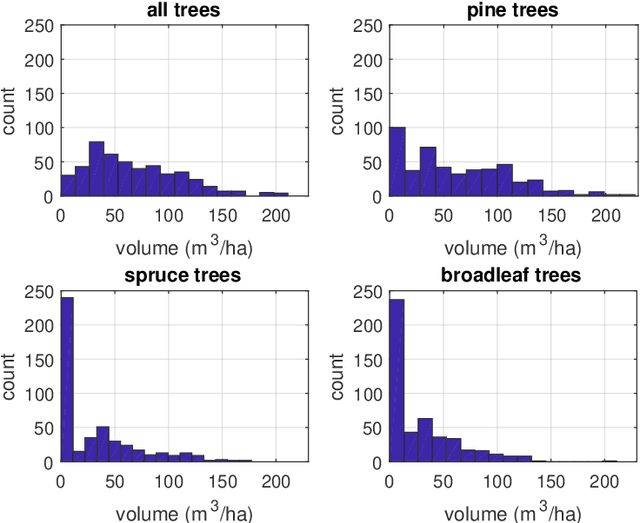

Abstract:In large-area forest inventories a trade-off between the amount of data to be sampled and the costs of collecting the data is necessary. It is not always possible to have a very large data sample when dealing with sampling-based inventories. It is therefore necessary to optimize the sampling design in order to achieve optimal population parameter estimation. On the contrary, the availability of remote sensing (RS) data correlated with the forest inventory variables is usually much higher. The combination of RS and the sampled field measurement data is often used for improving the forest inventory parameter estimation. In addition, it is also reasonable to study the utilization of RS data in inventory sampling, which can further improve the estimation of forest variables. In this study, we propose a data sampling method based on Bayesian optimization which uses RS data in forest inventory sample selection. The presented method applies the learned functional relationship between the RS and inventory data in new sampling decisions. We evaluate our method by conducting simulated sampling experiments with both synthetic data and measured data from the Aland region in Finland. The proposed method is benchmarked against two baseline methods: simple random sampling and the local pivotal method. The results of the simulated experiments show the best results in terms of MSE values for the proposed method when the functional relationship between RS and inventory data is correctly learned from the available training data.
Estimating the Prediction Performance of Spatial Models via Spatial k-Fold Cross Validation
May 28, 2020Abstract:In machine learning one often assumes the data are independent when evaluating model performance. However, this rarely holds in practise. Geographic information data sets are an example where the data points have stronger dependencies among each other the closer they are geographically. This phenomenon known as spatial autocorrelation (SAC) causes the standard cross validation (CV) methods to produce optimistically biased prediction performance estimates for spatial models, which can result in increased costs and accidents in practical applications. To overcome this problem we propose a modified version of the CV method called spatial k-fold cross validation (SKCV), which provides a useful estimate for model prediction performance without optimistic bias due to SAC. We test SKCV with three real world cases involving open natural data showing that the estimates produced by the ordinary CV are up to 40% more optimistic than those of SKCV. Both regression and classification cases are considered in our experiments. In addition, we will show how the SKCV method can be applied as a criterion for selecting data sampling density for new research area.
* 18 pages, 12 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge