Jonathon Chambers
Finger Texture Biometric Characteristic: a Survey
Jun 07, 2020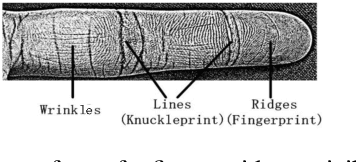
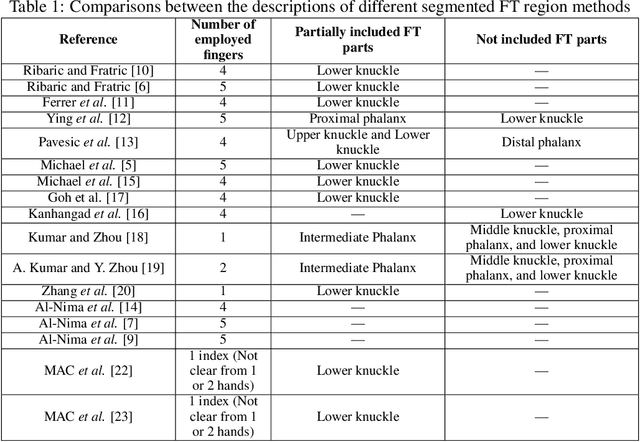

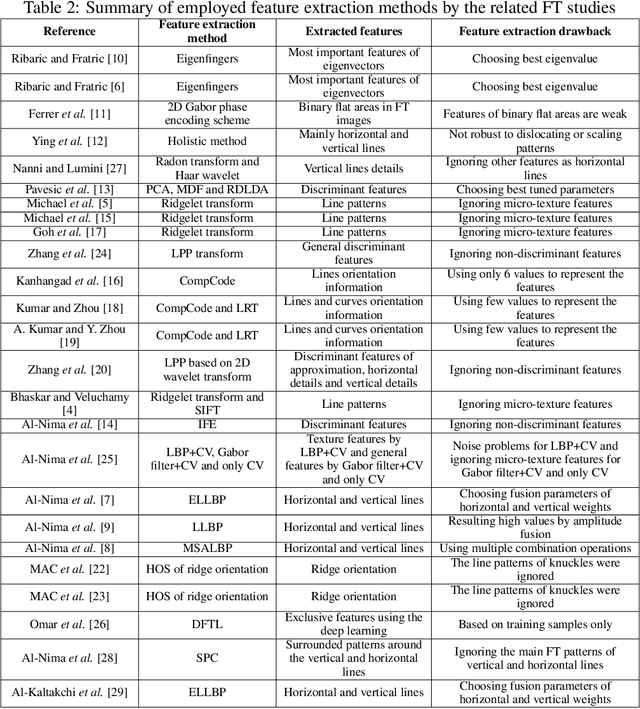
Abstract:\begin{abstract} In recent years, the Finger Texture (FT) has attracted considerable attention as a biometric characteristic. It can provide efficient human recognition performance, because it has different human-specific features of apparent lines, wrinkles and ridges distributed along the inner surface of all fingers. Also, such pattern structures are reliable, unique and remain stable throughout a human's life. Efficient biometric systems can be established based only on FTs. In this paper, a comprehensive survey of the relevant FT studies is presented. We also summarise the main drawbacks and obstacles of employing the FT as a biometric characteristic, and provide useful suggestions to further improve the work on FT. \end{abstract}
Multi-Target Tracking and Occlusion Handling with Learned Variational Bayesian Clusters and a Social Force Model
Nov 05, 2015



Abstract:This paper considers the problem of multiple human target tracking in a sequence of video data. A solution is proposed which is able to deal with the challenges of a varying number of targets, interactions and when every target gives rise to multiple measurements. The developed novel algorithm comprises variational Bayesian clustering combined with a social force model, integrated within a particle filter with an enhanced prediction step. It performs measurement-to-target association by automatically detecting the measurement relevance. The performance of the developed algorithm is evaluated over several sequences from publicly available data sets: AV16.3, CAVIAR and PETS2006, which demonstrates that the proposed algorithm successfully initializes and tracks a variable number of targets in the presence of complex occlusions. A comparison with state-of-the-art techniques due to Khan et al., Laet et al. and Czyz et al. shows improved tracking performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge