Jonathan Rusert
BinarySelect to Improve Accessibility of Black-Box Attack Research
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Adversarial text attack research is useful for testing the robustness of NLP models, however, the rise of transformers has greatly increased the time required to test attacks. Especially when researchers do not have access to adequate resources (e.g. GPUs). This can hinder attack research, as modifying one example for an attack can require hundreds of queries to a model, especially for black-box attacks. Often these attacks remove one token at a time to find the ideal one to change, requiring $n$ queries (the length of the text) right away. We propose a more efficient selection method called BinarySelect which combines binary search and attack selection methods to greatly reduce the number of queries needed to find a token. We find that BinarySelect only needs $\text{log}_2(n) * 2$ queries to find the first token compared to $n$ queries. We also test BinarySelect in an attack setting against 5 classifiers across 3 datasets and find a viable tradeoff between number of queries saved and attack effectiveness. For example, on the Yelp dataset, the number of queries is reduced by 32% (72 less) with a drop in attack effectiveness of only 5 points. We believe that BinarySelect can help future researchers study adversarial attacks and black-box problems more efficiently and opens the door for researchers with access to less resources.
VertAttack: Taking advantage of Text Classifiers' horizontal vision
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Text classification systems have continuously improved in performance over the years. However, nearly all current SOTA classifiers have a similar shortcoming, they process text in a horizontal manner. Vertically written words will not be recognized by a classifier. In contrast, humans are easily able to recognize and read words written both horizontally and vertically. Hence, a human adversary could write problematic words vertically and the meaning would still be preserved to other humans. We simulate such an attack, VertAttack. VertAttack identifies which words a classifier is reliant on and then rewrites those words vertically. We find that VertAttack is able to greatly drop the accuracy of 4 different transformer models on 5 datasets. For example, on the SST2 dataset, VertAttack is able to drop RoBERTa's accuracy from 94 to 13%. Furthermore, since VertAttack does not replace the word, meaning is easily preserved. We verify this via a human study and find that crowdworkers are able to correctly label 77% perturbed texts perturbed, compared to 81% of the original texts. We believe VertAttack offers a look into how humans might circumvent classifiers in the future and thus inspire a look into more robust algorithms.
Don't sweat the small stuff, classify the rest: Sample Shielding to protect text classifiers against adversarial attacks
May 03, 2022



Abstract:Deep learning (DL) is being used extensively for text classification. However, researchers have demonstrated the vulnerability of such classifiers to adversarial attacks. Attackers modify the text in a way which misleads the classifier while keeping the original meaning close to intact. State-of-the-art (SOTA) attack algorithms follow the general principle of making minimal changes to the text so as to not jeopardize semantics. Taking advantage of this we propose a novel and intuitive defense strategy called Sample Shielding. It is attacker and classifier agnostic, does not require any reconfiguration of the classifier or external resources and is simple to implement. Essentially, we sample subsets of the input text, classify them and summarize these into a final decision. We shield three popular DL text classifiers with Sample Shielding, test their resilience against four SOTA attackers across three datasets in a realistic threat setting. Even when given the advantage of knowing about our shielding strategy the adversary's attack success rate is <=10% with only one exception and often < 5%. Additionally, Sample Shielding maintains near original accuracy when applied to original texts. Crucially, we show that the `make minimal changes' approach of SOTA attackers leads to critical vulnerabilities that can be defended against with an intuitive sampling strategy.
A Girl Has A Name, And It's Adversarial Authorship Attribution for Deobfuscation
Mar 22, 2022
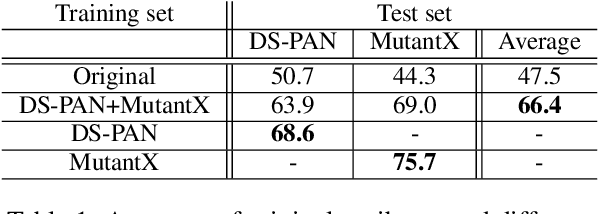
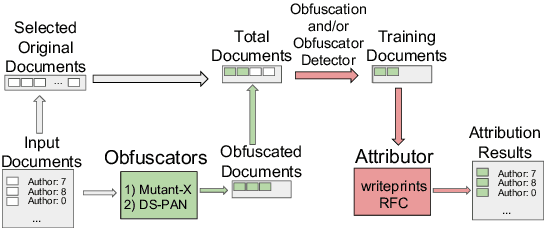
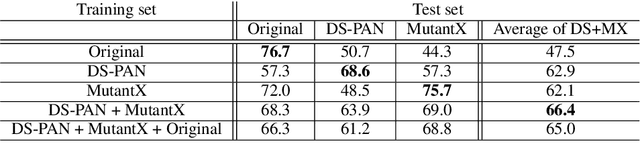
Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing have enabled powerful privacy-invasive authorship attribution. To counter authorship attribution, researchers have proposed a variety of rule-based and learning-based text obfuscation approaches. However, existing authorship obfuscation approaches do not consider the adversarial threat model. Specifically, they are not evaluated against adversarially trained authorship attributors that are aware of potential obfuscation. To fill this gap, we investigate the problem of adversarial authorship attribution for deobfuscation. We show that adversarially trained authorship attributors are able to degrade the effectiveness of existing obfuscators from 20-30% to 5-10%. We also evaluate the effectiveness of adversarial training when the attributor makes incorrect assumptions about whether and which obfuscator was used. While there is a a clear degradation in attribution accuracy, it is noteworthy that this degradation is still at or above the attribution accuracy of the attributor that is not adversarially trained at all. Our results underline the need for stronger obfuscation approaches that are resistant to deobfuscation
Suum Cuique: Studying Bias in Taboo Detection with a Community Perspective
Mar 22, 2022

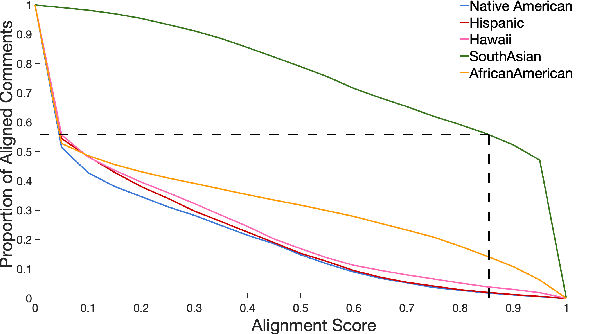
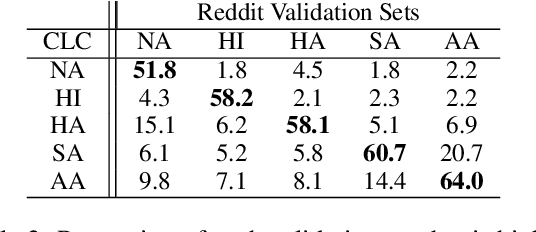
Abstract:Prior research has discussed and illustrated the need to consider linguistic norms at the community level when studying taboo (hateful/offensive/toxic etc.) language. However, a methodology for doing so, that is firmly founded on community language norms is still largely absent. This can lead both to biases in taboo text classification and limitations in our understanding of the causes of bias. We propose a method to study bias in taboo classification and annotation where a community perspective is front and center. This is accomplished by using special classifiers tuned for each community's language. In essence, these classifiers represent community level language norms. We use these to study bias and find, for example, biases are largest against African Americans (7/10 datasets and all 3 classifiers examined). In contrast to previous papers we also study other communities and find, for example, strong biases against South Asians. In a small scale user study we illustrate our key idea which is that common utterances, i.e., those with high alignment scores with a community (community classifier confidence scores) are unlikely to be regarded taboo. Annotators who are community members contradict taboo classification decisions and annotations in a majority of instances. This paper is a significant step toward reducing false positive taboo decisions that over time harm minority communities.
On The Robustness of Offensive Language Classifiers
Mar 21, 2022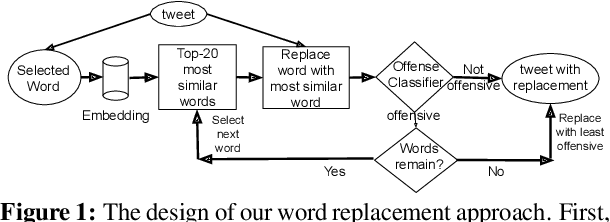
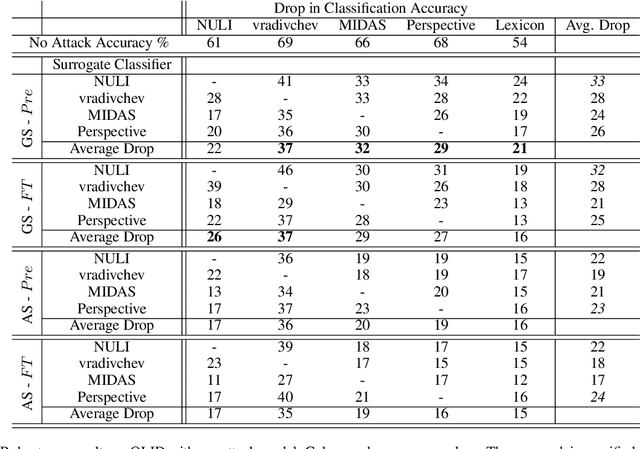
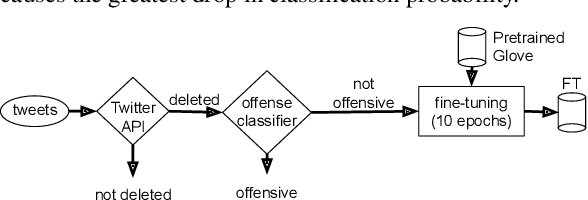

Abstract:Social media platforms are deploying machine learning based offensive language classification systems to combat hateful, racist, and other forms of offensive speech at scale. However, despite their real-world deployment, we do not yet comprehensively understand the extent to which offensive language classifiers are robust against adversarial attacks. Prior work in this space is limited to studying robustness of offensive language classifiers against primitive attacks such as misspellings and extraneous spaces. To address this gap, we systematically analyze the robustness of state-of-the-art offensive language classifiers against more crafty adversarial attacks that leverage greedy- and attention-based word selection and context-aware embeddings for word replacement. Our results on multiple datasets show that these crafty adversarial attacks can degrade the accuracy of offensive language classifiers by more than 50% while also being able to preserve the readability and meaning of the modified text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge