John Neiber
Knowledge-guided Self-supervised Learning for estimating River-Basin Characteristics
Sep 14, 2021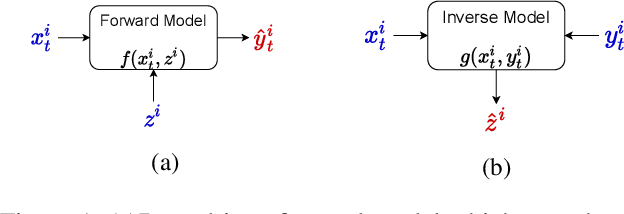
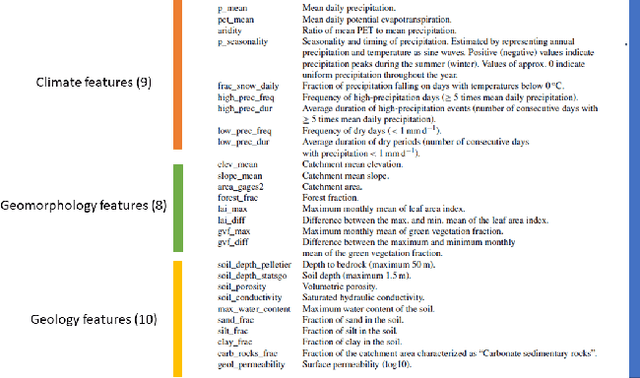
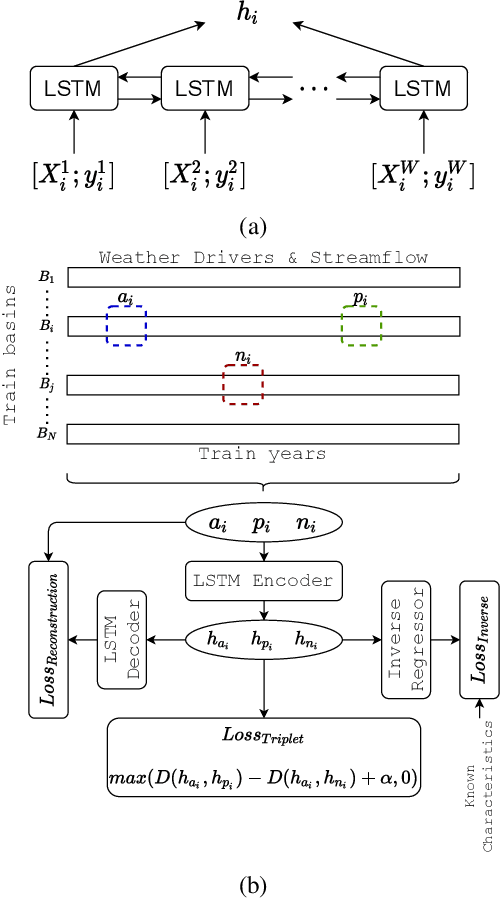
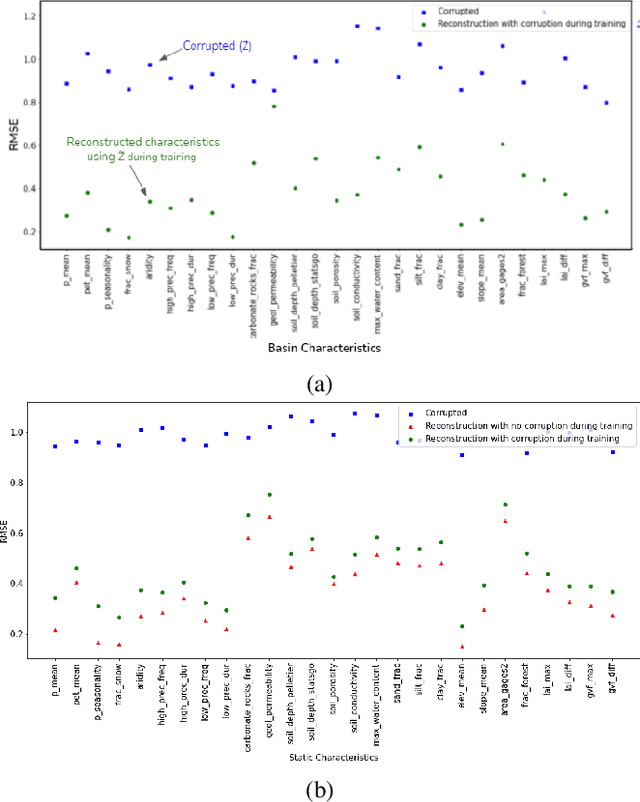
Abstract:Machine Learning is being extensively used in hydrology, especially streamflow prediction of basins/watersheds. Basin characteristics are essential for modeling the rainfall-runoff response of these watersheds and therefore data-driven methods must take into account this ancillary characteristics data. However there are several limitations, namely uncertainty in the measured characteristics, partially missing characteristics for some of the basins or unknown characteristics that may not be present in the known measured set. In this paper we present an inverse model that uses a knowledge-guided self-supervised learning algorithm to infer basin characteristics using the meteorological drivers and streamflow response data. We evaluate our model on the the CAMELS dataset and the results validate its ability to reduce measurement uncertainty, impute missing characteristics, and identify unknown characteristics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge