Joe O'Connor
PromptBoosting: Black-Box Text Classification with Ten Forward Passes
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:We describe PromptBoosting, a query-efficient procedure for building a text classifier from a neural language model (LM) without access to the LM's parameters, gradients, or hidden representations. This form of "black-box" classifier training has become increasingly important as the cost of training and inference in large-scale LMs grows. But existing black-box LM classifier learning approaches are themselves computationally inefficient, typically specializing LMs to the target task by searching in a large space of (discrete or continuous) prompts using zeroth-order optimization methods. Instead of directly optimizing in prompt space, PromptBoosting obtains a small pool of prompts via a gradient-free approach and then constructs a large pool of weak learners by pairing these prompts with different elements of the LM's output distribution. These weak learners are then ensembled using the AdaBoost algorithm. The entire learning process requires only a small number of forward passes and no backward pass. Experiments show that PromptBoosting achieves state-of-the-art performance in multiple black-box few-shot classification tasks, and matches or outperforms full fine-tuning in both few-shot and standard learning paradigms, while training 10x faster than existing black-box methods.
What Context Features Can Transformer Language Models Use?
Jun 15, 2021
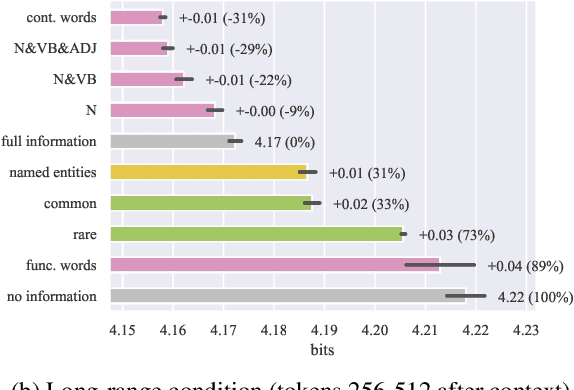
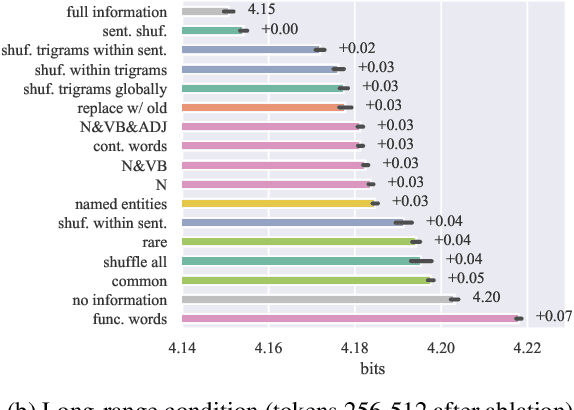
Abstract:Transformer-based language models benefit from conditioning on contexts of hundreds to thousands of previous tokens. What aspects of these contexts contribute to accurate model prediction? We describe a series of experiments that measure usable information by selectively ablating lexical and structural information in transformer language models trained on English Wikipedia. In both mid- and long-range contexts, we find that several extremely destructive context manipulations -- including shuffling word order within sentences and deleting all words other than nouns -- remove less than 15% of the usable information. Our results suggest that long contexts, but not their detailed syntactic and propositional content, are important for the low perplexity of current transformer language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge