Jisu Han
D-TPT: Dimensional Entropy Maximization for Calibrating Test-Time Prompt Tuning in Vision-Language Models
Oct 10, 2025



Abstract:Test-time adaptation paradigm provides flexibility towards domain shifts by performing immediate adaptation on unlabeled target data from the source model. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) leverage their generalization capabilities for diverse downstream tasks, and test-time prompt tuning has emerged as a prominent solution for adapting VLMs. In this work, we explore contrastive VLMs and identify the modality gap caused by a single dominant feature dimension across modalities. We observe that the dominant dimensions in both text and image modalities exhibit high predictive sensitivity, and that constraining their influence can improve calibration error. Building on this insight, we propose dimensional entropy maximization that regularizes the distribution of textual features toward uniformity to mitigate the dependency of dominant dimensions. Our method alleviates the degradation of calibration performance in test-time prompt tuning, offering a simple yet effective solution to enhance the reliability of VLMs in real-world deployment scenarios.
Ranked Entropy Minimization for Continual Test-Time Adaptation
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Test-time adaptation aims to adapt to realistic environments in an online manner by learning during test time. Entropy minimization has emerged as a principal strategy for test-time adaptation due to its efficiency and adaptability. Nevertheless, it remains underexplored in continual test-time adaptation, where stability is more important. We observe that the entropy minimization method often suffers from model collapse, where the model converges to predicting a single class for all images due to a trivial solution. We propose ranked entropy minimization to mitigate the stability problem of the entropy minimization method and extend its applicability to continuous scenarios. Our approach explicitly structures the prediction difficulty through a progressive masking strategy. Specifically, it gradually aligns the model's probability distributions across different levels of prediction difficulty while preserving the rank order of entropy. The proposed method is extensively evaluated across various benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness through empirical results. Our code is available at https://github.com/pilsHan/rem
Option-aware Temporally Abstracted Value for Offline Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Offline goal-conditioned reinforcement learning (GCRL) offers a practical learning paradigm where goal-reaching policies are trained from abundant unlabeled (reward-free) datasets without additional environment interaction. However, offline GCRL still struggles with long-horizon tasks, even with recent advances that employ hierarchical policy structures, such as HIQL. By identifying the root cause of this challenge, we observe the following insights: First, performance bottlenecks mainly stem from the high-level policy's inability to generate appropriate subgoals. Second, when learning the high-level policy in the long-horizon regime, the sign of the advantage signal frequently becomes incorrect. Thus, we argue that improving the value function to produce a clear advantage signal for learning the high-level policy is essential. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective solution: Option-aware Temporally Abstracted value learning, dubbed OTA, which incorporates temporal abstraction into the temporal-difference learning process. By modifying the value update to be option-aware, the proposed learning scheme contracts the effective horizon length, enabling better advantage estimates even in long-horizon regimes. We experimentally show that the high-level policy extracted using the OTA value function achieves strong performance on complex tasks from OGBench, a recently proposed offline GCRL benchmark, including maze navigation and visual robotic manipulation environments.
Hierarchical and Modular Network on Non-prehensile Manipulation in General Environments
Feb 28, 2025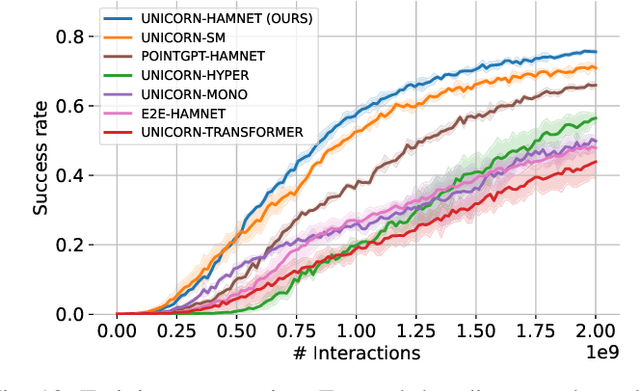
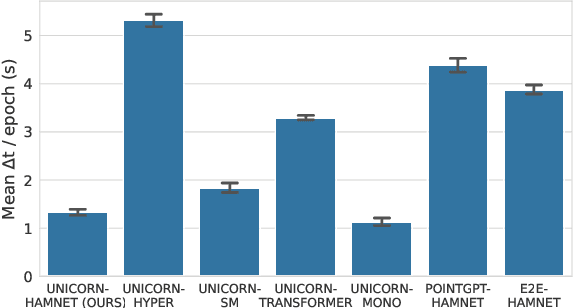
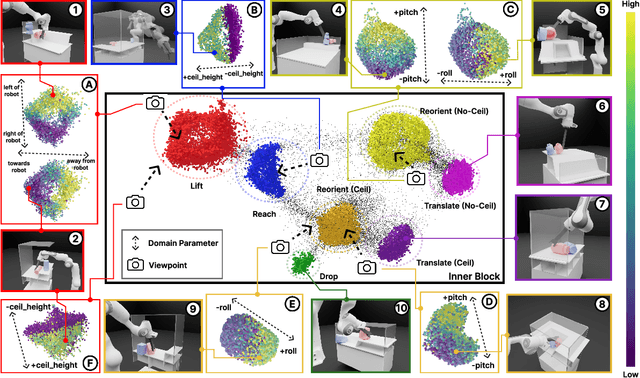
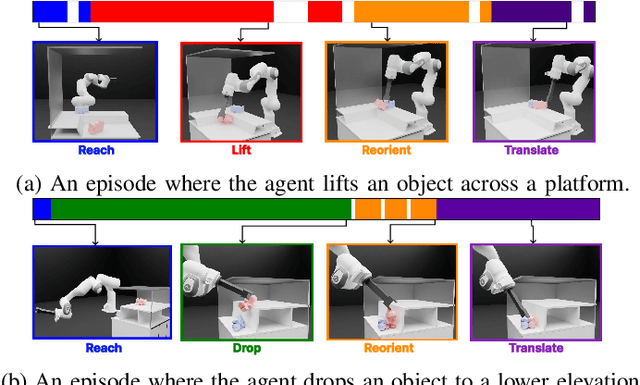
Abstract:For robots to operate in general environments like households, they must be able to perform non-prehensile manipulation actions such as toppling and rolling to manipulate ungraspable objects. However, prior works on non-prehensile manipulation cannot yet generalize across environments with diverse geometries. The main challenge lies in adapting to varying environmental constraints: within a cabinet, the robot must avoid walls and ceilings; to lift objects to the top of a step, the robot must account for the step's pose and extent. While deep reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated impressive success in non-prehensile manipulation, accounting for such variability presents a challenge for the generalist policy, as it must learn diverse strategies for each new combination of constraints. To address this, we propose a modular and reconfigurable architecture that adaptively reconfigures network modules based on task requirements. To capture the geometric variability in environments, we extend the contact-based object representation (CORN) to environment geometries, and propose a procedural algorithm for generating diverse environments to train our agent. Taken together, the resulting policy can zero-shot transfer to novel real-world environments and objects despite training entirely within a simulator. We additionally release a simulation-based benchmark featuring nine digital twins of real-world scenes with 353 objects to facilitate non-prehensile manipulation research in realistic domains.
Semantic Prompting with Image-Token for Continual Learning
Mar 18, 2024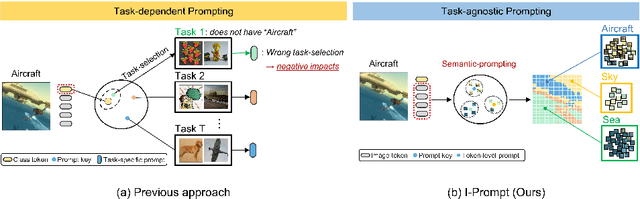
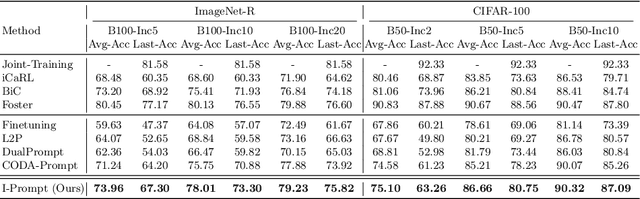
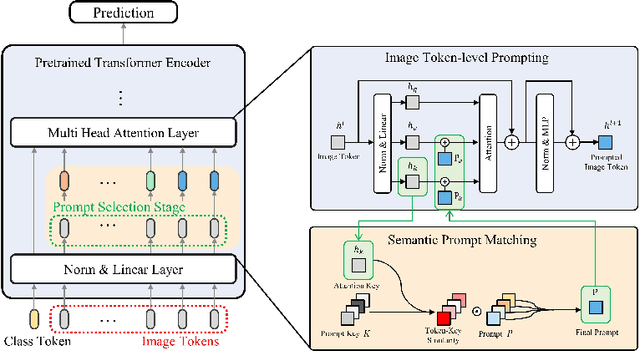
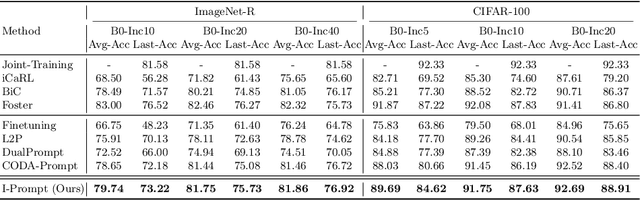
Abstract:Continual learning aims to refine model parameters for new tasks while retaining knowledge from previous tasks. Recently, prompt-based learning has emerged to leverage pre-trained models to be prompted to learn subsequent tasks without the reliance on the rehearsal buffer. Although this approach has demonstrated outstanding results, existing methods depend on preceding task-selection process to choose appropriate prompts. However, imperfectness in task-selection may lead to negative impacts on the performance particularly in the scenarios where the number of tasks is large or task distributions are imbalanced. To address this issue, we introduce I-Prompt, a task-agnostic approach focuses on the visual semantic information of image tokens to eliminate task prediction. Our method consists of semantic prompt matching, which determines prompts based on similarities between tokens, and image token-level prompting, which applies prompts directly to image tokens in the intermediate layers. Consequently, our method achieves competitive performance on four benchmarks while significantly reducing training time compared to state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, we demonstrate the superiority of our method across various scenarios through extensive experiments.
SRIL: Selective Regularization for Class-Incremental Learning
May 09, 2023



Abstract:Human intelligence gradually accepts new information and accumulates knowledge throughout the lifespan. However, deep learning models suffer from a catastrophic forgetting phenomenon, where they forget previous knowledge when acquiring new information. Class-Incremental Learning aims to create an integrated model that balances plasticity and stability to overcome this challenge. In this paper, we propose a selective regularization method that accepts new knowledge while maintaining previous knowledge. We first introduce an asymmetric feature distillation method for old and new classes inspired by cognitive science, using the gradient of classification and knowledge distillation losses to determine whether to perform pattern completion or pattern separation. We also propose a method to selectively interpolate the weight of the previous model for a balance between stability and plasticity, and we adjust whether to transfer through model confidence to ensure the performance of the previous class and enable exploratory learning. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which surpasses the performance of existing methods through extensive experimental protocols using CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Subset, and ImageNet-Full.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge