Jinmao Li
Enhancing Complex Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs through Evidence Pattern Retrieval
Feb 03, 2024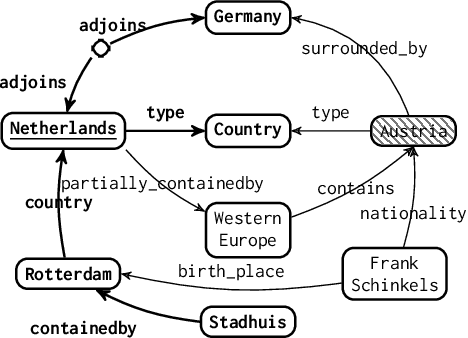
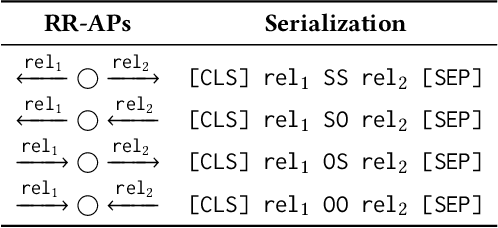
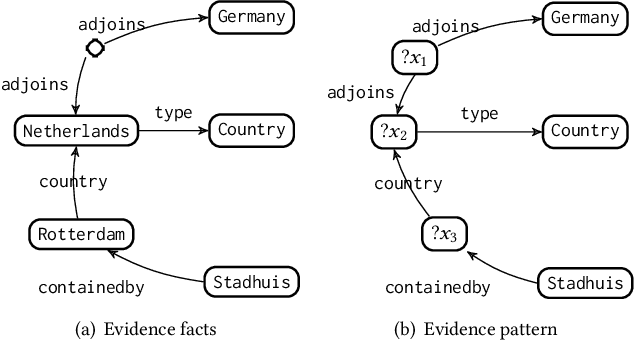
Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) methods for KGQA consist of two stages: subgraph extraction and answer reasoning. We argue current subgraph extraction methods underestimate the importance of structural dependencies among evidence facts. We propose Evidence Pattern Retrieval (EPR) to explicitly model the structural dependencies during subgraph extraction. We implement EPR by indexing the atomic adjacency pattern of resource pairs. Given a question, we perform dense retrieval to obtain atomic patterns formed by resource pairs. We then enumerate their combinations to construct candidate evidence patterns. These evidence patterns are scored using a neural model, and the best one is selected to extract a subgraph for downstream answer reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that the EPR-based approach has significantly improved the F1 scores of IR-KGQA methods by over 10 points on ComplexWebQuestions and achieves competitive performance on WebQuestionsSP.
Automatic Rule Generation for Time Expression Normalization
Aug 31, 2021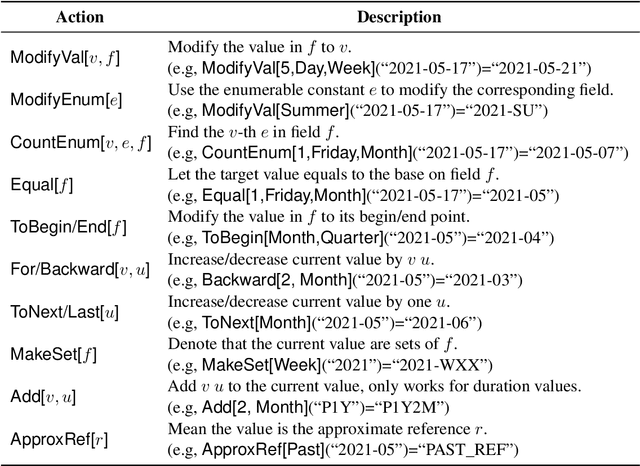
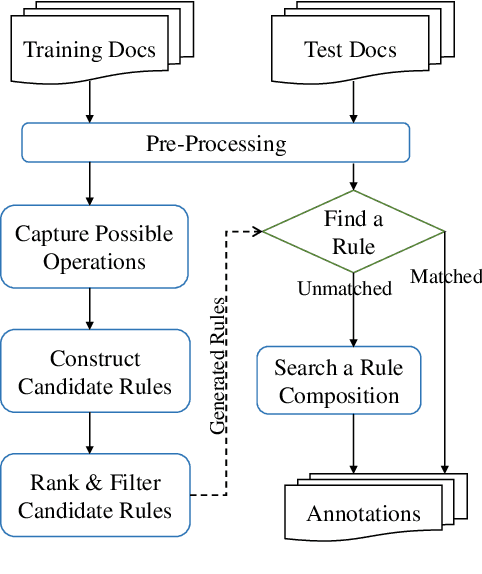
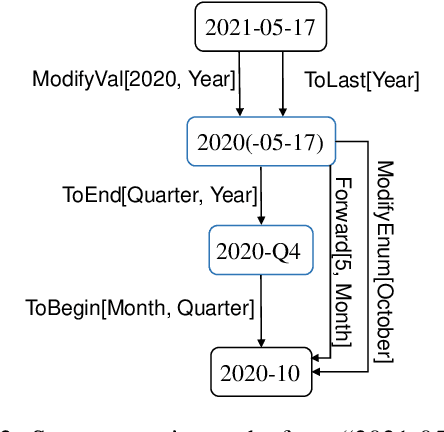
Abstract:The understanding of time expressions includes two sub-tasks: recognition and normalization. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the recognition of time expressions while research on normalization has lagged behind. Existing SOTA normalization methods highly rely on rules or grammars designed by experts, which limits their performance on emerging corpora, such as social media texts. In this paper, we model time expression normalization as a sequence of operations to construct the normalized temporal value, and we present a novel method called ARTime, which can automatically generate normalization rules from training data without expert interventions. Specifically, ARTime automatically captures possible operation sequences from annotated data and generates normalization rules on time expressions with common surface forms. The experimental results show that ARTime can significantly surpass SOTA methods on the Tweets benchmark, and achieves competitive results with existing expert-engineered rule methods on the TempEval-3 benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge