Jinkwan Jang
What If TSF: A Benchmark for Reframing Forecasting as Scenario-Guided Multimodal Forecasting
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Time series forecasting is critical to real-world decision making, yet most existing approaches remain unimodal and rely on extrapolating historical patterns. While recent progress in large language models (LLMs) highlights the potential for multimodal forecasting, existing benchmarks largely provide retrospective or misaligned raw context, making it unclear whether such models meaningfully leverage textual inputs. In practice, human experts incorporate what-if scenarios with historical evidence, often producing distinct forecasts from the same observations under different scenarios. Inspired by this, we introduce What If TSF (WIT), a multimodal forecasting benchmark designed to evaluate whether models can condition their forecasts on contextual text, especially future scenarios. By providing expert-crafted plausible or counterfactual scenarios, WIT offers a rigorous testbed for scenario-guided multimodal forecasting. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/jinkwan1115/WhatIfTSF.
Towards Robust Real-World Multivariate Time Series Forecasting: A Unified Framework for Dependency, Asynchrony, and Missingness
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Real-world time series data are inherently multivariate, often exhibiting complex inter-channel dependencies. Each channel is typically sampled at its own period and is prone to missing values due to various practical and operational constraints. These characteristics pose fundamental challenges related to channel dependency, sampling asynchrony, and missingness, all of which must be addressed to enable robust and reliable forecasting in practical settings. However, most existing architectures are built on oversimplified assumptions, such as identical sampling periods across channels and fully observed inputs at test time, which often do not hold in real-world scenarios. To bridge this gap, we propose ChannelTokenFormer, a Transformer-based forecasting model with a flexible architecture designed to explicitly capture cross-channel interactions, accommodate channel-wise asynchronous sampling, and effectively handle missing values. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets modified to reflect practical settings, along with one real-world industrial dataset, demonstrate the superior robustness and accuracy of ChannelTokenFormer under challenging real-world conditions.
When Vision Models Meet Parameter Efficient Look-Aside Adapters Without Large-Scale Audio Pretraining
Dec 08, 2024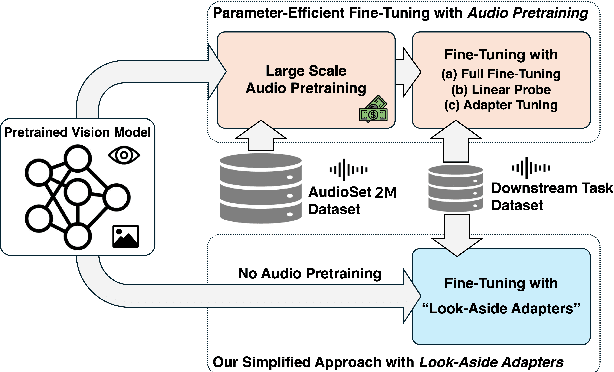
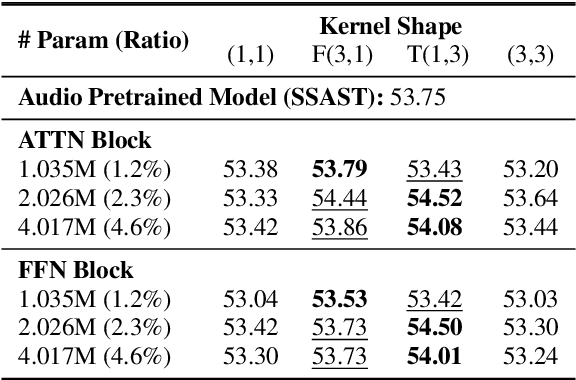
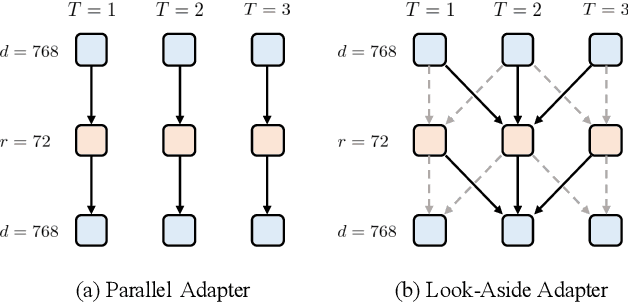
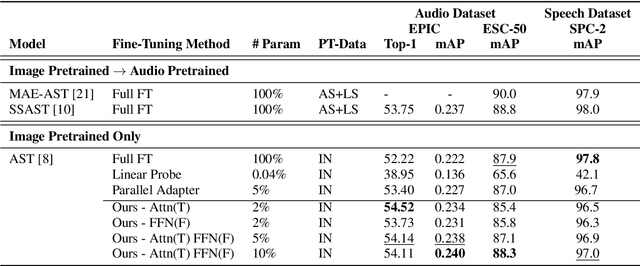
Abstract:Recent studies show that pretrained vision models can boost performance in audio downstream tasks. To enhance the performance further, an additional pretraining stage with large scale audio data is typically required to infuse audio specific knowledge into the vision model. However, such approaches require extensive audio data and a carefully designed objective function. In this work, we propose bypassing the pretraining stage by directly fine-tuning the vision model with our Look Aside Adapter (LoAA) designed for efficient audio understanding. Audio spectrum data is represented across two heterogeneous dimensions time and frequency and we refine adapters to facilitate interactions between tokens across these dimensions. Our experiments demonstrate that our adapters allow vision models to reach or surpass the performance of pretrained audio models in various audio and speech tasks, offering a resource efficient and effective solution for leveraging vision models in audio applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge