Jingyu Lei
CORE: Compact Object-centric REpresentations as a New Paradigm for Token Merging in LVLMs
Nov 18, 2025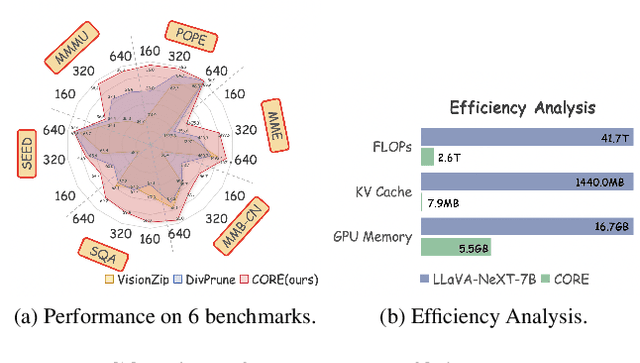
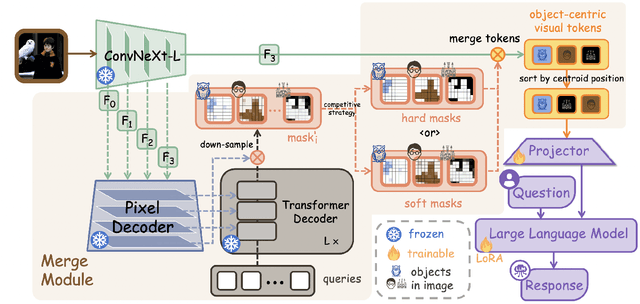
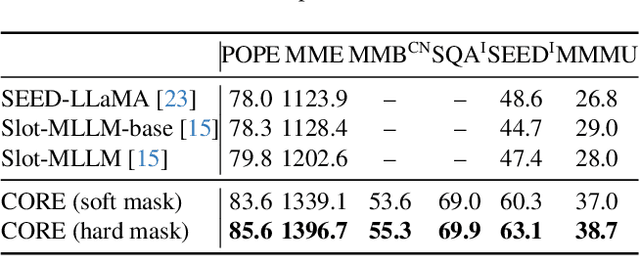
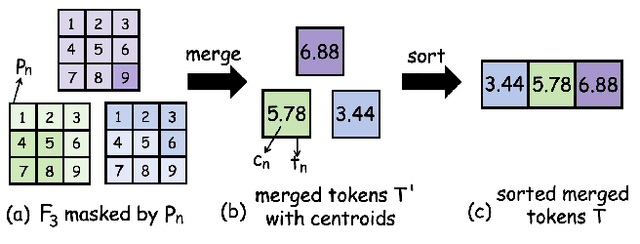
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) usually suffer from prohibitive computational and memory costs due to the quadratic growth of visual tokens with image resolution. Existing token compression methods, while varied, often lack a high-level semantic understanding, leading to suboptimal merges, information redundancy, or context loss. To address these limitations, we introduce CORE (Compact Object-centric REpresentations), a new paradigm for visual token compression. CORE leverages an efficient segmentation decoder to generate object masks, which serve as a high-level semantic prior to guide the merging of visual tokens into a compact set of object-centric representations. Furthermore, a novel centroid-guided sorting mechanism restores a coherent spatial order to the merged tokens, preserving vital positional information. Extensive experiments show that CORE not only establishes a new state-of-the-art on six authoritative benchmarks for fixed-rate compression, but also achieves dramatic efficiency gains in adaptive-rate settings. Even under extreme compression, after aggressively retaining with only 2.2% of all visual tokens, CORE still maintains 97.4% of baseline performance. Our work demonstrates the superiority of object-centric representations for efficient and effective LVLM processing.
Exploring Biomarker Relationships in Both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through a Bayesian Network Analysis Approach
Jun 24, 2024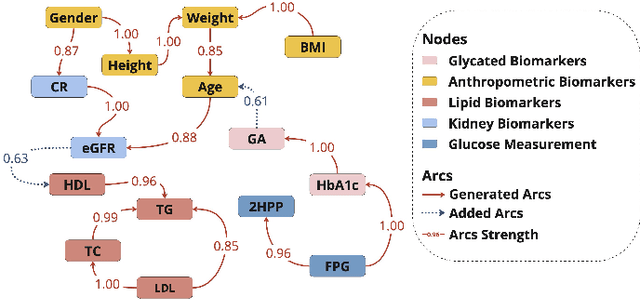
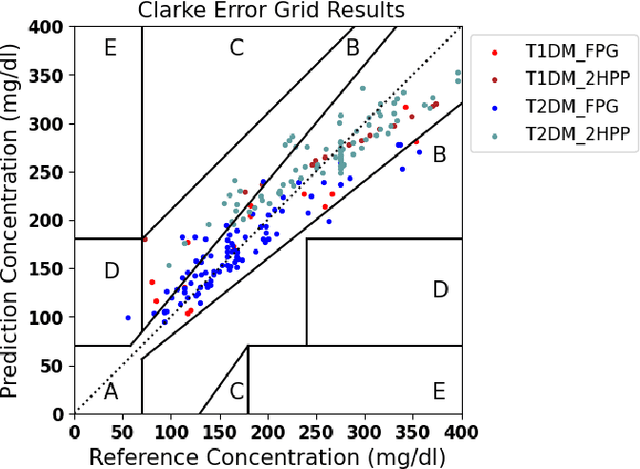
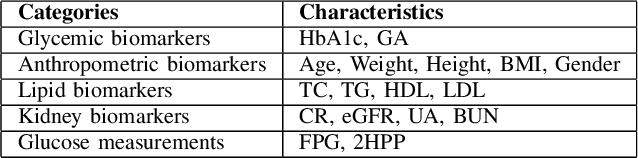
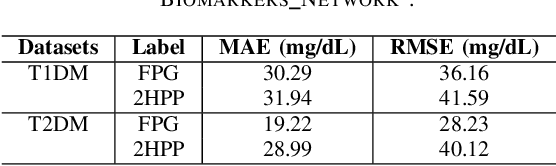
Abstract:Understanding the complex relationships of biomarkers in diabetes is pivotal for advancing treatment strategies, a pressing need in diabetes research. This study applies Bayesian network structure learning to analyze the Shanghai Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus datasets, revealing complex relationships among key diabetes-related biomarkers. The constructed Bayesian network presented notable predictive accuracy, particularly for Type 2 diabetes mellitus, with root mean squared error (RMSE) of 18.23 mg/dL, as validated through leave-one-domain experiments and Clarke error grid analysis. This study not only elucidates the intricate dynamics of diabetes through a deeper understanding of biomarker interplay but also underscores the significant potential of integrating data-driven and knowledge-driven methodologies in the realm of personalized diabetes management. Such an approach paves the way for more custom and effective treatment strategies, marking a notable advancement in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge