Jihe Wang
CiliaGraph: Enabling Expression-enhanced Hyper-Dimensional Computation in Ultra-Lightweight and One-Shot Graph Classification on Edge
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are computationally demanding and inefficient when applied to graph classification tasks in resource-constrained edge scenarios due to their inherent process, involving multiple rounds of forward and backward propagation. As a lightweight alternative, Hyper-Dimensional Computing (HDC), which leverages high-dimensional vectors for data encoding and processing, offers a more efficient solution by addressing computational bottleneck. However, current HDC methods primarily focus on static graphs and neglect to effectively capture node attributes and structural information, which leads to poor accuracy. In this work, we propose CiliaGraph, an enhanced expressive yet ultra-lightweight HDC model for graph classification. This model introduces a novel node encoding strategy that preserves relative distance isomorphism for accurate node connection representation. In addition, node distances are utilized as edge weights for information aggregation, and the encoded node attributes and structural information are concatenated to obtain a comprehensive graph representation. Furthermore, we explore the relationship between orthogonality and dimensionality to reduce the dimensions, thereby further enhancing computational efficiency. Compared to the SOTA GNNs, extensive experiments show that CiliaGraph reduces memory usage and accelerates training speed by an average of 292 times(up to 2341 times) and 103 times(up to 313 times) respectively while maintaining comparable accuracy.
A Study on Evaluation Standard for Automatic Crack Detection Regard the Random Fractal
Jul 23, 2020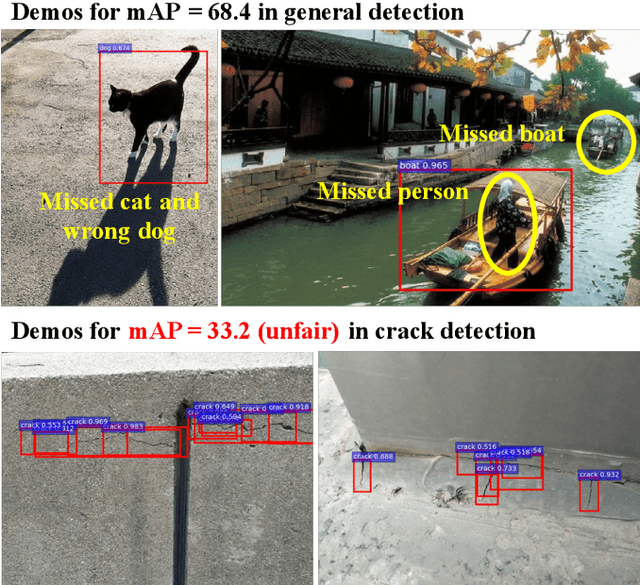
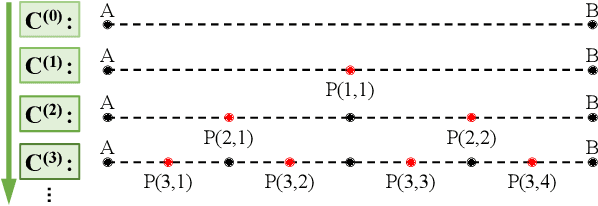
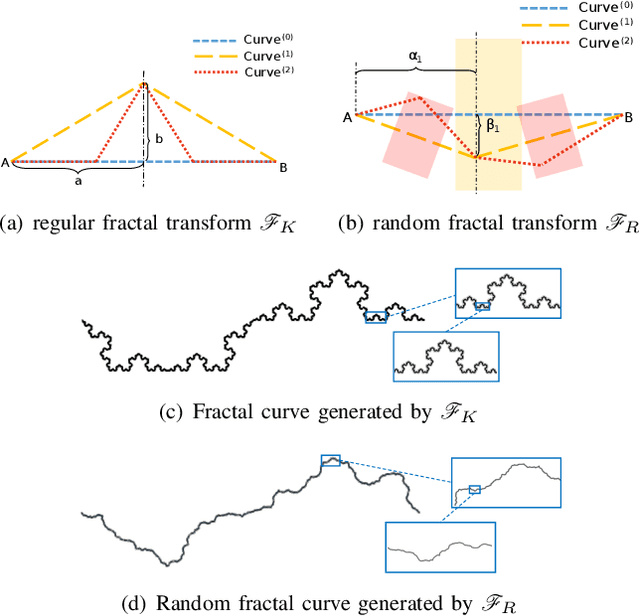
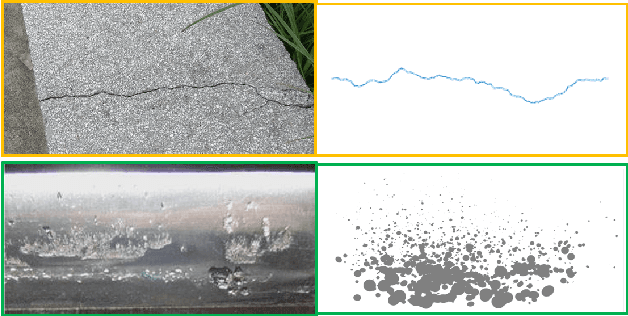
Abstract:A reasonable evaluation standard underlies construction of effective deep learning models. However, we find in experiments that the automatic crack detectors based on deep learning are obviously underestimated by the widely used mean Average Precision (mAP) standard. This paper presents a study on the evaluation standard. It is clarified that the random fractal of crack disables the mAP standard, because the strict box matching in mAP calculation is unreasonable for the fractal feature. As a solution, a fractal-available evaluation standard named CovEval is proposed to correct the underestimation in crack detection. In CovEval, a different matching process based on the idea of covering box matching is adopted for this issue. In detail, Cover Area rate (CAr) is designed as a covering overlap, and a multi-match strategy is employed to release the one-to-one matching restriction in mAP. Extended Recall (XR), Extended Precision (XP) and Extended F-score (Fext) are defined for scoring the crack detectors. In experiments using several common frameworks for object detection, models get much higher scores in crack detection according to CovEval, which matches better with the visual performance. Moreover, based on faster R-CNN framework, we present a case study to optimize a crack detector based on CovEval standard. Recall (XR) of our best model achieves an industrial-level at 95.8, which implies that with reasonable standard for evaluation, the methods for object detection are with great potential for automatic industrial inspection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge