Jiawen Lyn
ALoRA: Allocating Low-Rank Adaptation for Fine-tuning Large Language Models
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is widely studied for its effectiveness and efficiency in the era of large language models. Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has demonstrated commendable performance as a popular and representative method. However, it is implemented with a fixed intrinsic rank that might not be the ideal setting for the downstream tasks. Recognizing the need for more flexible downstream task adaptation, we extend the methodology of LoRA to an innovative approach we call allocating low-rank adaptation (ALoRA) that enables dynamic adjustments to the intrinsic rank during the adaptation process. First, we propose a novel method, AB-LoRA, that can effectively estimate the importance score of each LoRA rank. Second, guided by AB-LoRA, we gradually prune abundant and negatively impacting LoRA ranks and allocate the pruned LoRA budgets to important Transformer modules needing higher ranks. We have conducted experiments on various tasks, and the experimental results demonstrate that our ALoRA method can outperform the recent baselines with comparable tunable parameters.
Image super-resolution reconstruction based on attention mechanism and feature fusion
Apr 08, 2020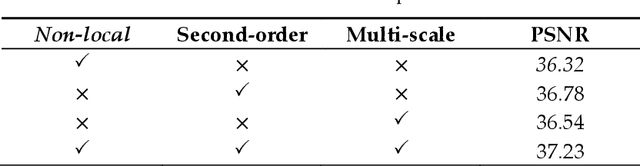
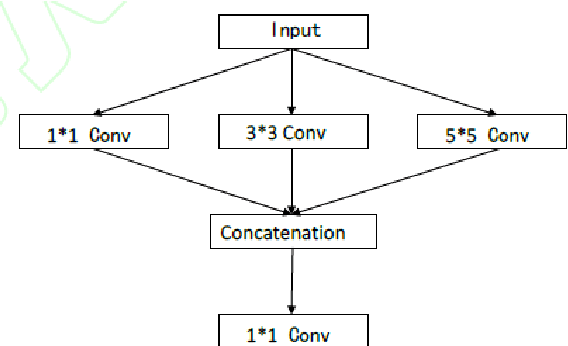
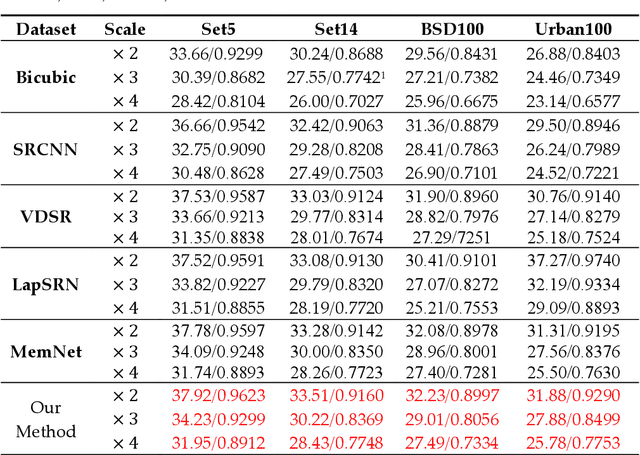
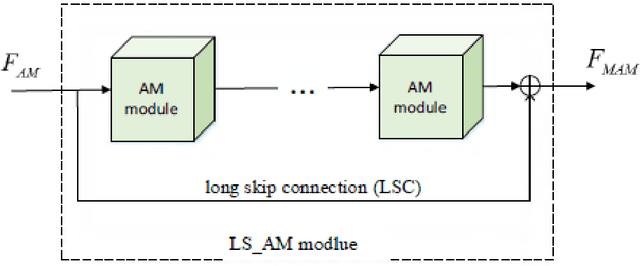
Abstract:Aiming at the problems that the convolutional neural networks neglect to capture the inherent attributes of natural images and extract features only in a single scale in the field of image super-resolution reconstruction, a network structure based on attention mechanism and multi-scale feature fusion is proposed. By using the attention mechanism, the network can effectively integrate the non-local information and second-order features of the image, so as to improve the feature expression ability of the network. At the same time, the convolution kernel of different scales is used to extract the multi-scale information of the image, so as to preserve the complete information characteristics at different scales. Experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve better performance over other representative super-resolution reconstruction algorithms in objective quantitative metrics and visual quality.
Multi-Level Feature Fusion Mechanism for Single Image Super-Resolution
Feb 14, 2020



Abstract:Convolution neural network (CNN) has been widely used in Single Image Super Resolution (SISR) so that SISR has been a great success recently. As the network deepens, the learning ability of network becomes more and more powerful. However, most SISR methods based on CNN do not make full use of hierarchical feature and the learning ability of network. These features cannot be extracted directly by subsequent layers, so the previous layer hierarchical information has little impact on the output and performance of subsequent layers relatively poor. To solve above problem, a novel Multi-Level Feature Fusion network (MLRN) is proposed, which can take full use of global intermediate features. We also introduce Feature Skip Fusion Block (FSFblock) as basic module. Each block can be extracted directly to the raw multiscale feature and fusion multi-level feature, then learn feature spatial correlation. The correlation among the features of the holistic approach leads to a continuous global memory of information mechanism. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that the method proposed by MLRN can be implemented, which is favorable performance for the most advanced methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge