Jiaolong Du
Scalable Overload-Aware Graph-Based Index Construction for 10-Billion-Scale Vector Similarity Search
Feb 28, 2025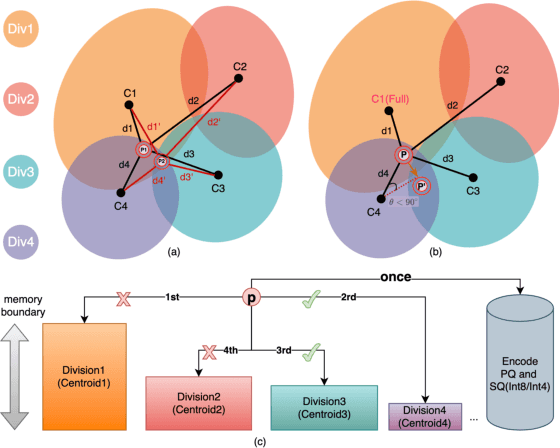
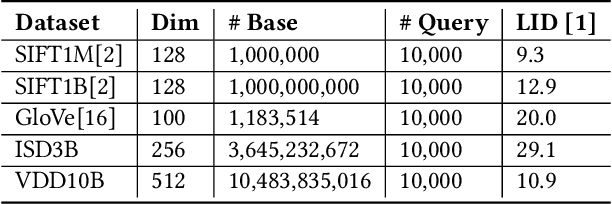
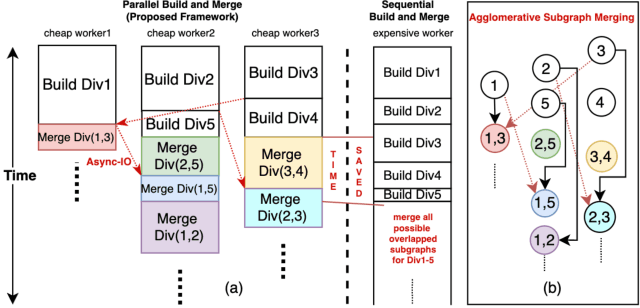
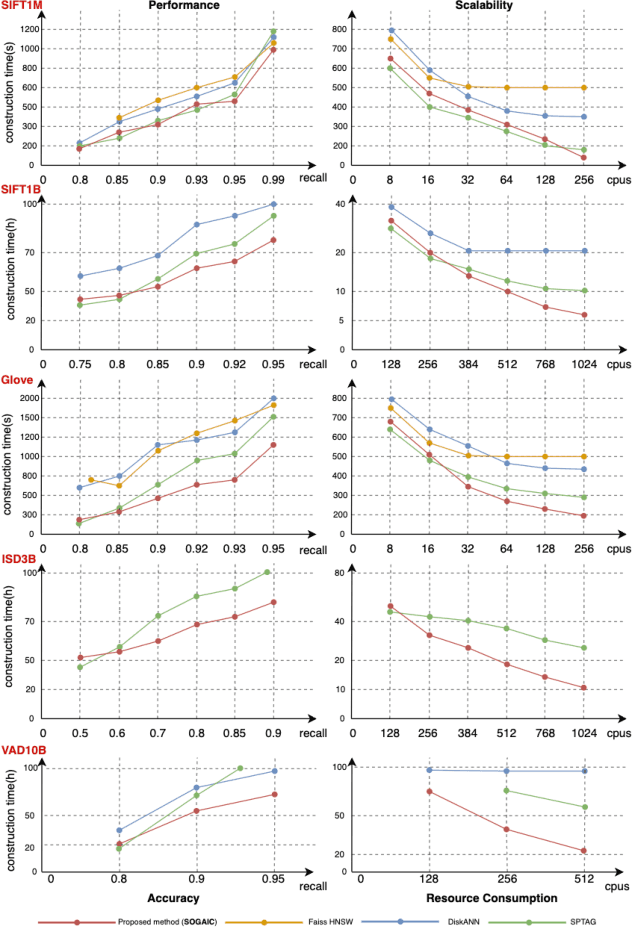
Abstract:Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search (ANNS) is essential for modern data-driven applications that require efficient retrieval of top-k results from massive vector databases. Although existing graph-based ANNS algorithms achieve a high recall rate on billion-scale datasets, their slow construction speed and limited scalability hinder their applicability to large-scale industrial scenarios. In this paper, we introduce SOGAIC, the first Scalable Overload-Aware Graph-Based ANNS Index Construction system tailored for ultra-large-scale vector databases: 1) We propose a dynamic data partitioning algorithm with overload constraints that adaptively introduces overlaps among subsets; 2) To enable efficient distributed subgraph construction, we employ a load-balancing task scheduling framework combined with an agglomerative merging strategy; 3) Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate a reduction of 47.3% in average construction time compared to existing methods. The proposed method has also been successfully deployed in a real-world industrial search engine, managing over 10 billion daily updated vectors and serving hundreds of millions of users.
A Real-Time Adaptive Multi-Stream GPU System for Online Approximate Nearest Neighborhood Search
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:In recent years, Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search (ANNS) has played a pivotal role in modern search and recommendation systems, especially in emerging LLM applications like Retrieval-Augmented Generation. There is a growing exploration into harnessing the parallel computing capabilities of GPUs to meet the substantial demands of ANNS. However, existing systems primarily focus on offline scenarios, overlooking the distinct requirements of online applications that necessitate real-time insertion of new vectors. This limitation renders such systems inefficient for real-world scenarios. Moreover, previous architectures struggled to effectively support real-time insertion due to their reliance on serial execution streams. In this paper, we introduce a novel Real-Time Adaptive Multi-Stream GPU ANNS System (RTAMS-GANNS). Our architecture achieves its objectives through three key advancements: 1) We initially examined the real-time insertion mechanisms in existing GPU ANNS systems and discovered their reliance on repetitive copying and memory allocation, which significantly hinders real-time effectiveness on GPUs. As a solution, we introduce a dynamic vector insertion algorithm based on memory blocks, which includes in-place rearrangement. 2) To enable real-time vector insertion in parallel, we introduce a multi-stream parallel execution mode, which differs from existing systems that operate serially within a single stream. Our system utilizes a dynamic resource pool, allowing multiple streams to execute concurrently without additional execution blocking. 3) Through extensive experiments and comparisons, our approach effectively handles varying QPS levels across different datasets, reducing latency by up to 40%-80%. The proposed system has also been deployed in real-world industrial search and recommendation systems, serving hundreds of millions of users daily, and has achieved good results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge