Jia-Jun Chen
Dynamic Oracle for Neural Machine Translation in Decoding Phase
Oct 16, 2017


Abstract:The past several years have witnessed the rapid progress of end-to-end Neural Machine Translation (NMT). However, there exists discrepancy between training and inference in NMT when decoding, which may lead to serious problems since the model might be in a part of the state space it has never seen during training. To address the issue, Scheduled Sampling has been proposed. However, there are certain limitations in Scheduled Sampling and we propose two dynamic oracle-based methods to improve it. We manage to mitigate the discrepancy by changing the training process towards a less guided scheme and meanwhile aggregating the oracle's demonstrations. Experimental results show that the proposed approaches improve translation quality over standard NMT system.
A Synthetic Approach for Recommendation: Combining Ratings, Social Relations, and Reviews
Jan 11, 2016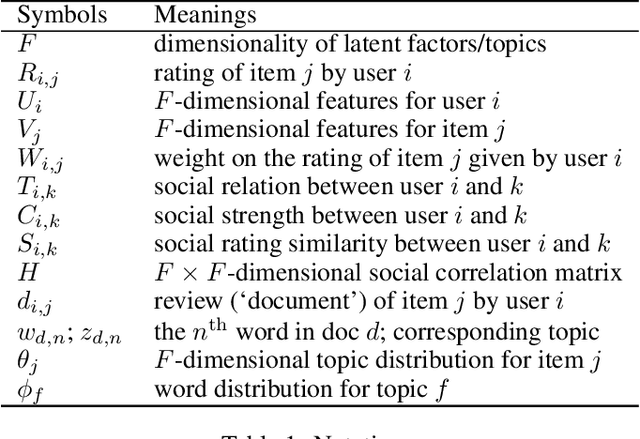
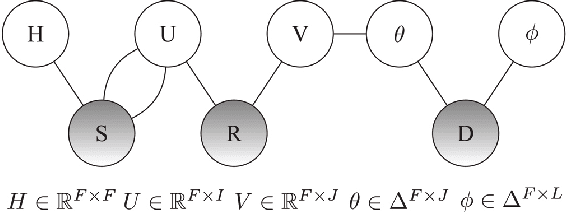
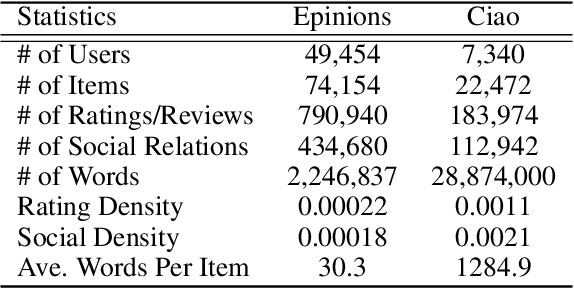
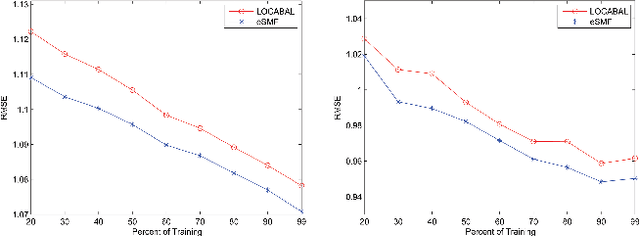
Abstract:Recommender systems (RSs) provide an effective way of alleviating the information overload problem by selecting personalized choices. Online social networks and user-generated content provide diverse sources for recommendation beyond ratings, which present opportunities as well as challenges for traditional RSs. Although social matrix factorization (Social MF) can integrate ratings with social relations and topic matrix factorization can integrate ratings with item reviews, both of them ignore some useful information. In this paper, we investigate the effective data fusion by combining the two approaches, in two steps. First, we extend Social MF to exploit the graph structure of neighbors. Second, we propose a novel framework MR3 to jointly model these three types of information effectively for rating prediction by aligning latent factors and hidden topics. We achieve more accurate rating prediction on two real-life datasets. Furthermore, we measure the contribution of each data source to the proposed framework.
* 7 pages, 8 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge