Jia Hou
Collaborative AI in Sentiment Analysis: System Architecture, Data Prediction and Deployment Strategies
Oct 23, 2024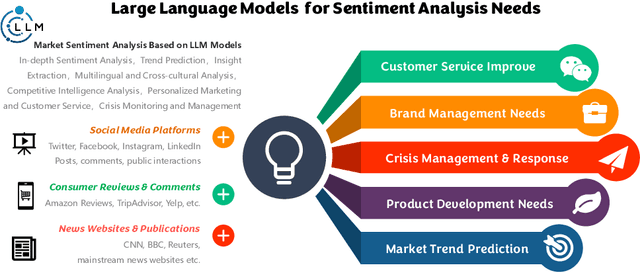
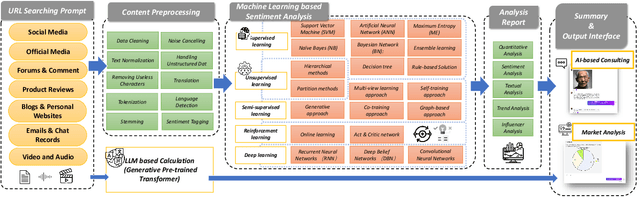
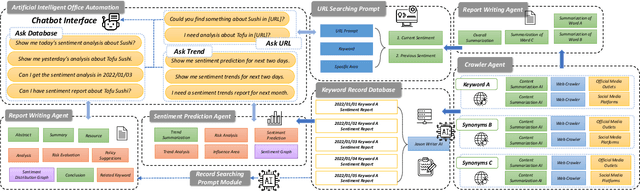
Abstract:The advancement of large language model (LLM) based artificial intelligence technologies has been a game-changer, particularly in sentiment analysis. This progress has enabled a shift from highly specialized research environments to practical, widespread applications within the industry. However, integrating diverse AI models for processing complex multimodal data and the associated high costs of feature extraction presents significant challenges. Motivated by the marketing oriented software development +needs, our study introduces a collaborative AI framework designed to efficiently distribute and resolve tasks across various AI systems to address these issues. Initially, we elucidate the key solutions derived from our development process, highlighting the role of generative AI models like \emph{chatgpt}, \emph{google gemini} in simplifying intricate sentiment analysis tasks into manageable, phased objectives. Furthermore, we present a detailed case study utilizing our collaborative AI system in edge and cloud, showcasing its effectiveness in analyzing sentiments across diverse online media channels.
Enhancing Sentiment Analysis with Collaborative AI: Architecture, Predictions, and Deployment Strategies
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:The advancement of large language model (LLM) based artificial intelligence technologies has been a game-changer, particularly in sentiment analysis. This progress has enabled a shift from highly specialized research environments to practical, widespread applications within the industry. However, integrating diverse AI models for processing complex multimodal data and the associated high costs of feature extraction presents significant challenges. Motivated by the marketing oriented software development +needs, our study introduces a collaborative AI framework designed to efficiently distribute and resolve tasks across various AI systems to address these issues. Initially, we elucidate the key solutions derived from our development process, highlighting the role of generative AI models like \emph{chatgpt}, \emph{google gemini} in simplifying intricate sentiment analysis tasks into manageable, phased objectives. Furthermore, we present a detailed case study utilizing our collaborative AI system in edge and cloud, showcasing its effectiveness in analyzing sentiments across diverse online media channels.
Robust Fuzzy-Learning For Partially Overlapping Channels Allocation In UAV Communication Networks
Jun 28, 2018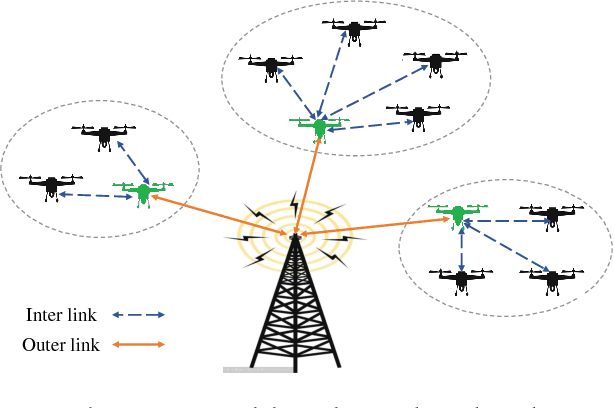



Abstract:In this paper, we consider a mesh-structured unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks exploiting partially overlapping channels (POCs). For general data-collection tasks in UAV networks, we aim to optimize the network throughput with constraints on transmission power and quality of service (QoS). As far as the highly mobile and constantly changing UAV networks are concerned, unfortunately, most existing methods rely on definite information which is vulnerable to the dynamic environment, rendering system performance to be less effective. In order to combat dynamic topology and varying interference of UAV networks, a robust and distributed learning scheme is proposed. Rather than the perfect channel state information (CSI), we introduce uncertainties to characterize the dynamic channel gains among UAV nodes, which are then interpreted with fuzzy numbers. Instead of the traditional observation space where the channel capacity is a crisp reward, we implement the learning and decision process in a mapped fuzzy space. This allows the system to achieve a smoother and more robust performance by optimizing in an alternate space. To this end, we design a fuzzy payoffs function (FPF) to describe the fluctuated utility, and the problem of POCs assignment is formulated as a fuzzy payoffs game (FPG). Assisted by an attractive property of fuzzy bi-matrix games, the existence of fuzzy Nash equilibrium (FNE) for our formulated FPG is proved. Our robust fuzzy-learning algorithm could reach the equilibrium solution via a least-deviation method. Finally, numerical simulations are provided to demonstrate the advantages of our new scheme over the existing scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge