Jhielson M. Pimentel
A Data-Driven Biophysical Computational Model of Parkinson's Disease based on Marmoset Monkeys
Jul 27, 2021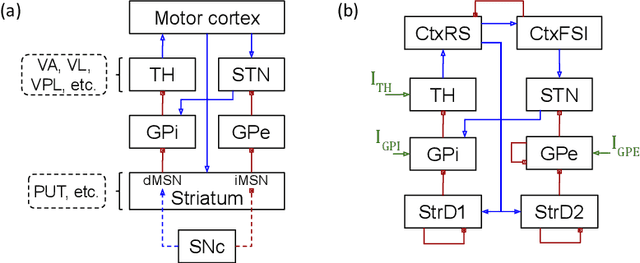
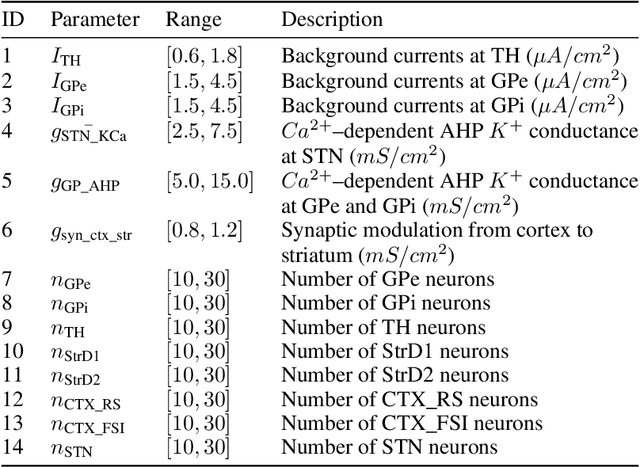
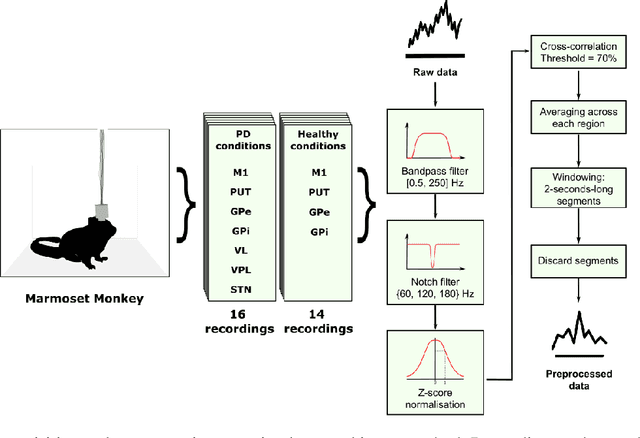

Abstract:In this work we propose a new biophysical computational model of brain regions relevant to Parkinson's Disease based on local field potential data collected from the brain of marmoset monkeys. Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, linked to the death of dopaminergic neurons at the substantia nigra pars compacta, which affects the normal dynamics of the basal ganglia-thalamus-cortex neuronal circuit of the brain. Although there are multiple mechanisms underlying the disease, a complete description of those mechanisms and molecular pathogenesis are still missing, and there is still no cure. To address this gap, computational models that resemble neurobiological aspects found in animal models have been proposed. In our model, we performed a data-driven approach in which a set of biologically constrained parameters is optimised using differential evolution. Evolved models successfully resembled single-neuron mean firing rates and spectral signatures of local field potentials from healthy and parkinsonian marmoset brain data. As far as we are concerned, this is the first computational model of Parkinson's Disease based on simultaneous electrophysiological recordings from seven brain regions of Marmoset monkeys. Results show that the proposed model could facilitate the investigation of the mechanisms of PD and support the development of techniques that can indicate new therapies. It could also be applied to other computational neuroscience problems in which biological data could be used to fit multi-scale models of brain circuits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge