Jerry Q. Cheng
Programming with AI: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, AlphaCode, and GitHub Copilot for Programmers
Nov 14, 2024
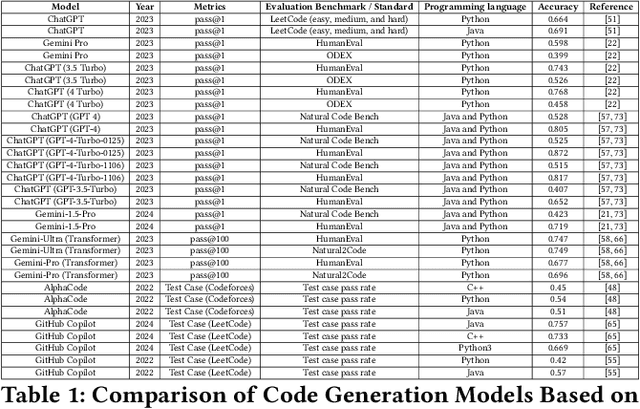
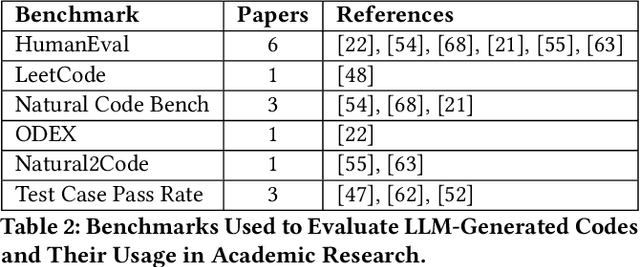
Abstract:Our everyday lives now heavily rely on artificial intelligence (AI) powered large language models (LLMs). Like regular users, programmers are also benefiting from the newest large language models. In response to the critical role that AI models play in modern software development, this study presents a thorough evaluation of leading programming assistants, including ChatGPT, Gemini(Bard AI), AlphaCode, and GitHub Copilot. The evaluation is based on tasks like natural language processing and code generation accuracy in different programming languages like Java, Python and C++. Based on the results, it has emphasized their strengths and weaknesses and the importance of further modifications to increase the reliability and accuracy of the latest popular models. Although these AI assistants illustrate a high level of progress in language understanding and code generation, along with ethical considerations and responsible usage, they provoke a necessity for discussion. With time, developing more refined AI technology is essential for achieving advanced solutions in various fields, especially with the knowledge of the feature intricacies of these models and their implications. This study offers a comparison of different LLMs and provides essential feedback on the rapidly changing area of AI models. It also emphasizes the need for ethical developmental practices to actualize AI models' full potential.
Divide-and-conquer methods for big data analysis
Feb 22, 2021Abstract:In the context of big data analysis, the divide-and-conquer methodology refers to a multiple-step process: first splitting a data set into several smaller ones; then analyzing each set separately; finally combining results from each analysis together. This approach is effective in handling large data sets that are unsuitable to be analyzed entirely by a single computer due to limits either from memory storage or computational time. The combined results will provide a statistical inference which is similar to the one from analyzing the entire data set. This article reviews some recently developments of divide-and-conquer methods in a variety of settings, including combining based on parametric, semiparametric and nonparametric models, online sequential updating methods, among others. Theoretical development on the efficiency of the divide-and-conquer methods is also discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge