Jennifer Webster
Spatiotemporal k-means
Nov 10, 2022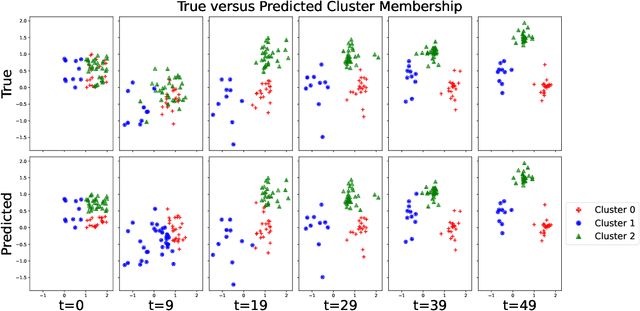

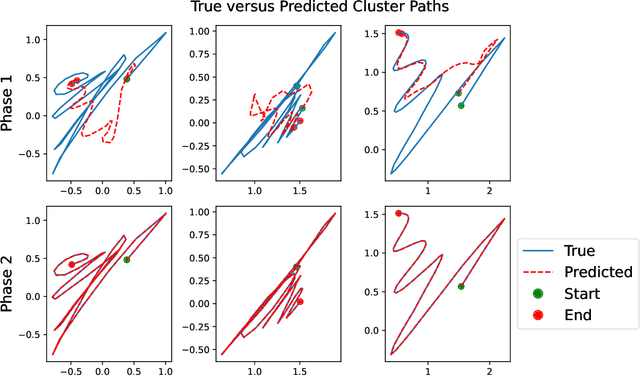
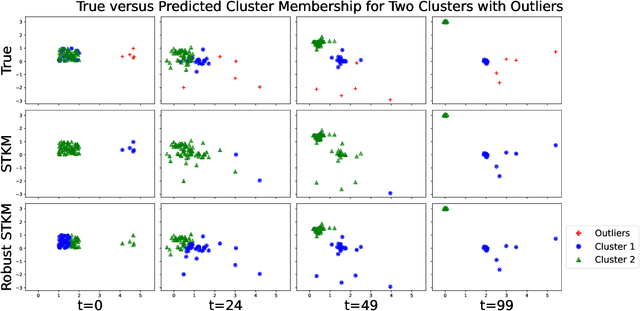
Abstract:Spatiotemporal data is readily available due to emerging sensor and data acquisition technologies that track the positions of moving objects of interest. Spatiotemporal clustering addresses the need to efficiently discover patterns and trends in moving object behavior without human supervision. One application of interest is the discovery of moving clusters, where clusters have a static identity, but their location and content can change over time. We propose a two phase spatiotemporal clustering method called spatiotemporal k-means (STKM) that is able to analyze the multi-scale relationships within spatiotemporal data. Phase 1 of STKM frames the moving cluster problem as the minimization of an objective function unified over space and time. It outputs the short-term associations between objects and is uniquely able to track dynamic cluster centers with minimal parameter tuning and without post-processing. Phase 2 outputs the long-term associations and can be applied to any method that provides a cluster label for each object at every point in time. We evaluate STKM against baseline methods on a recently developed benchmark dataset and show that STKM outperforms existing methods, particularly in the low-data domain, with significant performance improvements demonstrated for common evaluation metrics on the moving cluster problem.
Personalized Prognostic Models for Oncology: A Machine Learning Approach
Jun 22, 2016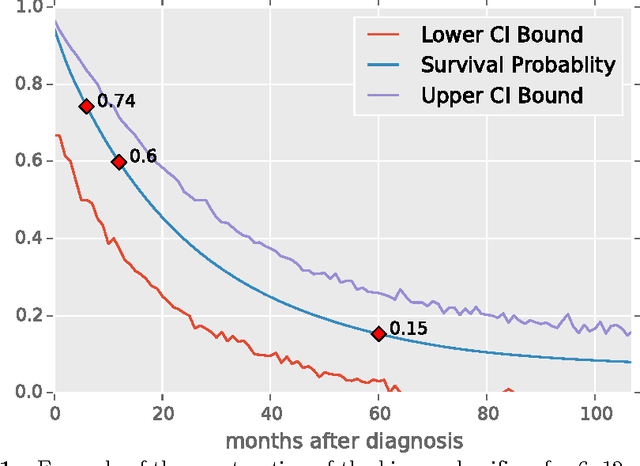
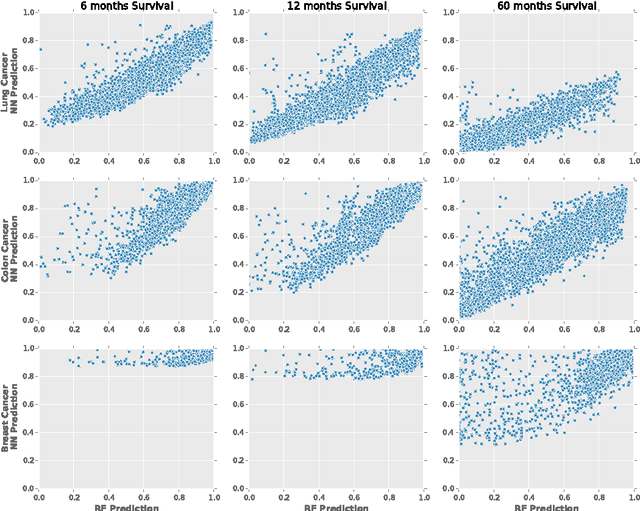
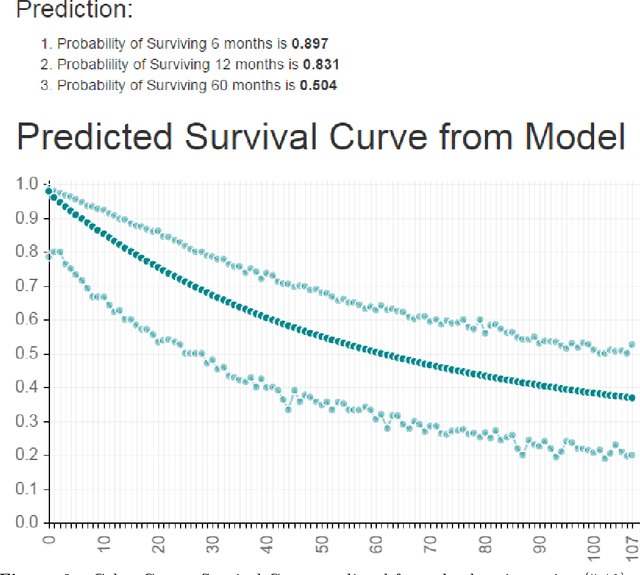
Abstract:We have applied a little-known data transformation to subsets of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) publically available data of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) to make it suitable input to standard machine learning classifiers. This transformation properly treats the right-censored data in the SEER data and the resulting Random Forest and Multi-Layer Perceptron models predict full survival curves. Treating the 6, 12, and 60 months points of the resulting survival curves as 3 binary classifiers, the 18 resulting classifiers have AUC values ranging from .765 to .885. Further evidence that the models have generalized well from the training data is provided by the extremely high levels of agreement between the random forest and neural network models predictions on the 6, 12, and 60 month binary classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge