Jelizaveta Konstantinova
Human-inspired Grasping Strategies of Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Applied to Robotic Manipulation
Oct 30, 2024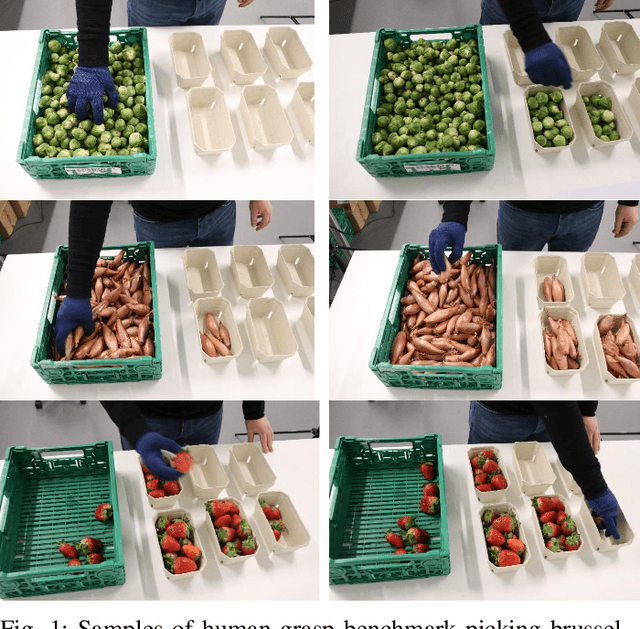
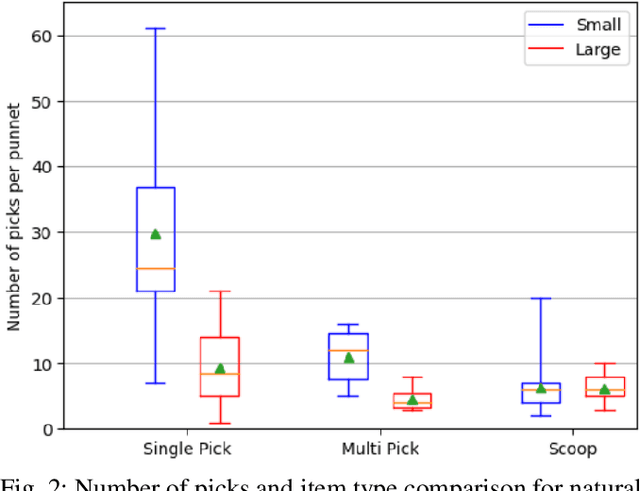
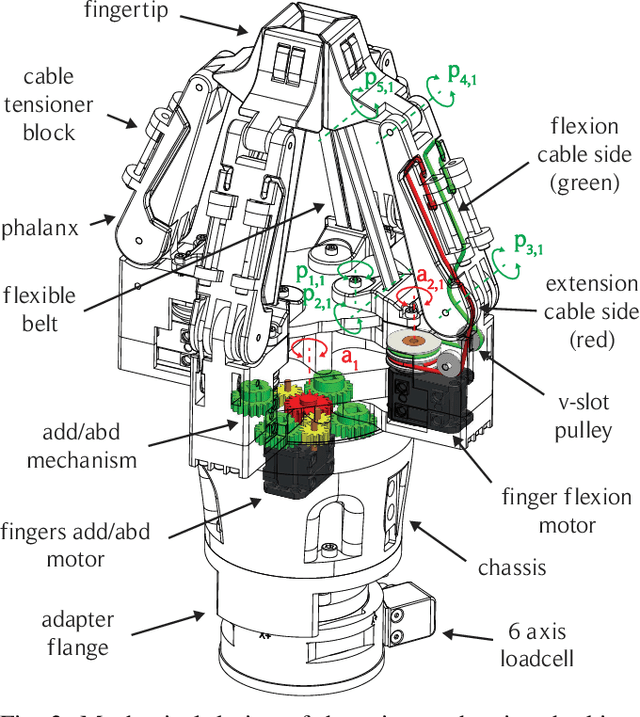
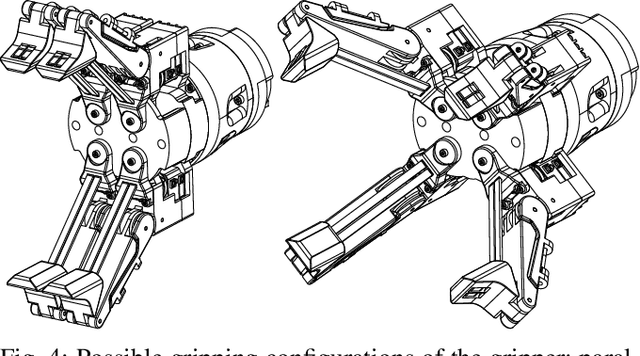
Abstract:Robotic manipulation of fresh fruits and vegetables, including the grasping of multiple loose items, has a strong industrial need but it still is a challenging task for robotic manipulation. This paper outlines the distinctive manipulation strategies used by humans to pick loose fruits and vegetables with the aim to better adopt them for robotic manipulation of diverse items. In this work we present a first version of a robotic setup designed to pick different single or multiple fresh items, featuring multi-fingered compliant robotic gripper. We analyse human grasping strategies from the perspective of industrial Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) used in the logistic sector. The robotic system was validated using the same KPIs, as well as taking into account human performance and strategies. This paper lays the foundation for future development of the robotic demonstrator for fresh fruit and vegetable intelligent manipulation, and outlines the need for generic approaches to handle the complexity of the task.
* *Authors contributed equally
A Methodology for Approaching the Integration of Complex Robotics Systems Illustrated through a Bi-manual Manipulation Case-Study
Mar 18, 2021



Abstract:The multidisciplinarity of robotics creates a need for robust integration methodologies that can facilitate the adoption of state-of-the-art research components in an industrial application. Unfortunately, there are no clear, community accepted guidelines or standards that define the integration of such components in a single robotic system. In this paper, we propose a methodology that assesses the software components of a candidate system on the basis of the effort required to integrate them and the impact their integration will have on a target system. We demonstrate how this methodology can be applied using an industrial tool packing system as an example. The system integrates a wide range of both in-house and third-party research outputs and software components. We prove the effectiveness of our approach by evaluating system performance with an experimental benchmark that assesses the robustness, reliability and operational speed of the system for the given packing task. We also demonstrate how our methodology can be used to predict the amount of integration time required for a component. The proposed integration methodology can be applied to any robotic system to facilitate its transition from the research to an industrial environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge