Jeffrey L. Rogers
Enabling the Evaluation of Driver Physiology Via Vehicle Dynamics
Sep 08, 2023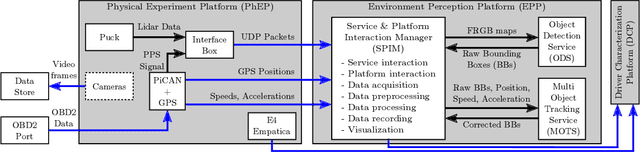

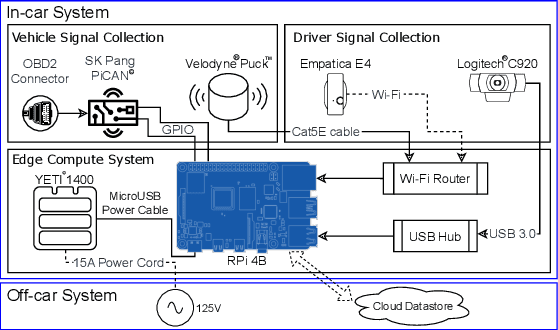
Abstract:Driving is a daily routine for many individuals across the globe. This paper presents the configuration and methodologies used to transform a vehicle into a connected ecosystem capable of assessing driver physiology. We integrated an array of commercial sensors from the automotive and digital health sectors along with driver inputs from the vehicle itself. This amalgamation of sensors allows for meticulous recording of the external conditions and driving maneuvers. These data streams are processed to extract key parameters, providing insights into driver behavior in relation to their external environment and illuminating vital physiological responses. This innovative driver evaluation system holds the potential to amplify road safety. Moreover, when paired with data from conventional health settings, it may enhance early detection of health-related complications.
* 7 pages, 11 figures, 2023 IEEE International Conference on Digital Health (ICDH)
A recommender for the management of chronic pain in patients undergoing spinal cord stimulation
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is a therapeutic approach used for the management of chronic pain. It involves the delivery of electrical impulses to the spinal cord via an implanted device, which when given suitable stimulus parameters can mask or block pain signals. Selection of optimal stimulation parameters usually happens in the clinic under the care of a provider whereas at-home SCS optimization is managed by the patient. In this paper, we propose a recommender system for the management of pain in chronic pain patients undergoing SCS. In particular, we use a contextual multi-armed bandit (CMAB) approach to develop a system that recommends SCS settings to patients with the aim of improving their condition. These recommendations, sent directly to patients though a digital health ecosystem, combined with a patient monitoring system closes the therapeutic loop around a chronic pain patient over their entire patient journey. We evaluated the system in a cohort of SCS-implanted ENVISION study subjects (Clinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT03240588) using a combination of quality of life metrics and Patient States (PS), a novel measure of holistic outcomes. SCS recommendations provided statistically significant improvement in clinical outcomes (pain and/or QoL) in 85\% of all subjects (N=21). Among subjects in moderate PS (N=7) prior to receiving recommendations, 100\% showed statistically significant improvements and 5/7 had improved PS dwell time. This analysis suggests SCS patients may benefit from SCS recommendations, resulting in additional clinical improvement on top of benefits already received from SCS therapy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge